FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
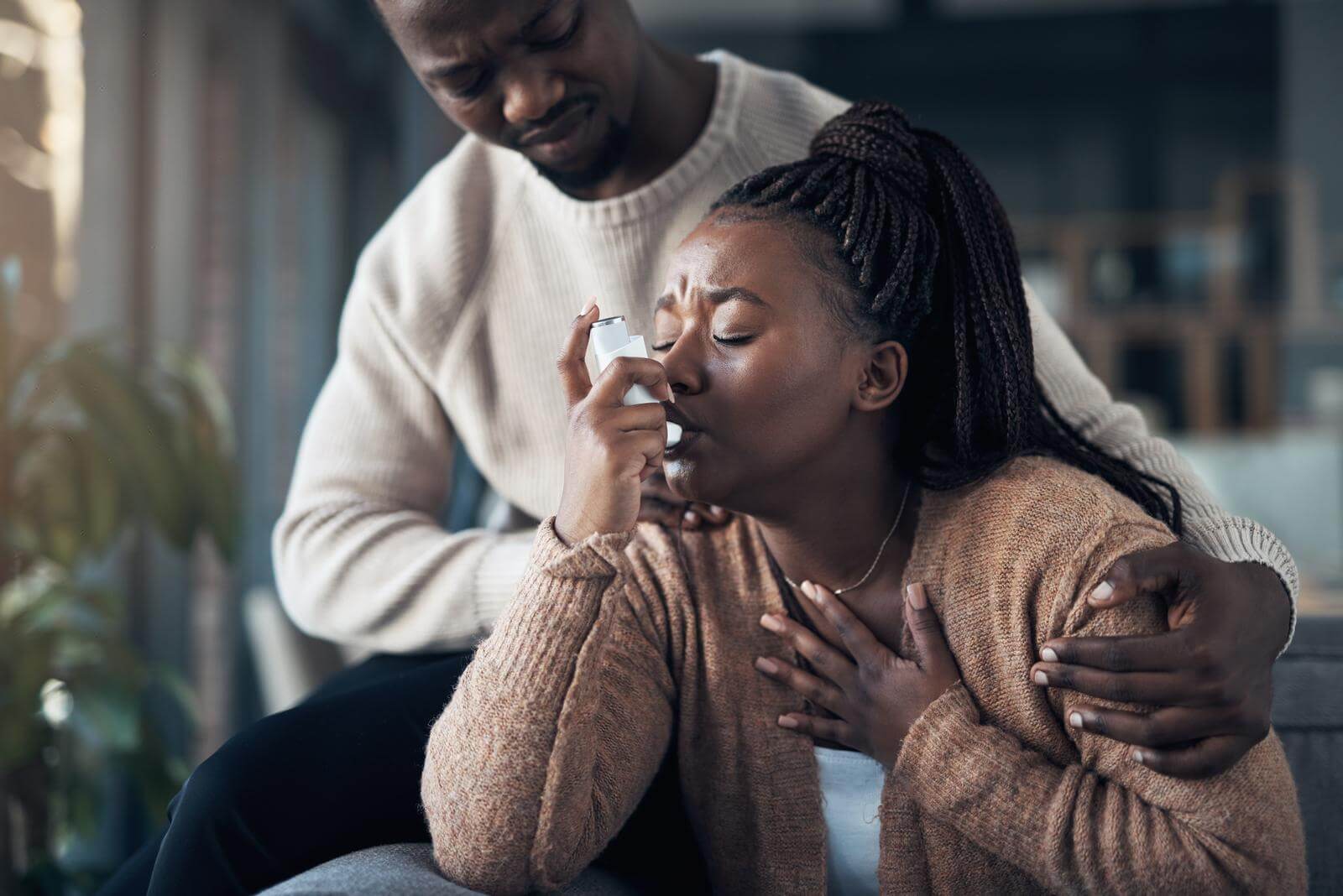
If you suffer from asthma, you’re not alone. According to the National Institutes of Health, more than 25 million people in the United States are affected by this chronic lung disease.
While there is no cure for asthma, there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms. In addition to medication, some people find relief by taking supplements and vitamins.
What are common Asthma Symptoms?
While asthma symptoms can differ from person to person, some common signs may indicate you or your child has asthma. If you experience any of the following symptoms, you must see a doctor for an evaluation.
Shortness of breath: This is typically the most noticeable symptom of asthma. You may feel like you can’t catch your breath or can only take shallow breaths. This can happen during physical activity or at rest.
Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound when you breathe is often one of the first signs of asthma, especially in children. It happens when air tries to move through narrowed airways.
Chest tightness: This feeling like something is squeezing or pressing on your chest is another common sign of asthma.
What do you need vitamins and supplements for Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic lung condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Although there is no cure for asthma, it can be controlled with medication and lifestyle changes.
Some people with asthma may also need to take vitamins and supplements to help manage their condition.
Vitamins and supplements can help people with asthma in several ways. For example, vitamin C can help to boost the immune system, while omega-3 fatty acids can help to reduce inflammation. Vitamin D and magnesium are also important nutrients for people with asthma.
If you have asthma, talk to your doctor about whether vitamins and supplements could help you manage your condition.
Here are 11 supplements and vitamins that may help asthma symptoms.
Supplements and Vitamins for asthma symptoms
Selenium

Taking selenium has many health benefits, especially for those who suffer from asthma symptoms.
A recent study showed that selenium could help to reduce the severity of asthma symptoms and can also help to prevent them from occurring in the first place.
Also, Scientific evidence suggests that asthma is linked to reduced circulatory levels of the antioxidant mineral selenium.
Asthma is a condition that affects the lungs and airways and can be very debilitating for sufferers.
The symptoms can include shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and tightness in the chest. Asthma can be a very serious condition and can even be fatal if not treated properly.
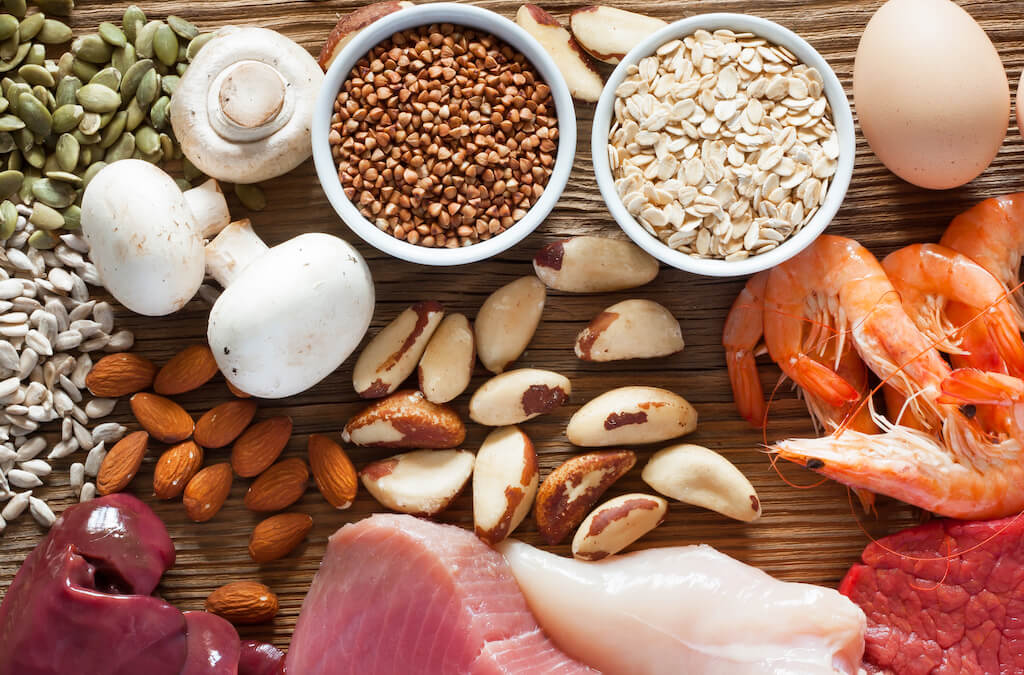
Selenium is a trace element that is found in many foods, including Brazil nuts, seafood, and meat.
It is also available in supplement form. Selenium is known to have many health benefits, including reducing the risk of cancer and heart disease.
A recent study on the health benefits of selenium for asthma sufferers was conducted by researchers at the University of Nottingham in the UK.
The study involved giving selenium supplements to a group of asthma sufferers for 12 weeks. The results showed that the selenium supplements effectively reduced the severity of asthma symptoms and prevented them from occurring in the first place.
The study showed that selenium could help to reduce the inflammation that is associated with asthma and can also help to improve lung function.
This is great news for asthma sufferers, as it can potentially avoid the need for medication or hospitalization.
If you suffer from asthma or know someone who does, it is worth considering taking selenium supplements.
Selenium has a wide range of health benefits and can effectively reduce the severity of asthma symptoms.
Vitamin B6
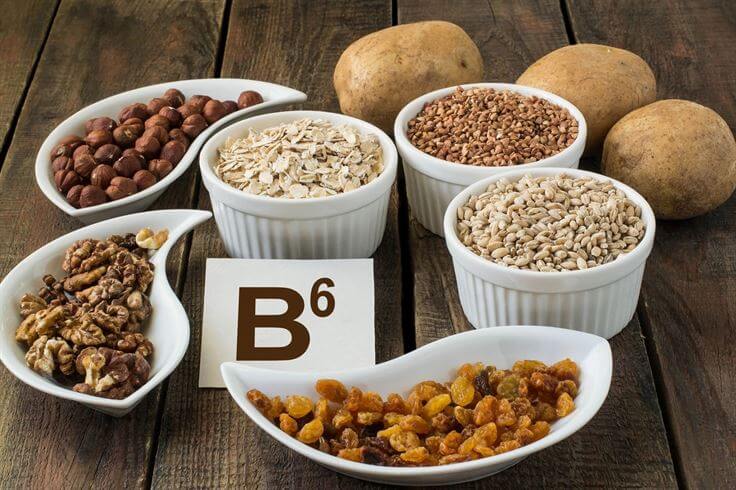

Vitamin B6 deficiency is common in asthmatics. This deficiency may be related to asthma or anti-asthma drugs (such as theophylline and aminophylline) that deplete vitamin B6.
Vitamin B6 is a vital nutrient that plays an important role in many bodily functions. It affects energy metabolism, brain function, and immune system health. Vitamin B6 is found in various foods, including meats, poultry, fish, beans, and nuts.
A recent study found that vitamin B6 may help to reduce asthma symptoms. The study looked at a group of children with asthma and a group of children without asthma. The children were given either a placebo or a vitamin B6 supplement.
The children who took the vitamin B6 supplement had significantly fewer asthma symptoms than those who took the placebo. The study also found that the vitamin B6 group had lower levels of a biomarker for inflammation.
These findings suggest that vitamin B6 could be a helpful addition to the treatment of asthma. Vitamin B6 supplements are generally safe and well-tolerated. If you have asthma, talk to your doctor about whether a vitamin B6 supplement could be right for you.
Vitamin B12

According to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America, asthma affects about 25 million people in the United States.
While there is no cure for asthma, there are treatments that can help control the symptoms. One such treatment is Vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin found in food, supplements, and some Asthma medications. This vitamin is essential for the proper function of the nervous system and the production of red blood cells.
Some research suggests that Vitamin B12 may help improve asthma symptoms. One study found that children with asthma who were given Vitamin B12 supplements had fewer asthma attacks and less need for Asthma medication.
Supplementing with B12 (particularly through intramuscular shots) markedly reduces asthma symptoms.
In one study of 85 patients, all benefited from 1000 mcg injections of B12 at weekly (and then less frequent) intervals—and the younger the patient, the better the response.
Among children under 10, 83 percent showed a moderate-to-marked improvement.
Some physicians have their patients self-administer daily shots in the following doses over ten days: 1000 mcg for two- to three-year-olds; 2000 mcg for three- to 12-year-olds; and 3000 mcg for teenagers and older.
If you’re considering taking Vitamin B12 supplements for your Asthma, talk to your doctor first. Vitamin B12 supplements are not right for everyone and can interact with certain medications.
Vitamin B12 is just one of many vitamins and nutrients that play a role in Asthma treatment. If you’re looking for ways to improve your Asthma symptoms, talk to your doctor about a tailored Asthma treatment plan that’s right for you.
Magnesium
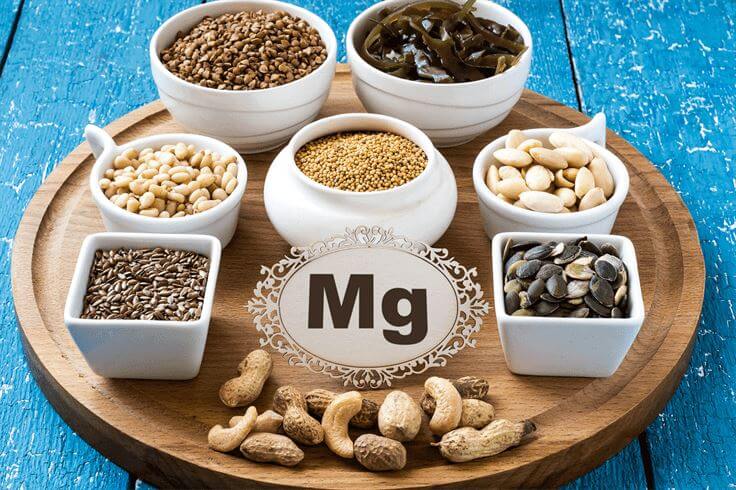

Several studies have shown that improvement in wheezing is related to blood magnesium levels. Magnesium may be a safe alternative to bronchodilators when children are suffering a severe asthma attack.
Like vitamin B6, magnesium has marked success when delivered by injection.
Magnesium is a mineral that is involved in many different bodily functions. It is needed for proper muscle and nerve function and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Magnesium is also involved in the production of energy in the body.
Recent research has shown that magnesium may also help treat asthma symptoms. One study looked at the effect of magnesium supplementation on exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, a narrowing of the airways that can occur during or after exercise.
The study found that magnesium supplementation was associated with reduced exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. In addition, the study found that magnesium supplementation was associated with a reduction in airway inflammation.
Another study looked at the effect of magnesium supplementation on airway reactivity, which is the ability of the airways to narrow in response to certain triggers. The study found that magnesium supplementation was associated with a reduction in airway reactivity.
These studies suggest that magnesium may help treat asthma symptoms by reducing airway inflammation and airway reactivity. More research is needed to confirm these findings, but the results are promising.
If you have asthma, talk to your doctor about whether magnesium supplementation might be right for you.
Vitamin D

Are you or a loved one suffering from asthma? If so, you’re not alone. According to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America, asthma affects about 25 million people in the United States.
While there is no cure for asthma, there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. One such treatment is vitamin D supplementation.
Vitamin D is a nutrient that is essential for good health. It helps the body absorb calcium, which is important for strong bones and teeth. Vitamin D also affects immunity, cell growth, and inflammation.
Recent research has shown that vitamin D may also benefit people with asthma. A study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that vitamin D supplementation reduced the severity of asthma symptoms in children.
Another study, published in the Annals of Epidemiology, found that vitamin D supplementation was associated with a reduced risk of asthma exacerbations.
Vitamin D is available in supplement form and can also be obtained from certain foods, such as fatty fish, eggs, and fortified milk. Exposure to sunlight is also a good way to get vitamin D.
If you’re considering vitamin D supplementation for asthma, talk to your doctor to see if it’s right for you.
Vitamin C

Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can help to protect the lungs from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to inflammation.
Vitamin C can help to neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation.
A recent study found that vitamin C supplementation may help to improve lung function in people with asthma.
The study found that people who took vitamin C supplements significantly improved their forced expiratory volume (FEV1). FEV1 measures how much air you can exhale in one second.
The study also found that vitamin C supplementation may help reduce asthma attacks’ severity. Asthma attacks are often triggered by allergies or exposure to irritants such as smoke or dust. Vitamin C can help to reduce the inflammation that leads to an asthma attack.
Vitamin C is found in various foods, including citrus fruits, tomatoes, potatoes, and green leafy vegetables. You can also get vitamin C from supplements.
If you take vitamin C supplements, it is important to take them with food to increase absorption.
Taking one g/day of vitamin C reduces the tendency of the bronchial passages to go into spasm, a benefit that has been confirmed in double-blind research trials.
Moreover, the beneficial effects of short-term vitamin C supplementation (less than three days) have also been observed.
If you have asthma, talk to your doctor about whether vitamin C supplementation may be right for you.
Vitamin E

Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that has a plethora of health benefits, including the ability to improve asthma symptoms.
A study published in the journal Respirology found that vitamin E supplementation improved asthma symptoms and quality of life in adults with mild-to-moderate asthma.
The study was a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that included 80 adults with mild-to-moderate asthma.
The participants were randomly assigned to receive either vitamin E (400 IU per day) or a placebo.
At the end of the study, the vitamin E group significantly improved asthma symptoms, quality of life, and lung function, compared to the placebo group.
These findings suggest that vitamin E may effectively treat asthma symptoms.
Another study published in Thorax found that vitamin E supplementation reduced asthma symptoms in children.
The study included 60 children with asthma aged 6-12 years.
The children were randomly assigned to receive either vitamin E (200 IU per day) or a placebo for eight weeks.
At the end of the study, the vitamin E group significantly improved asthma symptoms compared to the placebo group.
These findings suggest that vitamin E may be an effective treatment for asthma symptoms in children.
Supplementing vitamin E can help lower asthma, rhinitis, and hay fever rates.
Studies have found that people with the highest daily vitamin E intake were least likely to suffer from allergen-sensitive atopic conditions such as asthma, rhinitis, and hay fever.
In addition, none of the other nutrients measured appeared to have the same protective effects as vitamin E, nor did the vitamin appear more effective in combination with any other nutrient.
Vitamin E is a safe and effective treatment for asthma symptoms. If you have asthma, talk to your doctor about whether vitamin E supplementation is right for you.
Fish oil

If you suffer from asthma, you know how difficult it can be to keep your symptoms under control. But did you know that fish oil may be able to help?
A growing body of research is beginning to suggest that fish oil may offer some benefits for people with asthma.
One study, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, found that fish oil supplements reduced asthma symptoms in children and adults.
Another study, published in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, found that fish oil supplements improved asthma control in children.
And a third study, published in The Lancet, found that fish oil supplements reduced the number of asthma attacks in adults.
Double-blind studies show that fish oil partially reduces reactions to allergens that can trigger attacks in some asthmatics.
So, what’s the link between fish oil and asthma?
Fish oil is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, which may help to reduce asthma symptoms.
If you’re interested in trying fish oil for your asthma, talk to your doctor first. Fish oil supplements can interact with some medications, so it’s important to make sure they are safe for you to take.
Essential fatty acids

When it comes to essential fatty acids and asthma, there is a lot of research out there on the subject. EFAs and their byproducts have been shown to play a significant role in asthma.
Higher intake of ‘good’ fats, such as flaxseed oil, can have anti-inflammatory, free radical-fighting and immune-enhancing effects and contribute to the relative strength of cell membranes.
Studies are encouraging and may be useful for sufferers of exercise-induced asthma.
Most of the studies seem to agree that these acids can positively affect asthma symptoms and may even help prevent the condition from developing in the first place.
There are a few different ways in which essential fatty acids can help to improve asthma symptoms.
First of all, they can help to reduce inflammation in the airways. This is important because asthma is often triggered by inflammation in the lungs. By reducing the inflammation, the airways can open up and make breathing easier for a person.
In addition, essential fatty acids can also help to improve the function of the immune system. This is important because the immune system is responsible for fighting off infections in the body.
If the immune system is not functioning properly, it can make it more difficult for a person to fight off an asthma attack.
Finally, essential fatty acids can also help improve the way the body metabolizes fats. This is important because asthma is often triggered by an imbalance in the body’s fat metabolism.
By improving the metabolism, the body can better use the fats that it takes in, which can help reduce asthma symptoms.
Overall, there is a lot of evidence to suggest that essential fatty acids can positively affect asthma symptoms.
If you are looking for a natural way to improve your asthma symptoms, you may consider adding these acids to your diet.
Perilla seed oil

If you suffer from asthma, you know how difficult it can be to find relief from your symptoms. Medications can help, but they often come with unwanted side effects.
If you’re looking for a more natural way to manage your asthma, you may want to try using perilla seed oil.
Perilla seed oil is derived from the seeds of the perilla plant. This plant is native to Asia and has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries.
Recent studies have shown that perilla seed oil can help to reduce asthma symptoms. One study found that perilla seed oil could reduce airway inflammation in rats.
Another study looked at the effects of perilla seed oil in people with asthma. This study found that perilla seed oil could improve lung function and reduce asthma symptoms.
Supplementing with perilla seed oil may help to improve lung function in certain asthma sufferers. Perilla seed oil is an extract of the Asian beefsteak plant (also known as Chinese basil or wild sesame).
It is high in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (LNA), which is thought to inhibit the generation of leukotrienes in asthma sufferers.
If you’re looking for a natural way to manage your asthma, perilla seed oil may be worth trying. This oil is available in supplement form and can be found online or in health food stores.
Evening primrose oil

If you’re one of the millions of Americans suffering from bronchial asthma, you may be looking for anything to help relieve your symptoms. Some people turn to Evening Primrose oil as a natural treatment.
Evening primrose oil is a plant-based oil high in essential fatty acids. These fatty acids are thought to help reduce inflammation throughout the body.
A small study published in Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology found that evening primrose oil may help reduce asthma symptoms.
In the study, 30 people with asthma were given either evening primrose oil or a placebo for four weeks.
The group taking evening primrose oil significantly decreased the number of asthma attacks and the severity of their symptoms.
While more research is needed, the study suggests that evening primrose oil may be a helpful natural treatment for bronchial asthma.
If you’re considering trying evening primrose oil, talk to your doctor first. The oil is available in capsules or as a liquid. It can be taken orally or applied topically to the skin.
Evening primrose oil is generally considered safe, but it can cause side effects like stomach upset, headaches, and skin rashes.
It can also interact with certain medications, so it’s important to check with your doctor before taking it.
Green-lipped mussels
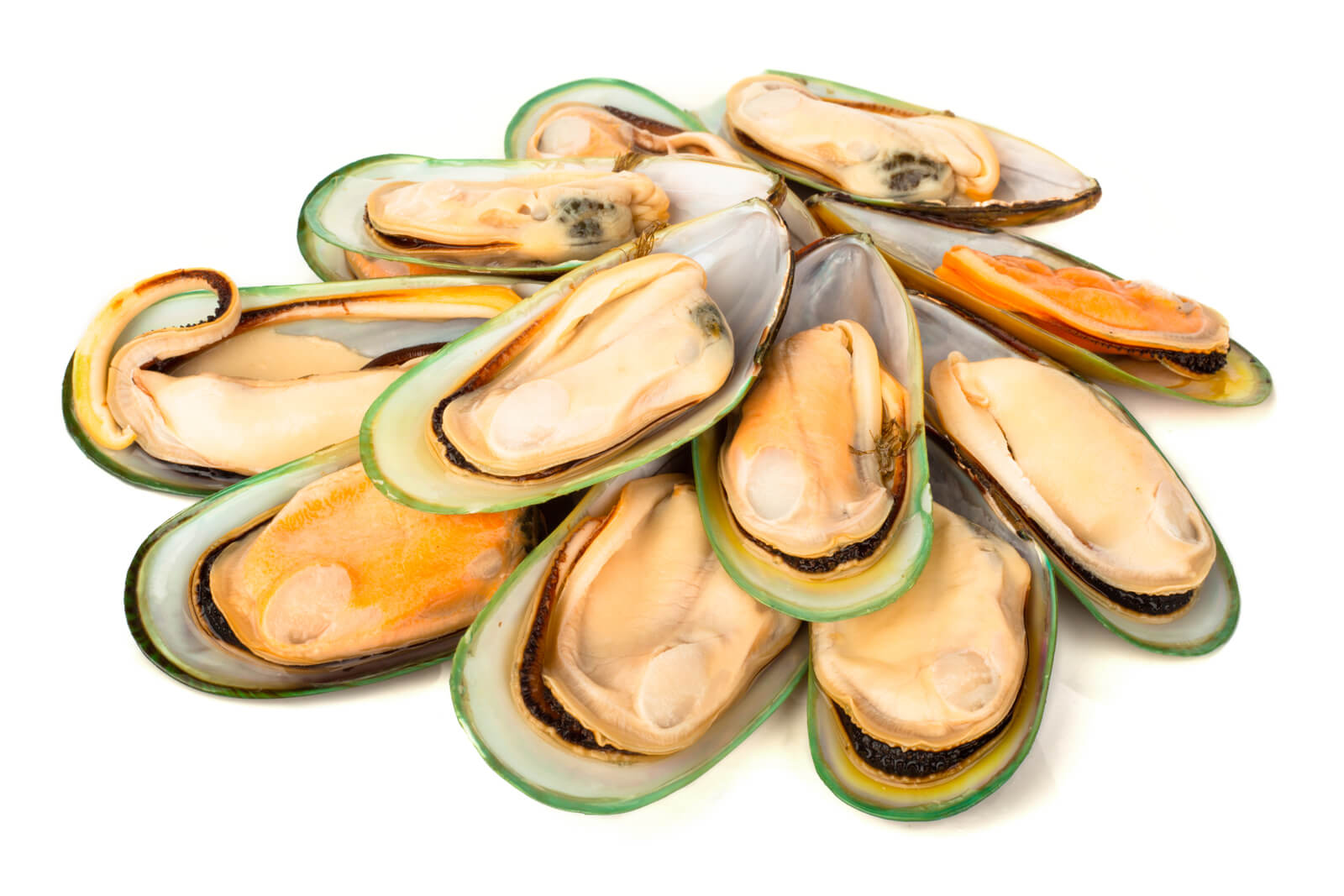

The green-lipped mussel is a type of shellfish that is native to New Zealand. It has been used for centuries by the Maori people for its medicinal properties.
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in the potential health benefits of green-lipped mussels for people with asthma.
Many studies have shown that green-lipped mussels can help reduce asthma symptoms.
In one study, people with asthma who took green-lipped mussel extract for four weeks significantly reduced asthma symptoms, including less wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Another study found that green-lipped mussel extract could reduce inflammation in the airways of people with asthma.
There is also some evidence that green-lipped mussels can help improve the quality of life for people with asthma.
In one study, people with asthma who took green-lipped mussel extract for 12 weeks reported a significant improvement in their quality of life, including fewer asthma-related symptoms and less interference with daily activities.
Supplementation with an extract of New Zealand green-lipped mussels (Perna canaliculus) can relieve symptoms and improve lung function in people with asthma.
While mussel extract is rich in omega-3 (EPA and DHA) fatty acids, the researchers suggest that eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA), found naturally in the green-lipped mussel, is responsible for its positive effects in asthma sufferers, as ETA is thought to be a more potent anti-inflammatory than either EPA or DHA, found in cod liver oil and other fish-oil supplements.
If you’re interested in trying green-lipped mussels for your asthma, talk to your doctor to see if it’s right for you.
While the research on green-lipped mussels and asthma is promising, it’s important to remember that these studies are small and more research is needed to confirm the benefits.
Conclusion
There are 11 supplements and vitamins that may help asthma symptoms. However, it is always best to speak with a doctor before taking any of these.
Some of these may interact with other medications or may not be right for everyone. Asthma is a serious condition and should always be treated as such.