FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Hypertension (HTN) or high blood pressure, sometimes called arterial hypertension, is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated.
Such conditions require the heart to work harder than usual to circulate blood through the blood vessels.
Blood pressure involves systolic and diastolic measurements, depending on whether the heart muscle is contracting (systole) or relaxed between beats (diastole).
Normal blood pressure at rest is within the range of 100-140mmHg systolic (top reading) and 60-90mmHg diastolic (bottom reading). High blood pressure is present if it is persistently at or above 140/90 mmHg.
Why talk about hypertension?
HBP (High Blood Pressure) is a significant risk factor for heart diseases, stroke, kidney failure, heart failure, and coronary heart disease.
As per statistics, Heart disease and stroke combined are the leading cause of death in developed countries.
HBP (High Blood Pressure) is a silent killer. This means you may never know that you have hypertension till your doctor measures your BP.
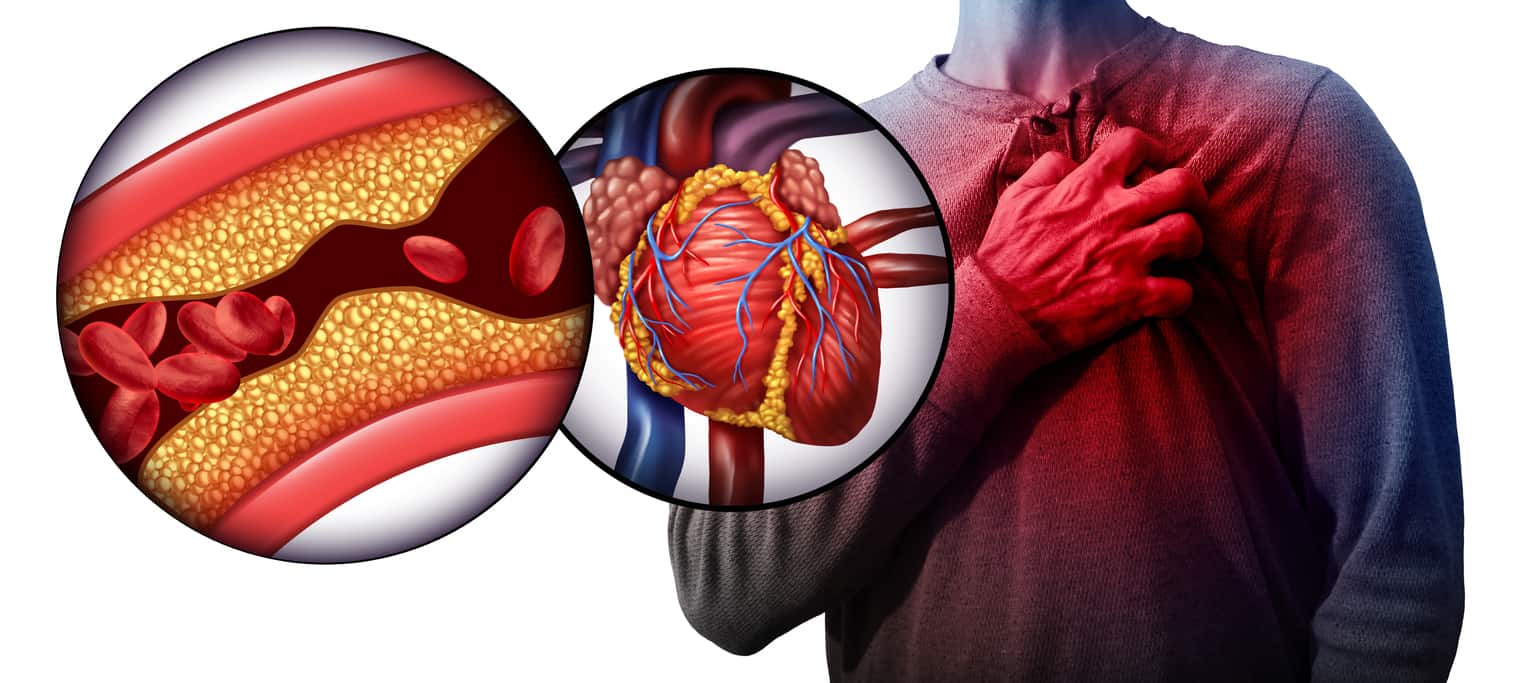
High Blood Pressure Explained
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood on the arteries or blood vessels in our body.
Further, this blood is pumped from the heart straight into the biggest artery called the aorta; then, it is distributed into other smaller arteries throughout the body.
Three main factors determine blood pressure;
- The heart
- The arteries
- The blood
The heart
The heart pumps the blood into the blood vessels. When the heart contracts (systolic blood pressure), it forces the blood into the aorta. Further, the force and rate at which the heart contracts will directly affect the blood pressure.
The greater the force, the higher the blood pressure. The time between contractions (diastolic blood pressure) when the heart relaxes affects blood pressure.
The arteries
The arteries are like pipes throughout our bodies. Their diameter or lumen size will directly affect the blood pressure.
If the diameter or lumen size is smaller for any reason, the blood pressure will go up because of more resistance.
If the lumen size is bigger, the blood pressure decreases due to less resistance. Our arteries contract and relax due to many reasons like temperature, exercise, unknown causes, and other reasons.
The blood
Blood itself affects blood pressure. The thickness and volume of blood directly affect the pressure.
If blood is thicker due to dehydration or other diseases, blood pressure will be higher.
If the blood is thinner, blood pressure will be lower due to decreased viscosity.
The volume also affects blood pressure. If the blood volume is increased for any reason, like in kidney failure, the blood pressure may be higher.
If the blood volume decreases, e.g., any blood loss like heavy bleeding, the blood pressure will be reduced.
These are the main factors that affect blood pressure. To sum this up; When someone has persistently high blood pressure, the condition is called hypertension.
Hypertension is classified as either primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension.
About 90–95% of cases are categorized as “primary hypertension,” which means high blood pressure with no apparent underlying medical cause.
The remaining 5–10% of cases (secondary hypertension) are caused by other conditions that affect the kidneys, arteries, heart, or endocrine system.
How is blood pressure measured?
Blood pressure is usually measured from one of your arm or forearm arteries.
A sphygmomanometer or blood pressure monitor is used to measure BP. The blood pressure measurement can either be manual or digital (electronic).
Health care providers usually use a manual one since its more accurate and reliable.
It’s effortless to use a digital one, you can buy it and use it at home, or most pharmacies and big supermarkets in some countries have it for you to use for free.
When measuring blood pressure, there are two readings, for example;
120/80 mmHg
The top value (120) is the blood pressure when the heart is contracting, also called systolic blood pressure.
The bottom value (80) is the blood pressure when the heart is relaxed, in-between contractions. This is called diastolic blood pressure.
Millimeters Mercury (mmHg) are the units used to measure BP.
What is normal blood pressure?
Normal BP is any readings below 120/80. Your BP changes, but any value close to this figure is acceptable.
To start the diagnosis of hypertension, your blood pressure has to be consistently high above 140/90 on three different occasions.
High blood pressure statistics
Worldwide stats:
According to World Health Organization, globally, it has been estimated that 26% of the world population has high blood pressure. And, it is expected that the figure will go beyond 29% in 2025.
Further, One in two people over the age of 60 has high blood pressure and of those who are 70 years and older, 70% have high blood pressure.
Moreover, 37% of those in developed countries are affected. In contrast, China and India have lower than average, with 17% of men affected and 14% of women having high blood pressure.
USA stats:
In the USA, 31.3% of the adult population has HBP (High Blood Pressure), 25% are pre-hypertensive. Also, 326,000 deaths already occurred in 2006, which is why HBP was linked as a contributor to death.
Moreover, in 2010, the US spent about $76,6 Billion on health care services, medications, and missed days of work.
Canada stats:
In 2010, 19% of the adult population had HBP, and out of which, 20% were pre-hypertensive.
Within 19% of the adult population, 60 years and older, 53% have been affected, and 24% are pre-hypertensive.
High Blood Pressure Facts
High blood pressure is a condition that affects the whole body. Below we will list some important facts you should know about HBP (High Blood Pressure).
High blood pressure (hypertension) is a silent killer. It means you may not have any signs and symptoms to show high blood pressure.
Blood pressure has to be measured to know it. You can stay for years without knowing that you have HBP.
HBP (High Blood Pressure) is a chronic condition that can cause damage to the arteries (atherosclerosis), cause heart disease like heart attack and heart failure, kidney failure, nose bleeds, and strokes.
Your risk of getting hypertension increases with your age. Healthy lifestyle changes are an important part of your treatment.
A family history of hypertension may increase your risk of getting HBP. It would help if you had your BP checked annually by your doctor.
Stages of hypertension
Hypertension has different stages depending on the blood pressure reading. This is very important because these stages may be treated differently.
In the USA, in 2003, the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC7) came up with criteria to determine these stages. These stages include;
Pre-Hypertension
The blood pressure is between 120/80 and 139/89
Stage 1
Blood pressure is between 140/90 and 159/99
Stage 2
Blood pressure is between 160/100 and 179/109
Stage 3 (In some countries)
Blood pressure higher than 180/110
High Blood Pressure Risk Factors
Hypertension is a major risk factor for
- Stroke
- Myocardial infarction (heart attacks)
- Heart failure
- Aneurysms of the arteries (e.g., aortic aneurysm)
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Chronic kidney disease.
Even moderate elevation of arterial blood pressure is associated with a shortened life expectancy.
Dietary and lifestyle changes can improve blood pressure control and decrease the risk of associated health complications.
However, drug treatment is often necessary for people whose lifestyle changes prove ineffective or insufficient.