FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
The ultimate benefit of lowering triglycerides and LDL and raising HDL is to decrease the risk of developing coronary heart disease or other severe cardiovascular conditions.
People with high cholesterol and triglycerides should set objectives for short-term and long-term goals.
Establish a program that includes a diet low in unhealthy fat, processed foods, simple carbohydrates, and sugar.
It would help if you exercised regularly to raise your fitness level and reduce body fat. If necessary, good and natural supplements can help you reach your objectives.
Your long-term goals are to lower bad cholesterol and triglycerides, reduce body weight to target levels, and maintain them for life through dietary adjustments and regular exercise.
If you are a heart disease patient, maintaining heart health will be of special concern over your lifetime.
Your targets will be lower than the established normal range. This usually requires a comprehensive approach, including a regular aerobic exercise schedule, relaxation program, strict diet, and medication regimen.
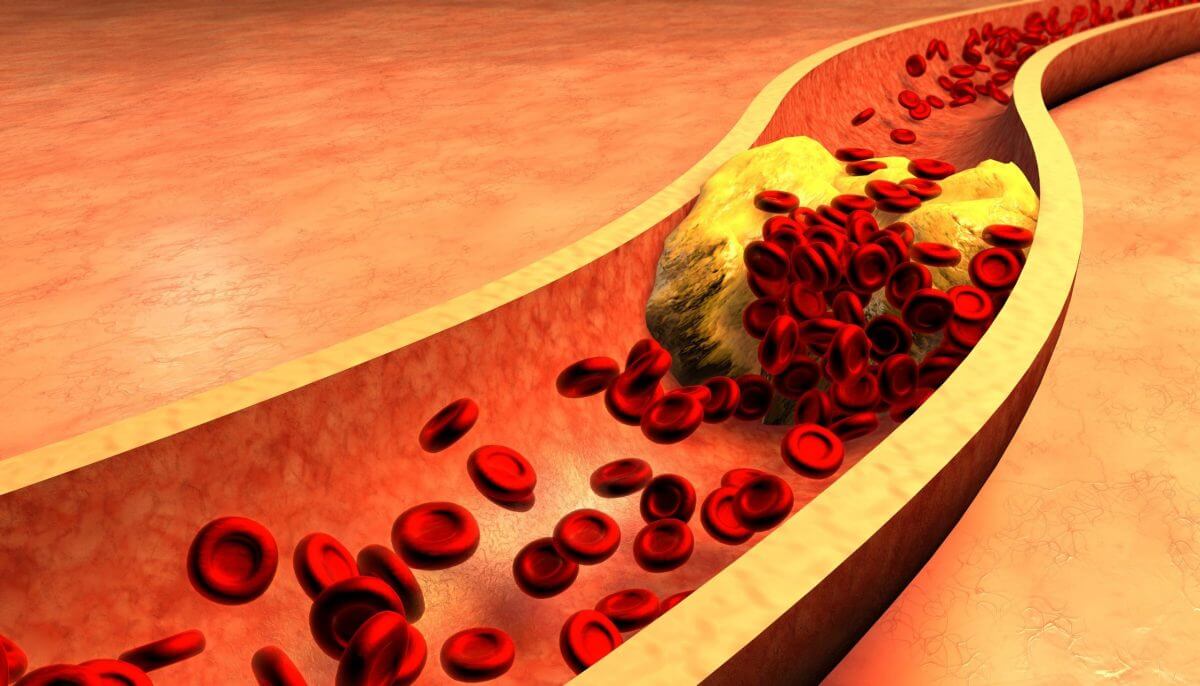
Lowering cholesterol and triglyceride levels means a lower risk of plaque formation, fewer arterial blockages, and a lower incidence of hemorrhaging and blood clotting.
With less plaque comes a reduction in atherosclerosis and incidences of angina, heart attack, and stroke. This, in turn, means increased longevity for coronary heart disease patients and a smaller chance that a heart attack, if it occurs, will be fatal.
Work with your doctor, a dietician or nutritionist, and a physical trainer to help develop and stick with your healthy heart program for life.
Exercise and Lowering Cholesterol
Regular physical activity is important in minimizing the risk of coronary heart disease.
A consistent exercise program can reduce LDL and raise the level of HDL. Exercise can also lower triglyceride levels and blood pressure, reduce weight, and improve your lungs’ and heart’s health and fitness.
Aerobic Activity

Aerobic activity greatly benefits the cardiovascular system, which should be a significant part of any exercise program.
Moreover, aerobic exercises such as cycling, jogging, walking, tennis, and swimming increase heart rate and blood flow.
Seek reputable advice and expertise when designing your exercise program to meet your specific needs.
Without such expertise, you may adopt a program, such as weight lifting, that does little to lower your blood cholesterol levels.
If you’ve been doing minimal aerobic activity for an extended period, are overweight, or have coronary heart disease, work up to your exercise program gradually and avoid accelerating your heart rate too quickly.
For example, you can begin with moderate walking and stair climbing every other day for at least thirty minutes.
When starting, your physician can best determine whether you should have supervision, such as that provided in a cardiac rehabilitation center.
Regular physical activity minimizes coronary heart disease risk, so choose activities you enjoy.
Fat Burning Exercise and Medications

Certain diets and medications can help reduce body fat for overweight people. However, exercise is considered one of the preferred fat burners.
Fat burners can target LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and body fat reserves. Fat burners like pills and special diets may specifically target cholesterol and excess body weight, but they’re costly and require strict compliance.
Before starting an exercise routine, diet, or pills, consult your doctor, as improper routines, diets, and the use of pills can lead to serious adverse effects on your health.
Think Lifelong Activity
To lower your cholesterol levels, you must think “long term.”
To make it more likely that you’ll maintain your program for many years, choose activities you enjoy that yield appropriate heart rates for cardiovascular health.
The Cholesterol Diet: Healthy Dieting for the Body
A healthy diet is among the most important approaches to reducing blood cholesterol and cardiovascular disease.
Planning a healthy diet means thinking differently about the types of food you eat and the quantity of food you consume.
Balanced diet

A balanced diet is essential, but you may have to consider a slightly different balance.
Generally, a low-fat diet should replace high fat and avoid unhealthy fat. Low-fat content in meals can eventually help somewhat to reduce fat levels in the blood.
But, the above fact will work only when we reduce the intake of carbohydrates.
Healthy regimens for people wishing to reduce cardiovascular disease risk must reduce bad cholesterol from processed food.
A cholesterol diet targets cholesterol intake, its levels in the blood, and its production by the body.
Reducing only high-fat foods may not be enough to reduce cholesterol levels in the blood because the body itself manufactures cholesterol.
Medication or other interventions may be needed for people with high levels of dietary changes.
Specific foods and food substitutes

A cholesterol-lowering diet may include specific foods and food substitutes.
An example is spreads made from unsaturated vegetable oils, or processed butter can be replaced with grass-fed butter.
Similarly, we can replace processed meat and dairy with grass-fed meat and dairy. Also, for healthy fish, you can opt for wild-caught fish.
Moreover, you can replace unhealthy and packed snacks with organic nuts and avocados.
Some people have made Benecol spread their butter substitute of choice, mainly because it contains sitostanol (plant stanol esters).
While small quantities of sitostanol have been shown to lower LDL cholesterol by blocking fat absorption, its use is intended for persons who do not require medical management for their high cholesterol.
Includes Avocados in the diet

Avocados are a great addition to a healthy diet.
Avocados, typically considered a high-fat food, actually contain “good” unsaturated fats. Because they are high in fiber and vitamins such as folic acid and vitamin E, avocados are a great addition to a healthy diet, as per research.
The Dietary Guidelines established by the USDA Department of Health and Human Services now recommend avocados as part of a healthy diet.
Diets with large amounts of simple carbohydrates such as refined cane sugar and/or high-fat foods (processed food or packed food) typically contribute to high body fat.
While much of the fat consumed is stored in the body, excess carbohydrates are also stored as fat.
Some researchers believe that meal frequency and making good food choices positively affect the body’s cholesterol levels.
A recent report has confirmed that people who eat smaller portions up to six times a day or more (“grazers”) had significantly lower cholesterol levels than those who ate two big meals daily.
Do dietary saturated fats matters?

Dietary saturated fat intake has not shown much difference or any association with CHD, stroke, or CVD.
If we reduce the intake of healthy cholesterol, then the body will make more cholesterol. You can get healthy cholesterol from avocados, nuts, cod liver oil, wild-caught fish, grass-fed meat, dairy, and butter.
A study suggested that reducing dietary saturated fat has reduced cardiovascular disease by 17%. Another study has shown that there are no convincing facts or association between saturated fat and CHD mortality.
A meta-analysis revealed that healthy saturated fat intake was not associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and CHD (Coronary heart disease).
Moreover, a systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted on fatty acids and their effect on cardiovascular health.
The study revealed no supportive evidence supporting the fact that high consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids and low consumption of saturated fat will affect cardiovascular health.
Read Nutrition Labels
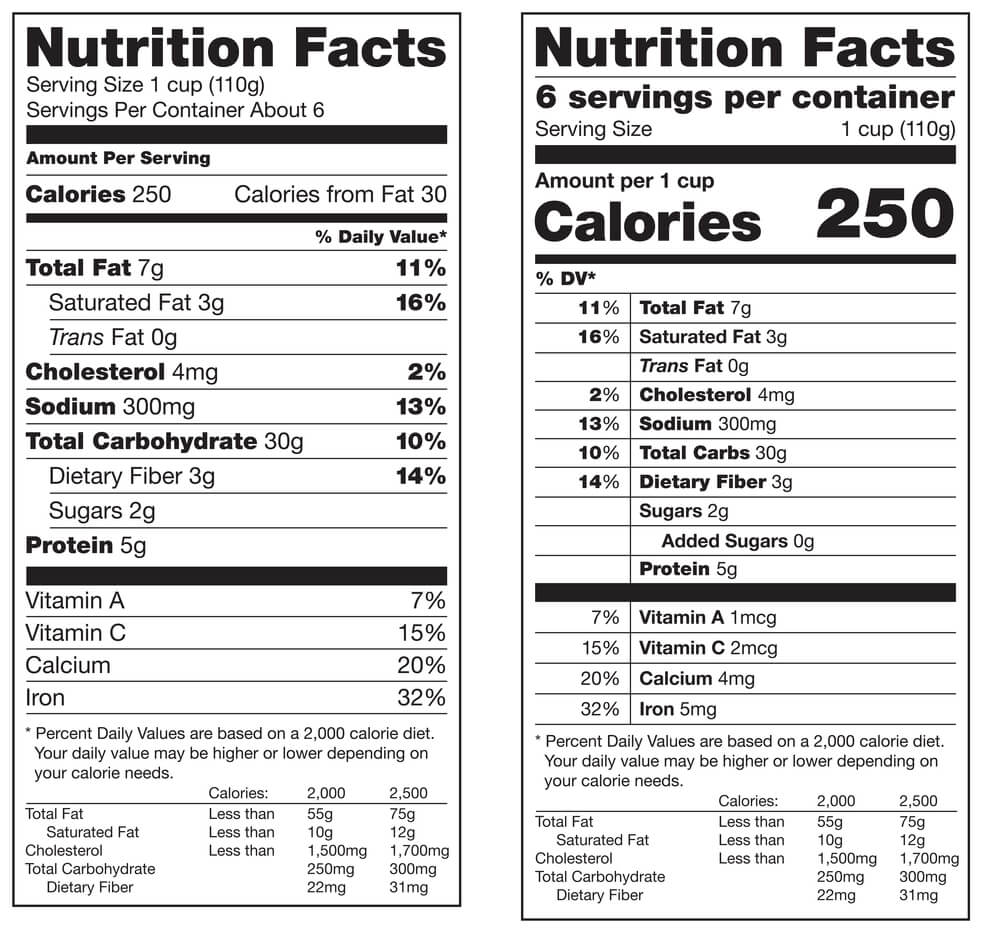
Food labels provide nutritional information to help in choosing a balanced diet.
Food labels provide nutritional information, including the total amount of food, fats, carbohydrates and proteins, cholesterol content, and key vitamins and minerals. This information helps you take an active role in choosing a balanced diet lower in cholesterol.
Two important ways to lower cholesterol are limiting their intake and avoiding foods with many simple carbohydrates, especially if they are processed and packed food with no clear nutrition labels.
Above all, you need to check the food labels and how much it contains unhealthy fat in hydrogenated vegetable oils, carbohydrates, and sugar.
What to check in food labels?
Check labels for the presence of unhealthy saturated fat and trans fat.
Many processed and snack items use less expensive saturated fats and often incorporate hydrogenated or partly-hydrogenated fats to give the product an appealing texture or consistency.
Recent findings indicate that corn syrup—a highly saturated form of sugar—has been an inexpensive sweetener in many packaged foods. Watch out for its high carbohydrate content.
Watch out for frozen and canned products that incorporate lard or oil and often has a great deal of sodium or salt.
Sodium is frequently used as a preservative in processed meats available in supermarkets and delis and is responsible for increasing blood pressure.
Labels can be important sources of information, even when specific quantities are not stated.
By law, companies are required to list the ingredients of a product in descending order by weight.
If an ingredient you’re trying to avoid appears at the head of the ingredient list, you might choose to avoid that particular product.
Sometimes companies are required to add warnings on labels. When the fat substitute olestra appeared to cause digestive tract problems for many consumers, products containing olestra were required to carry a warning on their labels.
Are Supplements a Good Thing?

Some supplements replace the fat you normally eat in your diet or help the body metabolize fat stored in the body.
According to research, supplements like cod liver oil containing omega-3 fatty acids help raise good HDL cholesterol.
Moreover, the findings have shown that consumption of CoQ10 has significantly decreased total cholesterol.
Additionally, Psyllium as a supplement has significantly reduced total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels.
Food supplements that claim to reduce cholesterol levels should be viewed with caution and not taken without the “green light” from your physician.
Niacin and soluble fiber of organic origin have benefited some people but have produced side effects in others.
Some products have been specifically designed to target cholesterol levels, but very little research evidence exists to establish their benefits. Often, the long-term effects of their use are unknown.
Cholesterol-Lowering Foods: Eating Well and Eating Smart
Eating well results from being smart about food types, preparation methods, and serving sizes.
This means you’re making good choices about what to buy for meals, how to cook particular foods while eating out, where to eat, and how to order.
For heart patients and those with cholesterol problems who want to be proactive in preventing problems, overall meal planning is an exercise to find an appropriate balance among essential nutrients.
When developing a cholesterol diet strategy, adding cholesterol-lowering foods is important to remove fat-laden food items from your diet.
Foods high in saturated fat and cholesterol should be limited. Some examples are butter, whole milk, cheese, egg yolks, and saturated oils (such as coconut).
These should be replaced by lower foods in saturated fat, such as olive oil, grass-fed milk, fruits and vegetables, whole-grain cereals, and pasta.
The American Heart Association recommends an average daily cholesterol intake of fewer than 300 milligrams.
Cholesterol-Lowering Foods
Cholesterol-lowering products contain non-hydrogenated, polyunsaturated, and monounsaturated oils (avocado and olive oil).
Moreover, food should contain high fiber and complex carbohydrates.
These include legumes (peas and beans) and whole grains such as barley, oats, egg, fruits, and vegetables—especially those rich in vitamins B, C, and E.
Cholesterol-lowering foods typically provide much less total fat, many more complex carbohydrates, and much more protein.
In the right proportions, they promote weight loss without cutting out major food groups, something that cannot be said of many of the heavily advertised, popular weight-loss diets.
Some foods help the cholesterol profile by raising the “good” cholesterol levels, HDL.
Omega-3 fatty acids in fish, avocados, and walnuts raise HDL levels. It also has blood thinning and antiarrhythmic properties that help maintain a normal heart rhythm and lower the risks of heart problems.
Moreover, it would be best to avoid drinks like carbonated drinks, sweetened, packed fruit juice, and alcohol consumption. These foods decrease the level of HDL (so-called “good cholesterol”) and increase LDL (so-called “bad cholesterol”).
Some studies suspect that high blood levels of the amino acid homocysteine may promote atherosclerosis. Increasing your intake of folic acid, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 can help reduce homocysteine levels.
Natural sources of vitamin B are beneficial. They include whole grains, leafy greens, molasses, brewer’s yeast, and nuts. While meats and liver are also good sources of vitamin B, they tend to be high in fat and cholesterol.
Food Preparation and Eating Out
Choosing better methods of food preparation can significantly reduce lipid intake. For example, grilling allows fats to spatter or drip away from the food instead of soaking them. Generally, pan-frying in oil or butter should be avoided.
Smart choices can also extend to eating out. While some fast food establishments employ low-fat cooking, they should be avoided unless they offer salad alternatives.
Many restaurants, bars, kiosks, and drive-ins specialize in fried foods, either pan or deep-fried.
If you choose to eat fried foods, try replacing them with baked food or select a place that uses olive or avocado oil in baking.
When salad dressings are part of the meal, ask for the dressing on the side to control the quantity eaten. Also, look for a salad dressing that is naturally made and unsweetened.
Many establishments accept special requests. Don’t hesitate to ask for a smaller serving.
Eating well means taking charge of your eating habits, knowing what and where to eat, and gaining family and friends’ support.
Making adjustments for the long term, lowering cholesterol, building a healthful diet, and using low-fat cooking strategies are all constructive measures that aid in preventing heart problems.
The bottom line
Cholesterol is vital in our body; without it, we cannot survive. But due to a bad lifestyle, we have an imbalance of LDL and HDL cholesterol.
Due to the rise of LDL cholesterol above normal, it disproportionates the functionality of cholesterol.
If your cholesterol is out of balance, the first step is to intervene in your current lifestyle.
You need to have super healthy foods that include more green vegetables, unsaturated fats, and fiber-rich foods in your lifestyle.
More importantly, you must avoid processed food that contributes to trans fat and raises insulin. Additionally, smoking and drinking should be avoided at any cost.
If you’re concerned about cholesterol, then visit the nearest medical center and have them checked with your doctor. Before that, you must fulfill the basic cholesterol test requirements like overnight fasting.