FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Chronic inflammation causes many diseases, including heart disease, cancer, diabetes, arthritis, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, anxiety, ADHD, autism, dementia, and even aging.
We’ve known for years that inflammation plays a role in these conditions. But until recently, we didn’t understand how it was causing these problems. Now we do. And thanks to science, we also know how to treat it. We know enough to cure most of these conditions.
But first, let us explain why inflammation is such a problem. It’s not just because it makes us feel lousy. It’s because it damages our bodies over time.
For example, inflammation causes cells to mutate and become cancerous. It destroys healthy tissue and creates scar tissue. It weakens bones and joints. It causes blood vessels to narrow and clog. It increases insulin resistance and raises cholesterol levels. All of these factors contribute to premature death.
And yet, inflammation is something we can control. There are natural supplements that help reduce inflammation, and they work well. They’re safe, affordable, and effective.
We will share everything you need about inflammation, its causes, symptoms, treatment, and supplementation. This will include information about the latest research and practical tips for reducing inflammation naturally.
What is Chronic Inflammation?
Inflammation is the body’s response to harmful products inside and outside the body. In short, vascular tissue becomes irritated and swells, so it cannot function well.
This is one way the body begins healing and getting rid of the harmful substance. However, inflammation can also harm the infected tissue if it remains infected and inflamed for too long.
One of the biggest dangers of chronic inflammation is that the harmful stimuli can escape past weak cells and enter the lymphatic system. This is how irritants enter the bloodstream as overly abused lymph nodes will begin to leak into the circulatory system.
People must take care of the inflammation to prevent the chronic stage inflammation that can cause a multitude of health problems. This includes and is not limited to debilitating and fatal diseases like arthritis or cancer.
The cells present in chronic inflammation are both destructing and healing tissue simultaneously. This leads to a confused state where the body cannot properly flush away harmful stimuli because the body’s cells have also become harmful to the infected tissue.
How Does Chronic Inflammation in the Body Occur?
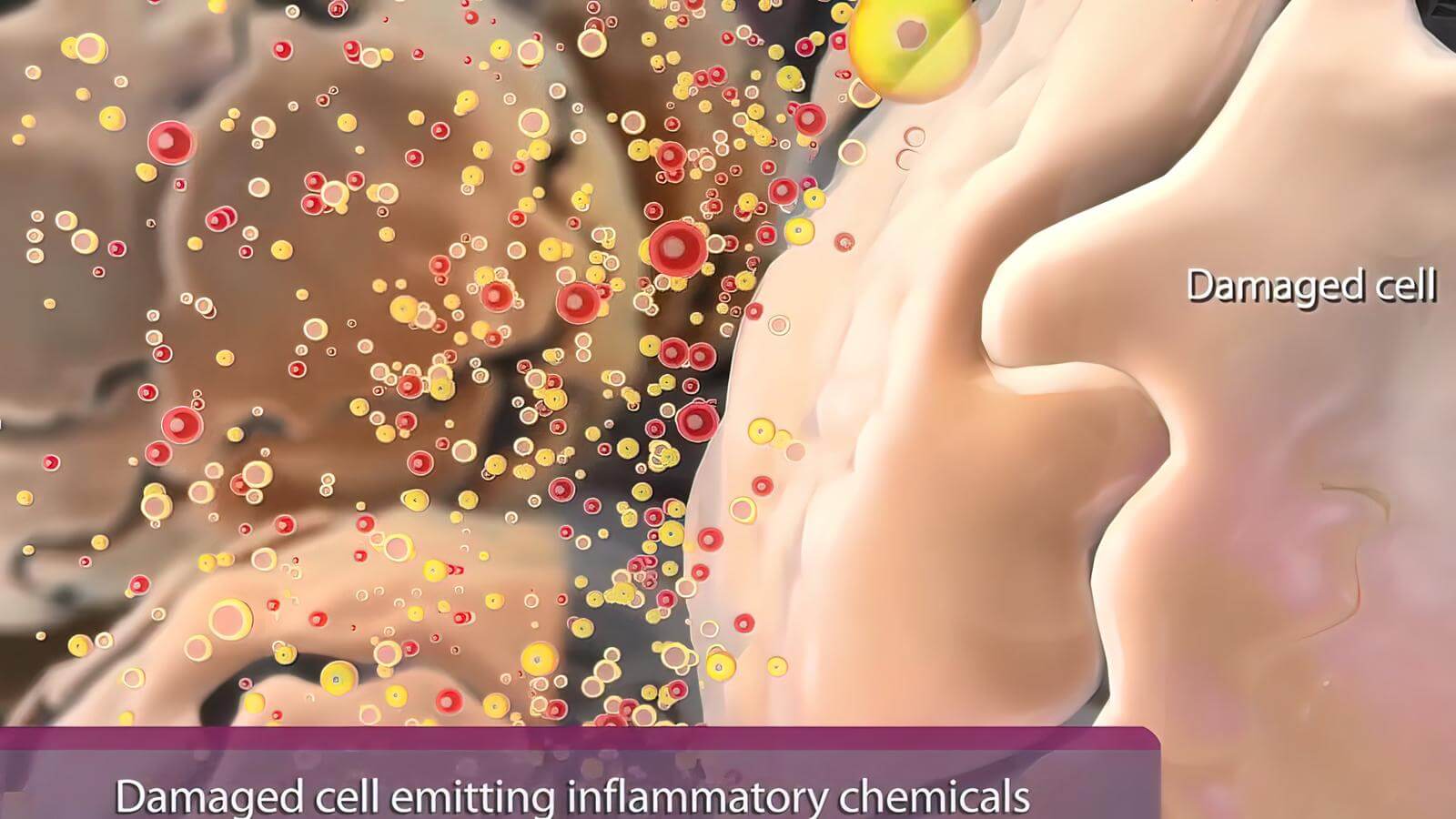
Inflammation that has a slow onset and persists for weeks or more is classified as chronic. The symptoms are not as severe as acute inflammation, but the condition is insidious and persistent.
Chronic inflammation may follow from acute inflammation or exist by itself. Acute inflammation will become chronic if the immune system cannot rid the body of the offending foreign agent or if the agent is constantly able to re-enter the body.
In the case of persistent infections, such as tuberculosis and autoimmune diseases, chronic fatigue will arise without the person first going through the acute inflammation stage.
The main cells involved in chronic infection are macrophages and lymphocytes.
Because both these cells have single nuclei, they are mononuclear cells. With the aid of chemical mediators such as lymphokines, macrophages do an excellent job of engulfing and neutralizing or killing foreign antigens.
Lymphocytes are the predominant cell in chronic inflammation. There are two types labeled T and B.
T-lymphocytes are produced in the thymus gland. They ensure cell-based immunity from infection.
B-lymphocytes originate in the bone marrow and ensure humoral (bodily fluid) immunity. B-lymphocyte activation produces plasma cells, which manufacture and secrete antibodies to fight specific antigens.
Macrophages and lymphocytes are interdependent in that the activation of one stimulates the actions of the other.
Certain chronic infections cells known as eosinophils accumulate. Within their cytoplasm are bright red granules. These granules contain a substance called ‘major basic protein,’ which can destroy certain antigens.
In chronic inflammation involving foreign particulate matter, such as splinters, macrophage cells can fuse together to form multinucleated giant cells. Tuberculosis may also cause macrophage cells to unite in this manner.
A key feature of chronic inflammation is collagen production. If too much collagen is formed, this can lead to the condition known as fibrosis.
Connective tissue cells known as fibroblasts enter the area of tissue injury and then go to work to produce collagen, which is necessary to replace the tissue lost during long-term inflammation.
The dilated blood vessels characteristic of acute inflammation are not evident in cases of chronic inflammation.
The two major complications associated with chronic infection are fibrosis leading to scarring and persistence.
The overabundance of collagen production over time can lead to scarring that can cause permanent distortion of the tissue, interfering with its function. Substances can continually stimulate chronic inflammation with low antigenic properties or by auto-immunity.
What Causes Chronic Inflammation?
Chronic inflammation is a major health problem that is linked to a variety of other health conditions. Some of the conditions that are linked to chronic inflammation include heart disease, stroke, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Chronic inflammation is also linked to other health problems, such as diabetes, obesity, and depression.
Cardiovascular disease is one of the chronic inflammation’s biggest results as dead cells attach themselves to artery walls.
As mentioned earlier, obesity is also a huge factor in this problem. If it is not treated, these can lead to many problems, such as strokes, heart attacks, and diabetes.
A patient with a wide range of problems like swollen ankles, tiredness, and difficulty digesting food could be linked to chronic inflammation.
The fact is that disorders do not cause chronic inflammation. Instead, these disorders are the result of chronic inflammation itself.
Many things can cause chronic inflammation. Some of the most common causes of chronic inflammation include:
1. Infections: Infections are a major cause of chronic inflammation. Bacteria, viruses, or fungi can cause infections.
2. Autoimmune diseases are another major cause of chronic inflammation. Autoimmune diseases are conditions in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells and tissues.
3. Toxins: Toxins are another major cause of chronic inflammation. Toxins can be found in the environment, food, or many other products.
4. Stress: Stress is another major cause of chronic inflammation. Stress can be physical, emotional, or psychological.
5. Genetics: Genetics is another major cause of chronic inflammation. Genetic factors can make some people more susceptible to chronic inflammation than others.
Chronic inflammation is a major health problem that is linked to a variety of other health conditions. If you think you may be suffering from chronic inflammation, you must see a doctor for the proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is caused by pathogens that cannot be broken down by mononuclear cells and fibroblasts. This type of inflammation is delayed, and it can last for years at a time if it is not treated. Many people may not even realize that they have chronic inflammation.
One of the most common symptoms is any long-term inflammation that has not disappeared within a couple of weeks. The area in question will be red, hot to the touch, swollen, and it may even have lost its immediate function.
These problems will continue to persist for weeks and months at a time. Chronic inflammation patients have also increased levels of the protein myostatin.
Acute inflammation is the immediate result of something damaging such as a break or burn. Thus, no immediate problems that have caused an inflamed area mark it as a chronic case.
Please note that there are quite a few diseases caused by chronic inflammation, such as asthma, inflammatory bowel, acne, autoimmune disease, cardiovascular disease, and many more.
Infected people should note inflamed areas and monitor their healing progress. Ulcers, constant fatigue, and high blood pressure also indicate chronic inflammation.
What is linked to chronic inflammation?
Chronic inflammation has been linked to many diseases, including heart disease, stroke, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Heart disease
Chronic inflammation has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. One theory is that inflammation causes the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Plaque is made up of cholesterol, fat, and other substances.
Over time, plaque can harden and narrow the arteries, making blood flow difficult. This can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Stroke
Chronic inflammation has also been linked to an increased risk of stroke. One theory is that inflammation damages the blood vessels, making them more likely to rupture. A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain is blocked or bursts. This can cause brain damage or death.
Cancer
Chronic inflammation has been linked to an increased risk of cancer. One theory is that inflammation damages DNA, making it more likely for cells to become cancerous. Cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the body. These cells can invade and damage healthy tissue.
Alzheimer’s disease
Chronic inflammation has been linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease. One theory is that inflammation damages the brain and leads to the buildup of a protein called beta-amyloid.
Beta-amyloid is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. It is believed to contribute to the death of brain cells and the decline in brain function.
Treatment for Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a condition in which the body’s inflammatory response is continually activated.
Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can occur when the body cannot shut off the inflammatory response. This can lead to many serious health problems.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating chronic inflammation. Treatment will vary depending on the underlying cause of the inflammation. However, some general treatment approaches can help to reduce inflammation and its symptoms.
Medicine
Medications to treat chronic inflammation include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
NSAIDs can help to reduce pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids can be taken orally or injected directly into the affected area to reduce inflammation. Immunosuppressants work by suppressing the immune system, which can help to reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle changes
Lifestyle changes that can help reduce chronic inflammation include quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress.
Quitting smoking can be particularly helpful in reducing inflammation. Eating a diet low in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can also help reduce inflammation. Getting regular exercise and managing stress can also help to reduce inflammation.
Dietary changes
Dietary changes are often recommended as a first step in treating chronic inflammation. This is because the foods we eat can significantly impact inflammation levels in the body.
Foods high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can promote inflammation, while foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory nutrients can help reduce it.
Exercise
Exercise is also often recommended for treating chronic inflammation. This is because exercise can help to reduce stress levels, which can, in turn, help to reduce inflammation.
Exercise can also help improve the immune system’s function, which can help reduce the incidence of infections, which can trigger inflammation.
Supplements
Certain supplements may also help treat chronic inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, for example, are known to have anti-inflammatory effects. Probiotics and vitamin D are also thought to help reduce inflammation.
If chronic inflammation is caused by an underlying health condition, such as an autoimmune disorder, treatment will focus on the underlying condition. In some cases, such as with rheumatoid arthritis, treatment may involve medication.
Chronic inflammation can be difficult to manage, but many treatment options are available. Working with a healthcare professional to create a personalized treatment plan is often the best approach.
Prevent and Cure Chronic Inflammation.
Prevention and curing of chronic inflammation have been successful in many patients by fighting it with drugs commonly used to treat heart disease and high cholesterol.
Inflammation can cause harmful cells to enter the bloodstream, leading to heart disease and clogged arteries. Thus, medicines used for this disease helps keeps infected cells away from the circulatory system.
A proper diet is also one of the best ways to regulate this disorder. Diets high in fiber and dairy have successfully kept chronic inflammation at bay.
Vitamin A is a great supplement because it has been linked to having caused an increased response to inflamed areas. Of course, anti-inflammatory supplements are also able to reduce overall inflammation.
Obesity is also one of the biggest components of chronic inflammation. It is very important that people overweight seek daily exercise and movement to keep their limbs and joints from becoming inflamed.
A healthy, low-calorie diet will help obese people begin fighting chronic inflammation for good. The best diets include plenty of natural products containing Omega-3 and probiotics, such as vegetables, fruit, fish, and poultry.
One should avoid red meat, sugars, and starches when possible to avoid bad fat intake. Of course, this also needs to be coupled with exercise to promote circulation and cardio movement. A solid night’s sleep will also help keep chronic inflammation away.
Staying healthy is the most important thing in fighting chronic inflammation. If people who show symptoms try to move and eat right, they will be well on their way to a better future.
This disorder can be prevented and cured if one can understand the risk when obese or showing symptoms.
Supplements for Inflammation
Anti-inflammatory supplements can immensely help people with inflammation. Supplements used following a proper diet and plenty of exercises will help keep chronic inflammation from occurring.
The ingredients used in supplements have been specially designed to help affected cells fight harmful infections. This will help the cells control the infected tissue and treat the inflammation once and for all.
What types of Anti Inflammatory Supplements Work best for Chronic Inflammation?
Anti-inflammatory supplements high in vitamins B, C, D, and E are the best to take.
Plus, any supplements that help you lower your cholesterol, as this is one of the key symptoms of someone with chronic inflammation.
Your ultimate goal is to lower your chances of contracting debilitating diseases caused by chronic inflammation. If you can treat symptoms and lower your risk immediately, you have a better chance of living a long, healthy life.
What are the Best Anti-Inflammatory Supplements
Inflammation is a normal immune response designed to protect the body from infection and injury. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to a host of health problems.
Many different supplements claim to be effective in reducing inflammation. But with so many options, it cannot be easy to know which one to choose.
Here are some of the best anti-inflammatory supplements that are effective in reducing inflammation:
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that have anti-inflammatory effects. They can be found in fish oil, flaxseed oil, and chia seeds.
There are many benefits to omega-3 fatty acids, and one of the most important is their role in reducing inflammation. Research has shown that omega-3 fatty acids can help decrease the production of inflammatory chemicals in the body, and they have been shown to be effective in treating various inflammatory conditions.
While omega-3 fatty acids are found in various foods, including fish, nuts, and seeds, they are also available in supplement form. Omega-3 supplements are usually taken in the form of capsules or liquids.
2. Curcumin
There are many different ways to treat inflammation, but curcumin is becoming more popular. Curcumin is a natural compound found in spice turmeric. It has powerful anti-inflammatory effects and is a very strong antioxidant.
Many people who take curcumin for inflammation find it helps reduce pain and swelling. It can also help to improve their joint function and range of motion. Curcumin can also help to reduce the risk of developing inflammatory diseases like arthritis.
If you want to try curcumin for your inflammation, you must talk to your doctor first. Curcumin can interact with some medications, so it is important to ensure it is safe for you.
3. Green Tea
Green tea is known for its many health benefits, one of which is reducing inflammation.
Studies have shown that the polyphenols in green tea can help to decrease the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cytokines are a type of protein that signals the body to create inflammation.
In one study, participants who drank four cups of green tea daily had lower levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines than those who did not.
Green tea may also help to reduce other inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). CRP is a protein that is produced in response to inflammation.
So, if you’re looking for a natural way to reduce inflammation, green tea may be a good option for you. Just be sure to drink it in moderation, as too much green tea can lead to side effects like nausea and vomiting.
4. Boswellia
Boswellia is an herb used for centuries in traditional Indian medicine. Also known as Indian frankincense, it has a long history of use for various conditions, including inflammation.
Boswellia is thought to work by reducing inflammation in the body. It does this by blocking the production of certain inflammatory chemicals, such as leukotrienes and prostaglandins. Boswellia also contains compounds that have been shown to inhibit the activity of certain enzymes involved in inflammation.
One study showed that Boswellia effectively reduced knee pain and stiffness in people with osteoarthritis. Another study found that Boswellia extract could reduce levels of several markers of inflammation in people with Crohn’s disease.
5. Ginger
Ginger is a common household spice with a long history of medicinal use. The main bioactive compound in ginger is Gingerol, which has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Studies show ginger can effectively reduce inflammation throughout the body, including inflammation of the joints, gut, and lungs.
6. Feverfew
Feverfew is one of the oldest and most widely used medicinal plants. The plant has a long history of treating inflammation, fever, and headaches.
Feverfew is effective in reducing inflammation in many studies. In one study, feverfew was found to be as effective as ibuprofen in reducing inflammation. Feverfew is also effective in treating other conditions, such as migraines, arthritis, and menstrual cramps.
7. Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a common spice used in cooking that has been linked to reducing inflammation. Studies have shown that cinnamon can help to reduce levels of inflammation markers in the blood, such as C-reactive protein and interleukin-6.
Additionally, cinnamon has been shown to improve other conditions associated with inflammation, such as arthritis and metabolic syndrome. While more research is needed to confirm these effects, cinnamon may be a helpful addition for those looking to reduce inflammation naturally.
8. Willow Bark
Willow bark is a traditional remedy for inflammation. The active ingredient in willow bark is salicin, similar to aspirin. Willow bark has been used for centuries to relieve pain and inflammation. Today, willow bark is available in supplements and can be taken orally or applied topically.
Willow bark is a safe and effective way to treat inflammation. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplement, particularly if you have a medical condition or are taking other medications.
9. Licorice Root
Licorice root has been traditionally used to treat various ailments, including inflammation.
Studies have shown that licorice root can help reduce inflammation by inhibiting the production of inflammatory chemicals in the body. Licorice root also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that can help to protect the body from damage caused by inflammation.
10. Bromelain
Bromelain is a natural anti-inflammatory agent. It is derived from the stem and fruit of the pineapple plant.
Bromelain effectively reduces inflammation and pain associated with arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and other conditions. Bromelain may also help to reduce the risk of developing cancer.
These are just a few of the many supplements that claim to be effective in reducing inflammation. Talk to your doctor before taking any supplements, as they may interact with your other medications.
The Bottom Line
Chronic inflammation is a serious condition that can lead to many health problems.
You must see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment if you think you may be suffering from chronic inflammation. Many supplements can help to reduce the symptoms of chronic inflammation.