FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
According to the experts, some teas help with cancer, heart disease, diabetes and encourage weight loss by lowering cholesterol and bringing mental alertness.
Also, many teas contain antimicrobial qualities. Drinking tea is an excellent alternative to drinking coffee.
Additionally, it is well established that the compounds in tea and their flavonoids are perfect for the heart and may reduce cancer development.
Teas That Help Weight Loss
Here are the best teas that help weight loss:
Green Tea

We all very well-know about the various benefits of Green tea to our health.
But do you know the fact that green tea is also helpful in losing weight?
The antioxidants present in green tea may help prevent arterial clogging, burn fat, stabilize oxidative stress on the brain, reduce the risk of neurological conditions like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease.
According to the study, green tea consumption will help you lose weight from 0.2 to 3.5 kg in over 12 weeks.
Also, green tea helps reduce the risk of stroke and improves cholesterol levels.
Oolong Tea
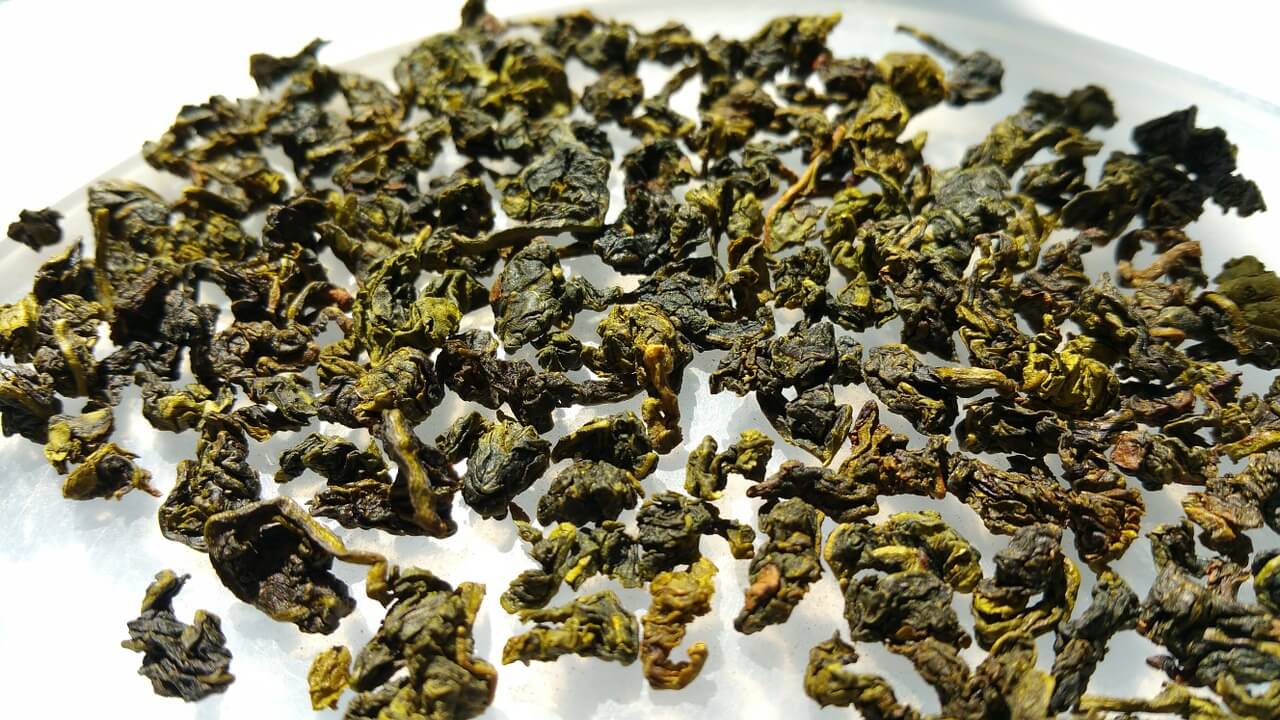

Oolong tea is made from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant, the same plant from which green and black teas are made from.
Antioxidants in oolong tea will also help the body burn more fat effectively and quickly, particularly tummy and upper arm fat. Regular consumption of oolong tea can block fat-building enzymes.
A recent study conducted on 102 Chinese women has revealed that drinking 4 cups of Oolong tea for 6 weeks has lost a kilogram of weight.
Bilberry Tea
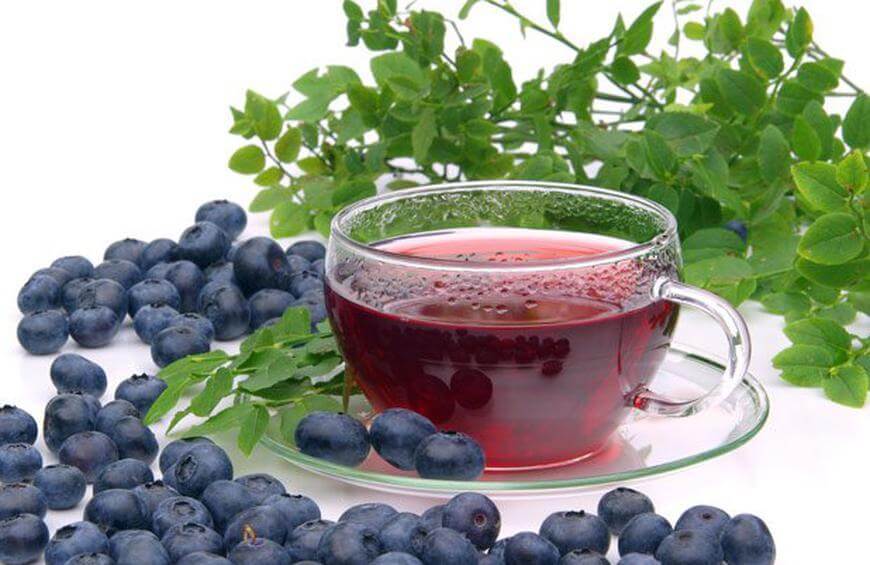

Bilberry fruit can act both as a food and a potential remedy for various health disorders.
There are some chemical compounds called anthocyanoside in bilberry with antioxidant properties.
When you consume this bilberry tea, it will stabilize the blood sugar levels and reduce cravings for fatty or sugary foods.
Some early research has shown that consuming bilberries tea daily for 33-35 days decreases the weight and waist circumference of obese and overweight women.
Black Tea
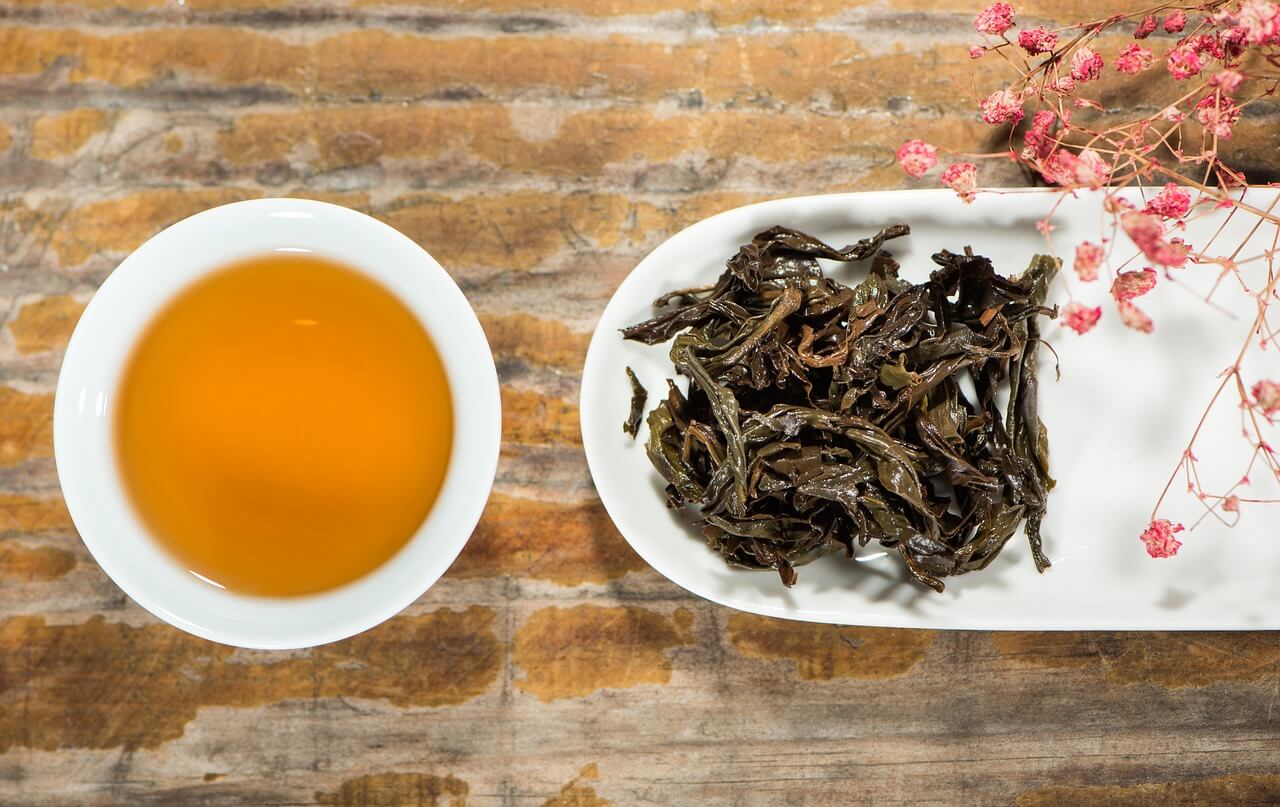

It is actually from the same plant as green tea, but the only difference is processing.
It results in those weight loss blasting chemical compounds to be more complex. Though they are still there, it is better to make it simpler.
The caffeine in black tea may also enhance weight loss. Antioxidants present in black tea may help boost your metabolism and burn body fat more effectively.
A study conducted on 111 people has shown that drinking three cups of black tea a day for three months increases weight loss and reduces belly fat.
Peppermint Tea
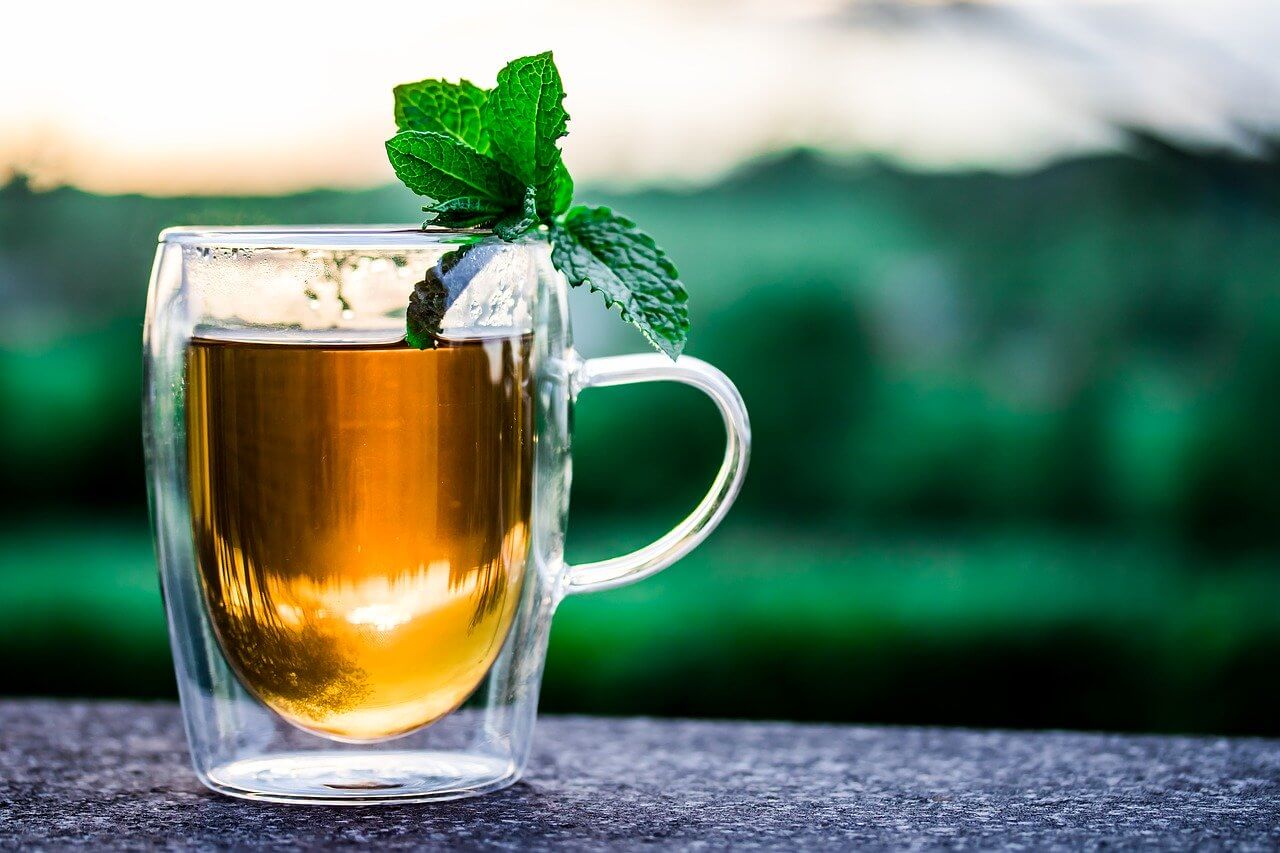

Peppermint tea can help you boost your digestive process and help you burn more calories.
Use the peppermint leaves to make a light and refreshing tea. You can consume the tea either in hot or chilled form.
Just take a tablespoon of dried or fresh leaves and add them to the boiling water and let it keep for five minutes. Then strain and add honey to add a little flavor to it.
Wrap Up:
These teas will help in suppressing the hunger hormones and increase your calorie burn.
If you drink regularly, then these herbal teas will help you lose weight and boost your metabolism.