FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
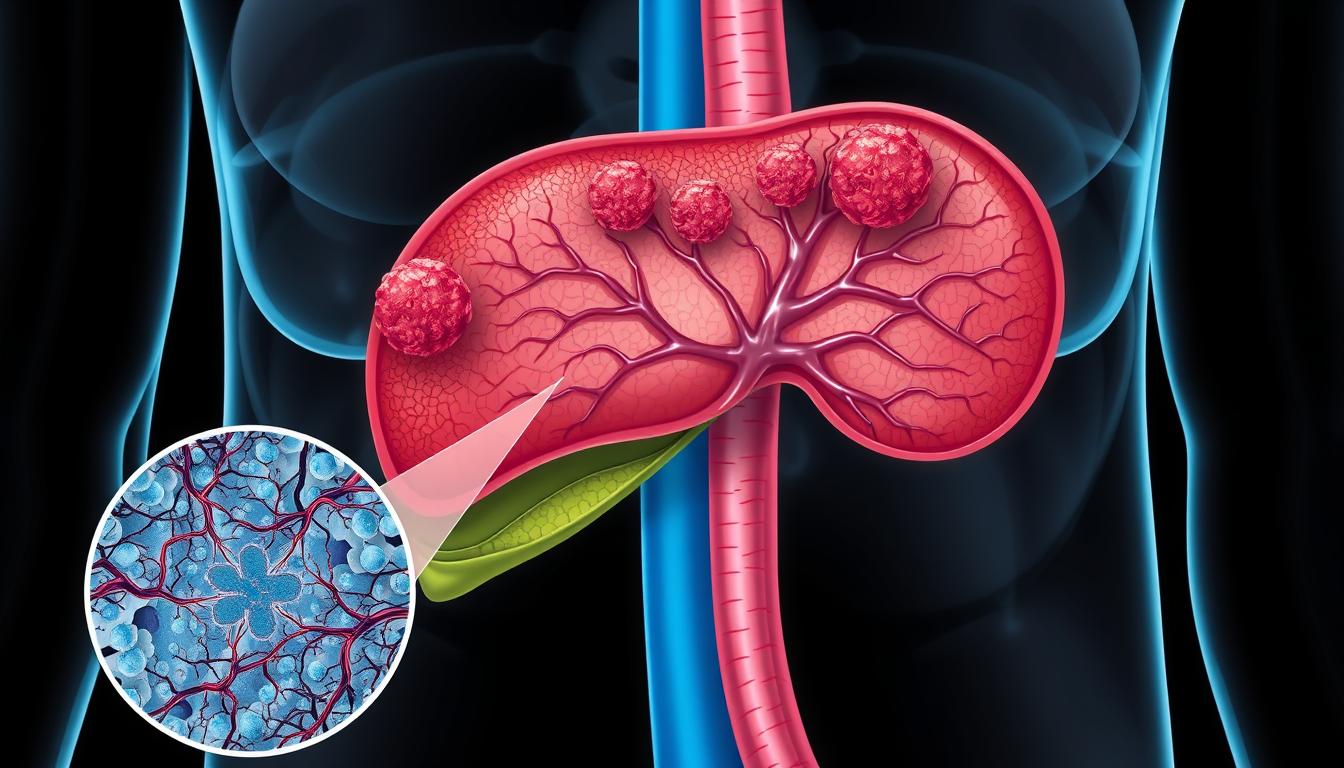
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a serious issue, making up more than 90% of primary liver tumors. It’s the fifth most common cancer globally and the second leading cause of death in men. Sadly, only 18% of people survive five years after diagnosis.
About 85% of patients with cirrhosis get HCC. This shows how critical it is to know about this deadly disease.
HCC has many risk factors, like viral hepatitis, alcohol damage, and fatty liver disease. With more cases due to obesity and diabetes, it’s key to understand its causes, signs, and treatments.
Key Takeaways
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer, accounting for over 90% of cases.
- HCC primarily affects individuals with chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infections.
- Significant risk factors for HCC include viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- HCC is a highly aggressive form of cancer, with a low five-year survival rate of just 18%.
- The incidence of HCC is expected to rise dramatically in the United States due to the increasing prevalence of obesity and diabetes.
What is Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common liver cancer. It starts in the liver’s main cells, called hepatocytes. This cancer can be divided into different types based on how much it looks like normal cells.
Definition and Types
HCC is a serious cancer that needs quick medical help. It happens when liver cells grow out of control, forming a tumor. HCC can be split into various types, each needing its own treatment.
In the USA, HCC is a big worry. Studies show its prevalence is changing. Worldwide, research helps us understand where and why HCC happens and how it affects people.
- Well-differentiated HCC tumors look like normal liver cells and grow slowly.
- Moderately differentiated HCC tumors look somewhat like normal cells but grow faster.
- Poorly differentiated HCC tumors are very aggressive, with cells that look a little like normal liver cells and grow quickly.
Knowing the cancer’s stage and how it will progress is key. This helps doctors choose the best treatment for HCC patients.
“Hepatocellular carcinoma is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive understanding of its epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment options to provide the best possible care for patients.”
Causes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common liver cancer. It can come from many causes. Chronic viral hepatitis, NAFLD, too much alcohol, and aflatoxins are the top reasons for this serious disease. Knowing these causes helps prevent and treat them early.
Viral Hepatitis
HBV and HCV infections cause over 70% of liver cancer worldwide. People with these infections, especially those with cirrhosis, are at high risk. In the U.S., HCV is the main cause of liver cancer. In Asia and Africa, HBV is more common.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
Obesity and metabolic disorders have increased NAFLD and NASH. NASH can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer, making it a growing concern.
Alcohol Consumption
Drinking too much alcohol, over 80 grams a day, can cause liver cancer. Heavy drinkers with cirrhosis are ten times more likely to get liver cancer.
Aflatoxins
Aflatoxin B1 is a strong cancer-causing agent found in Aspergillus fungi. It’s common in sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, and China, leading to more liver cancer.
It’s key to tackle these causes to lower liver cancer rates and improve treatment results. Preventive steps like the hepatitis B vaccine, reducing aflatoxin exposure, and managing NAFLD and alcohol use are vital.
“Chronic viral hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and excessive alcohol consumption are the leading causes of hepatocellular carcinoma, a deadly form of liver cancer.”
Risk Factors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common liver cancer. It has many causes. Viral hepatitis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease are the main ones. But other factors can also raise the risk of getting this disease.
Cirrhosis is a big risk factor. It’s a chronic liver condition with scarring and poor function. It can come from viral hepatitis, too much alcohol, or fatty liver disease. People with cirrhosis are more likely to get HCC.
Metabolic syndrome is another risk. It includes obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Being overweight or having type 2 diabetes can raise liver cancer risk, especially with other factors.
Iron overload disorders, like hereditary hemochromatosis, can also lead to HCC. These genetic conditions cause too much iron in the liver. This can harm liver cells and increase cancer risk.
Genetic disorders like glycogen storage disease and Wilson’s disease also raise HCC risk. These rare conditions can harm liver function and make it more likely to get liver cancer.
Environmental toxins, like aflatoxins in contaminated foods, can also cause HCC. This is especially true when combined with viral hepatitis.
Knowing all the risk factors for HCC is key to preventing and finding it early. Healthcare workers can lower the risk of this serious liver cancer by tackling these factors.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) might not show symptoms early on, especially in those without cirrhosis. As it grows, symptoms like abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, ascites, and fever can appear.
Common Symptoms
HCC symptoms are often not clear-cut. They can mean many things. People might feel pain in the right upper abdomen. They might also lose weight without trying, turn yellow, have fluid in their belly, or feel feverish.
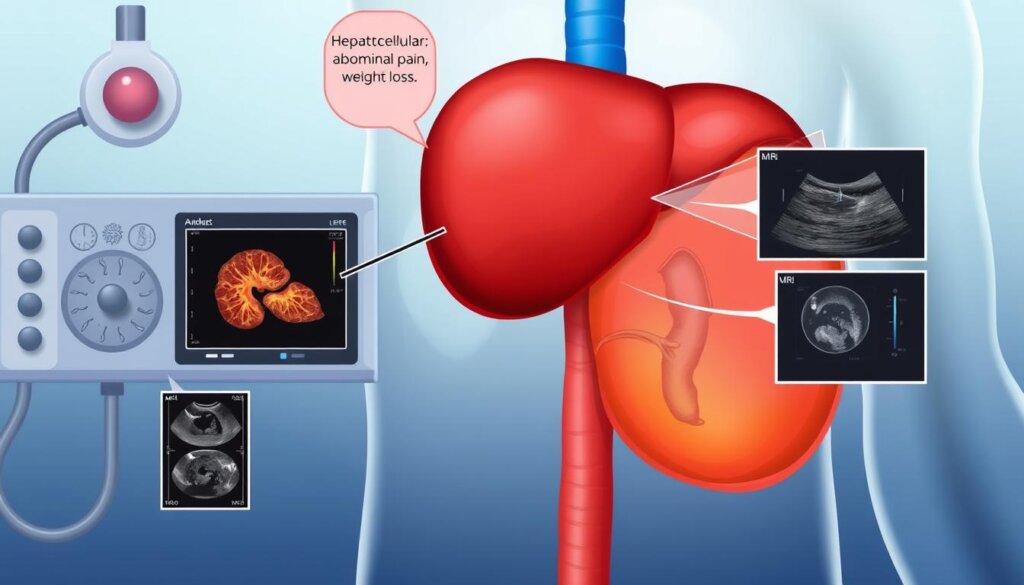
Diagnostic Tests
Doctors use several tests to find HCC. Blood tests check liver health and alpha-fetoprotein levels. Imaging like CT scans, MRI, or ultrasound show tumors in the liver. Sometimes, a biopsy is needed for a sure diagnosis, but not always.
Finding HCC early is key to better treatment. High-risk people with liver disease should get regular checks. This helps catch liver cancer early when it’s easier to treat.
Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
Blood Tests | Measure liver function and check for elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels, which can indicate liver cancer. |
Imaging Studies | Provide visual confirmation of the presence and characteristics of a liver tumor using techniques like CT scans, MRI, or ultrasound. |
Liver Biopsy | Obtaining a tissue sample for a definitive diagnosis is not always necessary if other test results are conclusive. |
“Early detection is crucial for improving the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.”
Staging and Prognosis
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common liver cancer. It is staged using the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) system. This system looks at tumor size, number, and spread. It also considers liver function and overall health.
The BCLC system helps decide treatment and predict outcomes. Survival rates vary widely. Early-stage cancers have over 50% survival rates. But, advanced cancers have a 0% survival rate.
Early detection is key. It allows for better treatment and better outcomes. Regular screening and monitoring for high-risk individuals can increase the chances of catching hepatocellular carcinoma in its earlier, more treatable stages.
Knowing the BCLC system and its prognosis is important. It helps guide treatment and sets realistic expectations. By staying informed and proactive, at-risk individuals can get a timely diagnosis and the right care.
Treatment Options for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common liver cancer. Treatment depends on the disease stage, patient health, and liver damage. Doctors might use surgery, ablation, targeted drugs, and immunotherapy to treat it.
Surgical Interventions
Early-stage cancer patients with healthy livers might get surgery or a liver transplant. Removing the tumor and some liver tissue is called liver resection. Liver transplant treats cancer and liver disease in patients with cirrhosis and small tumors. But, finding donor organs and meeting strict criteria can be hard.
Ablation Therapies
Ablation therapies destroy tumors without removing the liver. They include radiofrequency, microwave, ethanol injection, cryoablation, and electroporation therapy. These are used for small tumors or when surgery isn’t possible.
Targeted Drug Therapy and Immunotherapy
Advanced cancer patients might get targeted drugs or immunotherapy. Targeted therapies, like sorafenib and Lenvatinib, block tumor growth. Immunotherapy uses the immune system to fight cancer, with drugs like Atezolizumab showing good results. These treatments can be used alone or together, based on the patient’s needs.
Choosing the right treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma is complex. It depends on the disease stage, patient health, and treatment risks and benefits. Working together, patients, oncologists, and liver specialists find the best treatment plan.
Prevention Strategies
Stopping hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) needs a few steps. Vaccination against hepatitis B virus (HBV) is key. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says all kids and some adults should get the HBV vaccine. This helps a lot because HBV is a big cause of HCC worldwide.
For those with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV), getting treated early is important. The CDC says to test all adults for HCV at least once. People at higher risk should get tested more often. Treatments for HCV can clear the virus, which might lower HCC risk.
Changing our lifestyle is also key. Drinking less alcohol can stop cirrhosis, a big HCC risk. Keeping a healthy weight and managing obesity and diabetes can also help. These steps can lower the risk of NAFLD and NASH, which are linked to HCC.
Screening for HCC in those at high risk is vital. This includes people with cirrhosis. By using these steps, we can greatly lower HCC’s impact.
Prevention Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
Hepatitis B Vaccination | Recommended for children, adults up to age 59, and older adults at risk to prevent chronic HBV infection, a leading cause of HCC. |
Hepatitis C Treatment | Timely treatment of chronic HCV infection can eliminate the virus and reduce the risk of HCC. |
Lifestyle Modifications | Limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing conditions like obesity and diabetes to prevent cirrhosis and NAFLD/NASH, which increase HCC risk. |
Regular Screening | Early detection of HCC through screening for high-risk individuals, such as those with cirrhosis, can lead to improved outcomes. |
By using these steps, we can really cut down on HCC. This will help people at risk stay healthier.
“Prevention is the best medicine when it comes to liver cancer. By taking proactive steps, we can protect ourselves and our loved ones from this devastating disease.”
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Living with the Condition
Getting a diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma can be scary. But there are ways to manage it and live better. Knowing how the disease affects you is key to facing challenges.
Living with this disease means dealing with physical symptoms and side effects. It can make you feel tired, lose your appetite, and struggle to do everyday things. Working with your doctor to manage these issues can make a big difference.
Hepatocellular carcinoma also affects your mind and feelings. You might feel anxious, sad, or unsure. It’s important to find ways to cope with these feelings. Counseling, support groups, and stress-reducing activities can help.
This disease can also change how you connect with others and find meaning. It can be hard to keep up with relationships and feel a sense of purpose. Talking to loved ones, doing things you enjoy, and exploring spirituality can help.
Dealing with hepatocellular carcinoma means looking at all aspects of your life. Getting help with counseling, pain management, and palliative care can improve your life. It helps you cope with the disease.
Remember, everyone’s experience with this disease is different. The best way to deal with it is to work with your healthcare team and get the support you need. This way, you can live as fully as possible despite the challenges.
Conclusion
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a serious liver cancer. But new ways to find and treat it offer hope. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer death. The number of HCC cases has gone up in recent years.
By knowing the causes and treatments, people can work with their doctors. This helps create a plan for better health and well-being.
Recent studies show good news for HCC management. The rate of finding one tumor early went up to 73%. And, finding tumors that have spread to blood vessels went down to 20% from 2012 to 2015.
Also, more people are getting treatments that can cure them. This has led to better survival rates. Treatments like surgery, liver transplants, and local treatments can help up to 75% of people live 5 years.
There are also new medicines like sorafenib. They help people with advanced HCC.
By learning about hepatocellular carcinoma, people can help manage their health. With ongoing research, the future looks brighter for those with HCC.
FAQ
What is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a cancer that starts in the liver. It is the most common type of liver cancer.
What are the main causes of hepatocellular carcinoma?
The main causes include viral hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and alcohol use. Aflatoxins also play a role.
What are the risk factors for developing hepatocellular carcinoma?
Risk factors include cirrhosis and metabolic syndrome. Obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia are part of it. Genetic disorders also increase risk.
What are the common symptoms of hepatocellular carcinoma?
Early stages may not show symptoms. But as it grows, symptoms like pain and weight loss appear. Jaundice, ascites, and fever are also signs.
How is hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosed?
Tests include blood tests and imaging like CT scans. MRI and liver biopsy may also be used.
How is hepatocellular carcinoma staged?
The Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) system is used. It looks at tumor size, spread, and liver function.
What are the treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma?
Treatment depends on the disease stage and health. Options include surgery, ablation, and targeted drugs. Immunotherapy is also used.
How can hepatocellular carcinoma be prevented?
Prevention includes hepatitis B vaccination and treating hepatitis C. Lifestyle changes like diet and exercise are also key.
How can individuals living with hepatocellular carcinoma manage their condition?
Living with HCC can be tough. But, there are ways to manage it. Supportive care and palliative care can help improve life quality.