FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
You’ve heard experts declare that inflammation is a significant health hazard, and you may be wondering, “Why is inflammation bad?”
Inflammation is not always harmful. Typically it’s good—even life-saving.
However, even though inflammation is usually a good thing, it is becoming increasingly clear that chronic inflammation is the cause of many diseases and may cause all chronic illnesses.
Let’s examine this apparent inconsistency.
Is inflammation good or bad?
Inflammation Is Necessary For Human Survival!
Your survival, in fact, all human survival, depends on inflammation.
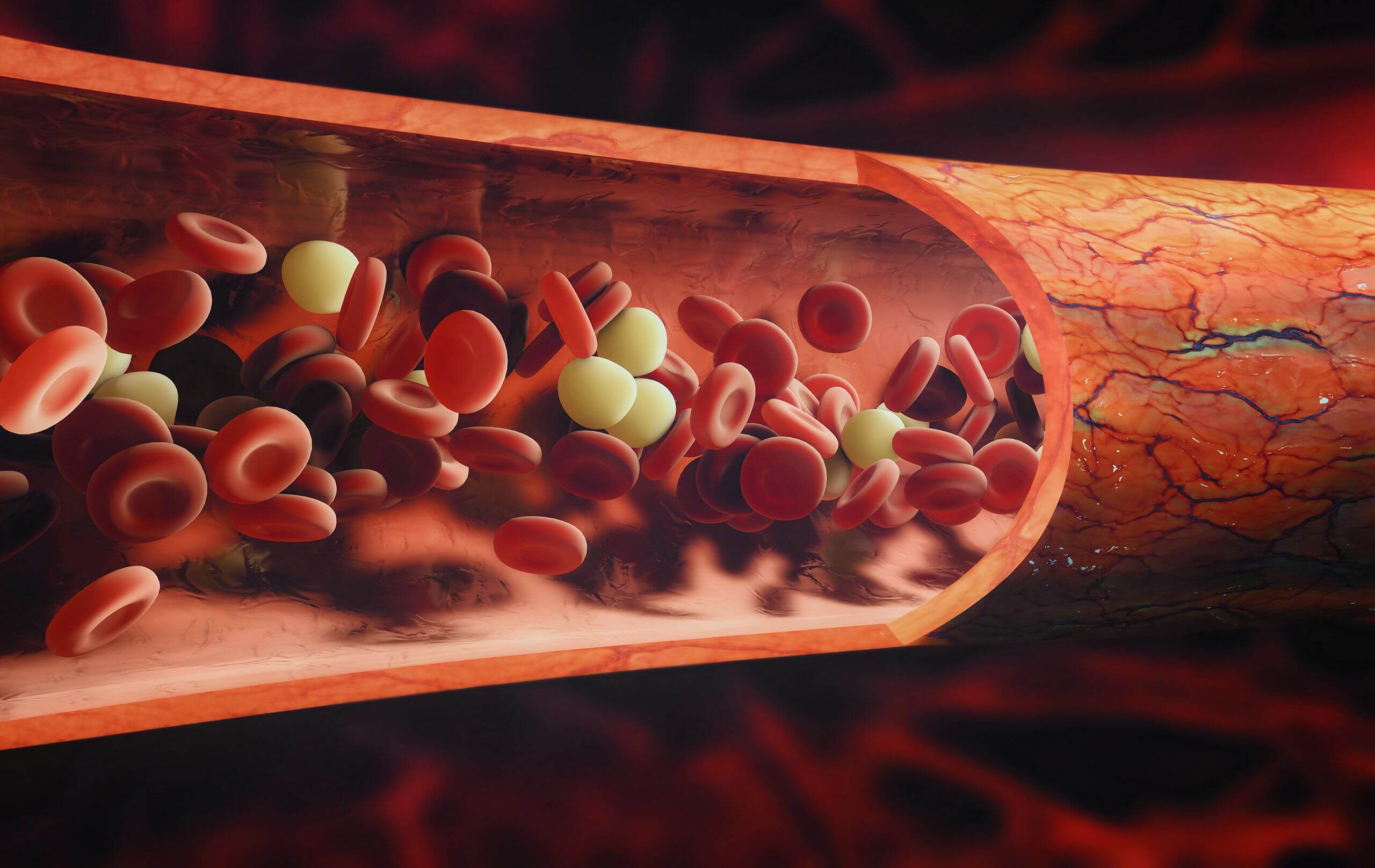
That’s because inflammation is a natural and automatic immune response to a disturbance to your body, such as an infection, irritation, or an injury.
This inflammatory response results in redness, swelling, heat, and pain in the affected area.
When you see these things, you know that your immune system is at work repairing the damage.
This type of acute inflammation is usually localized and short-term.
When you’ve broken a bone, burned yourself, or been invaded by some type of microorganism, your body’s immune system is programmed to respond in this way.
Then, when the threat has been controlled, your immune system turns off the response.
But on the other hand, Chronic Inflammation is a significant health threat.
When your immune system does not turn off the inflammatory response, and the inflammation becomes chronic (continues for a long time), that is a major health threat.
Chronic inflammation is seen as a disease when your immune system does not stop defending when the body cannot rectify it.
It keeps fighting the problem even after it is gone. This means it starts attacking healthy tissue.
Wherein the healthy body tissue is being attacked determines which inflammation-related diseases you may incur.
What type of diseases can you get with chronic inflammation?
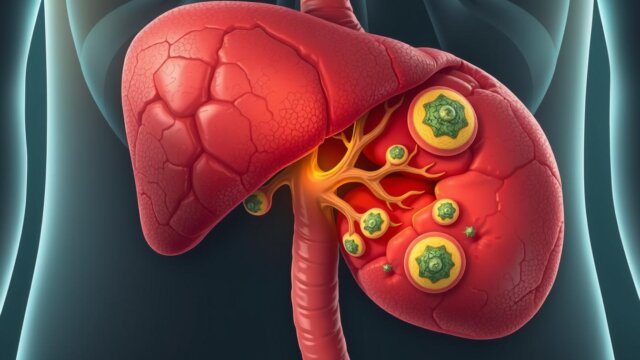
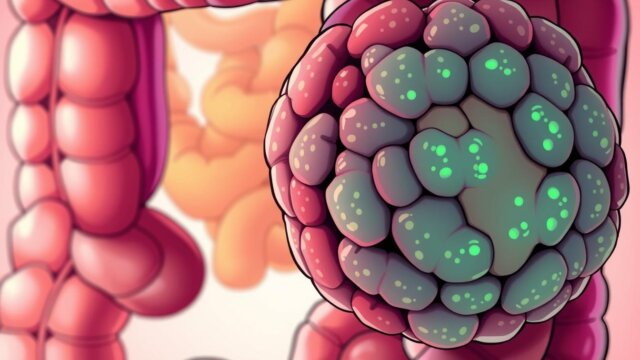
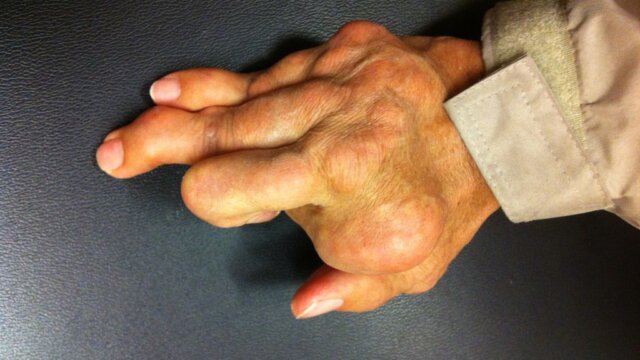
Chronic inflammation plays a major role in the following diseases:
- Heart disease
- Cancers
- Diabetes
- Asthma
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Lupus
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn’s disease
- Barrett’s esophagus
- Macular degeneration
- Obesity.
Chronic Inflammation also affects central nervous system disorders such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease.
Further, researchers on neuroinflammation have stated that chronic inflammation is a prime mover in some diseases, and in others, it plays a lesser role.
What are the Symptoms of Chronic Inflammation?
Low-level of chronic inflammation commonly produces these types of symptoms:
- Body aches and pains
- Congestion
- Frequent infections
- Diarrhea
- Dry eyes
- Indigestion
- Shortness of breath
- Skin outbreaks
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Weight gain and obesity
How Can You Find Out If You Have Chronic Inflammation?
The main test for chronic inflammation is a blood test called C-Reactive Protein, or CRP.
If your CRP test is positive, you are at substantial risk for a heart attack even if your cholesterol is normal and you are taking cholesterol drugs.
Another test for chronic inflammation, besides the CRP, is an inflammatory marker test, the IL-6.
Studies have shown that your chances of developing type two diabetes can be predicted by the outcome of the CRP and IL-6 tests together.
How do you get rid of Chronic Inflammation?
If you have Chronic Inflammation, or if you want to avoid getting it, what can you do?
The suggested natural remedies for chronic inflammation include many of the recommended things to combat other health problems.
To fight chronic inflammation, you should . . .
1. Improve your diet. Limit or cut out trans fats and refined carbohydrates. Increase your intake of healthy fats, such as Omega-3s and olive oil, unrefined carbohydrates, and antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables.
2. Maintain healthy body weight.
3. Get adequate sleep, at least 7 hours a night.
4. Reduce stress.
5. Take a good, pure Omega 3 fish oil supplement because fish oil with Omega 3 is a natural anti-inflammatory fighter.