FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
You would have heard of the body mass index or BMI before, but are you really aware of its importance in your health and life.
Body mass index is a numeric scale used to measure your weight relative to your height, a loose indicator of the percentage of body fat.
This index is ideal for noting great risks that are associated with being overweight and obese. A BMI takes into account an individual’s age, weight, height and placed in a category that is either a healthy weight, obese, overweight, or morbidly overweight or obese.
Let’s look into the reason why your BMI is important.
Reasons Your BMI Is Important
Constant studies link diseases decreased longevity and high ratios of body fat per pound a person weighs.
With this being said, a person must understand what obesity could do to their health.
High BMI Related Health Issue
Here are some health issues that a high BMI can indicate:
Cardiovascular Disease

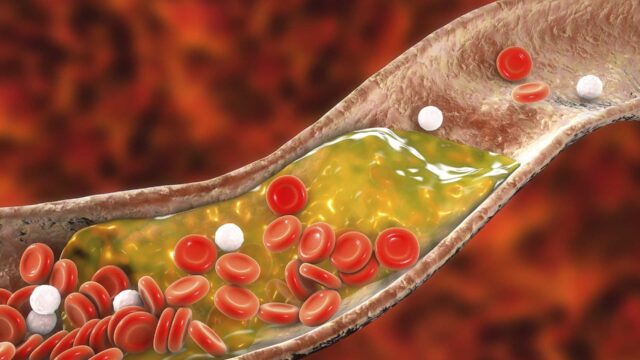
Inactivity, consuming bad foods, and overindulgence in fatty foods can result in cardiovascular disease in which fat stores harden and take over the arteries and lead to other problems.
According to data from the Framingham Heart Study, the rise of BMI by 1 kg/m2 increases the risk of heart failure by 5% for men and 7% for women.
Moreover, another study has shown the correlation between increased body mass index (BMI) and the increased risk of Cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Eating healthier and lowering your body mass index can help ward off the odds of getting cardiovascular disease.
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is one of the leading culprits that can be curbed and naturally treated with diet and exercise. If your BMI is high, chances are you have high blood pressure or at least pre-hypertension.
A present study found the relationship between the different levels of body mass index (BMI) and the changing risk of hypertension.
Strokes and Heart Attacks

Strokes and heart attacks are usually caused by plaque build-up in the arteries and blood. Plaque is a result of the hardening of fat that is not naturally broken down in the body.
This is a result of fat accruing from over-consumption of high-fat content foods.
Several studies have indicated that a high body mass index (BMI) may increase stroke risk.
Moreover, another recent study showed that high BMI and a higher percentage of body fat is greatly associated with coronary heart disease, heart failure, hypertension, and obesity.
Knowing your BMI and using a BMI calculator can help you address this problem and adjust your diet accordingly.
There are many more health issues, such as the increased risk of breast cancer, high risk of diabetes, and high cholesterol, that indicate a high ratio BMI.
That’s why it is important to know your BMI and always make efforts to remain in a healthy weight to body fat ratio.
Low BMI Ratio and The Risks Associated
Although a BMI calculator can help you determine whether your body consists of more fat than it should, having a low amount of body fat can also detriment your health.
When a person contains 18.5 BMI or less, they are at risk of not having enough body fat to sustain their body functions and are considered malnourished.
Here are some health issues associated with low body fat:
Low Immunity
When you are not getting adequate nutrition and your body fat BMI is below 18%.
You may suffer from low immunity, and your body is at greater risk of infection.
A study concluded that a low immune system and low nutrition have a greater risk factor for metabolic and endocrine disorders.
Cancer Risks
Studies have demonstrated that malnourished people do not get enough fat in their diet and fall prey to numerous cancers.
In a recent study, low BMI is highly associated with breast cancer in young women.
Good foods such as vegetables and fruits have elements that protect cell growth and defend against cancers and related diseases.
Osteoporosis, Bone Fractures & Breaks
Proper nutrition and fat intake helps to promote healthy bone growth. If you do not consume enough foods with healthy vitamins and minerals, you are more likely to get attacked with brittle bones, arthritis, and even osteoporosis.
A study concluded that low BMI is an important risk factor for low bone mass and increased bone loss in postmenopausal women.
Another study suggested that low BMI is associate with the high-risk factor of fractures in men.
In addition to these health issues, medical scientists have also linked digestive diseases and respiratory disorders to malnutrition.
It is best if you stay within a healthy BMI range between 18.-24.99. Use the BMI Calculator to determine your BMI and health risk range.