FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Glaucoma, a group of diseases that can lead to vision loss and even blindness, is a global concern, standing as the second leading cause of blindness in the United States and worldwide.
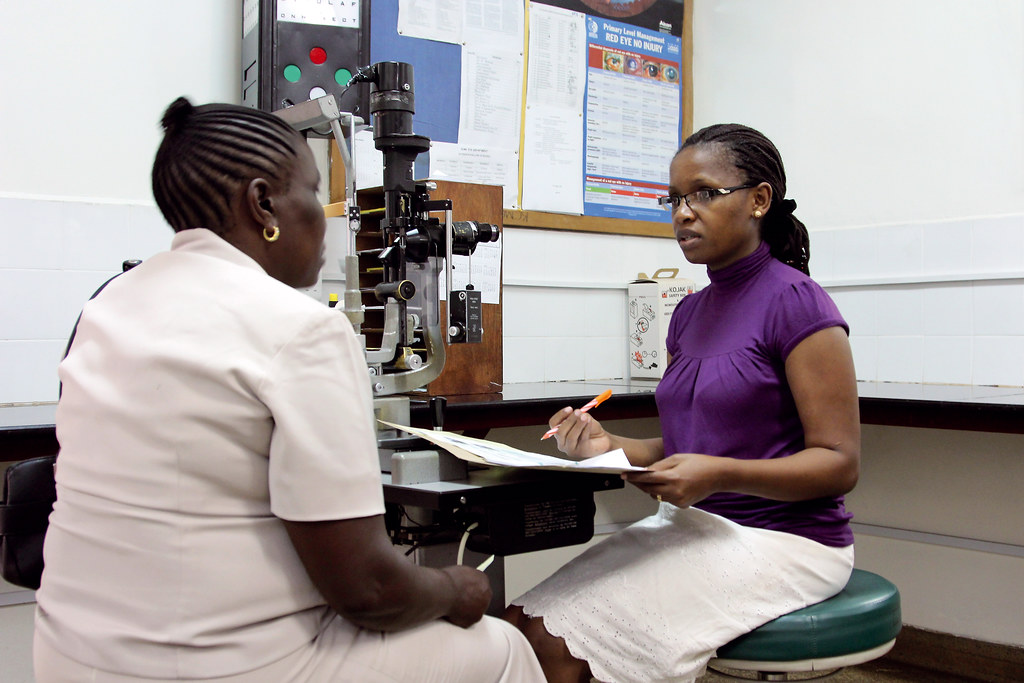
In the midst of this, a Glaucoma Specialist emerges as a beacon of hope. They are Eye M.D.s (Ophthalmologists) with specific fellowship training in glaucoma.
These specialists play a crucial role in managing and treating glaucoma, particularly in advanced stages where routine treatments may not suffice.
Their expertise is not confined to diagnosing the disease and offering preventative advice, they also perform surgeries to save a patient’s vision. This requires a doctoral degree in ophthalmology, experience in glaucoma management, and proficiency in using ophthalmologist equipment.
Through this article, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the role and qualifications of a Glaucoma Specialist, emphasizing the importance of their expertise in eye care.
Qualifications and Training
Embarking on the journey to become a Glaucoma Specialist requires a rigorous educational and training pathway.
Initially, an aspiring specialist must earn a bachelor’s degree in a science field, followed by completion of medical school. This is the foundation of their medical education.
Subsequently, these medical graduates must secure an ophthalmology residency program, which typically spans three years. This residency provides hands-on clinical experience, allowing them to diagnose, treat, and regularly assess patients with various eye conditions.
Upon completion of the residency, an additional one to two years of specialized training is required as part of a glaucoma fellowship.
This program hones their skills in the diagnosis and management of diseases like glaucoma that may cause optic nerve damage by increasing intraocular pressure. This specialized training equips them with the necessary expertise to deliver the best possible care to their patients.
Finally, a successful glaucoma specialist must possess excellent communication and interpersonal skills and a keen attention to detail.
Staying abreast with the latest technological advances in treatments and equipment is also crucial to ensure they provide their patients with the most current and effective treatment options.
Diagnosing and Differentiating Types of Glaucoma
Glaucoma, a group of eye diseases, can cause significant vision loss by damaging the optic nerve. The two primary types are Open-Angle and Angle-Closure, with several variations stemming from these base types.
Each type of glaucoma carries its unique characteristics and symptoms, and, as such, requires specialized diagnostic methods by a Glaucoma Specialist. (source)
Open-angle glaucoma, the most prevalent type, often presents with no early symptoms. This silent onset makes regular testing crucial, especially for high-risk individuals. Primary symptoms include a gradual loss of peripheral vision and tunnel vision in advanced stages. (source)
Angle-Closure Glaucoma, on the other hand, can manifest as a medical emergency with severe eye pain, blurred vision, and nausea. (source)
Glaucoma Specialists employ a range of diagnostic methods, such as optic nerve imaging and tonometry, to accurately diagnose and differentiate between glaucoma types. Tonometry, for instance, measures the pressure inside the eye, a key factor in diagnosing glaucoma.
Treatment Options
Glaucoma treatment involves a variety of options, including medications, laser therapy, and surgery. Each is designed to lower intraocular pressure and prevent vision loss, albeit through different mechanisms.
For example, medications like eye drops and pills work by either reducing fluid production in the eye or increasing its outflow.
Laser therapies, such as Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty and Cyclophotocoagulation, create alternative pathways for fluid to drain from the eye or decrease fluid production. Surgical procedures, like Trabeculectomy and Drainage Implant Devices, provide more long-term solutions by creating new, permanent pathways for fluid drainage.
Choosing the most suitable treatment plan is a personalized process. A Glaucoma Specialist considers various factors, including the severity of the disease, the patient’s response to medication, and any other existing health issues. Regular follow-ups are crucial to monitor the treatment’s effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Importance of Regular Screenings and Check-ups
Glaucoma, a group of eye disorders, often goes undiagnosed due to its silent nature. It is especially prevalent among populations of low socioeconomic status, older age, African or Hispanic ancestry, and those with a family history of the disease, hypertension, or Type 2 diabetes. (source)
Glaucoma Specialists play a crucial role in early detection and treatment. They perform comprehensive eye examinations involving several tests such as Tonometry, Ophthalmoscopy, Perimetry, Gonioscopy, and Pachymetry, essential for detecting early signs of Glaucoma. (source)
Timely intervention by these specialists can significantly prevent vision loss. Regular screenings and check-ups are critical, especially for those with increased risk factors.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends regular eye exams for those over age 40 and more frequent or earlier exams for those with risk factors for glaucoma. (source)
Impact of Timely Intervention
Screening patients over 80 years of age could reduce the prevalence of blindness by 10.9%, and earlier and more frequent screenings could have an even more significant impact. (source)
Therefore, raising public awareness about the importance of regular screenings and early treatment, even for those with no symptoms, is crucial.
Collaborative Role of Glaucoma Specialists with Other Eye Care Professionals
In the evolving landscape of eye care, the role of glaucoma specialists has become increasingly collaborative. The growing number of glaucoma patients necessitates a teamwork-oriented approach to treatment, with the need for specialist intervention varying across different stages of the disease (Ophthalmology Management).
Optometrists, skilled in assessing and detecting ocular diseases, play a complementary role, often initiating topical therapy for glaucoma and referring patients to ophthalmologists for further treatment (NCBI). The collaboration between these professionals leads to a more comprehensive and effective approach to managing glaucoma.
Successful collaborations in the field of eye care have been seen in Australia, where over 75% of vision care services are provided by optometrists, with the majority also holding therapeutic endorsement.
Ophthalmologists, on the other hand, take on the leadership role in glaucoma management (NCBI).
Such collaborative practices not only streamline the patient care process but also facilitate the sharing of knowledge and updates in technologies or procedures, such as minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (Ophthalmology Management).
Frequently Asked Questions
A Glaucoma Specialist is an Eye M.D. or Ophthalmologist who has undergone additional fellowship training specific to glaucoma.
They handle cases where routine treatment methods fail to manage advanced stages of glaucoma, a disease that can lead to vision loss or even blindness. (source)
What’s the difference between Ophthalmologists, Optometrists, and Opticians?
Ophthalmologists are medical doctors who specialize in eye and vision care, including surgery.
Optometrists provide primary vision care but don’t perform surgery. Their role in glaucoma care varies, from performing refractions to assisting with postoperative care.
Opticians, conversely, are technicians trained to design, verify, and fit eyeglass lenses and frames, contact lenses, and other devices to correct eyesight. (source)
What does glaucoma treatment and management entail?
Glaucoma treatment involves regular monitoring, medication, or surgery. The goal is to lower pressure in the eye that can damage the optic nerve.
The right treatment for each patient depends on the severity and progression of the disease. In cases of advanced glaucoma, a glaucoma specialist can offer expert care. (source)
Conclusion
In wrapping up, a Glaucoma Specialist’s role is crucial in preserving and protecting patients’ vision. They are the guiding light in the complex labyrinth of glaucoma, a potentially blinding eye condition that affects millions worldwide.
These healthcare professionals bring their specialized training and expertise to the fore, providing accurate diagnoses, creating individualized treatment plans, and offering medical management to slow disease progression and safeguard vision.
Like an experienced captain navigating a ship through turbulent seas, a Glaucoma Specialist steers patients through the stormy waters of Glaucoma, ensuring their sight remains intact. As the old saying goes, prevention is better than cure.
Therefore, regular screenings and check-ups with a Glaucoma Specialist are vital to maintaining optimal eye health.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Seek the expertise of a Glaucoma Specialist today and protect your precious gift of sight.