FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, affects millions in the U.S. each year. It’s the third most common cancer found here. But the good news is that over 90% of those treated early are alive five years later. This shows why knowing the symptoms and how to prevent it is key.
Colon cancer starts with small, noncancerous clumps called polyps in the colon. These can grow into cancerous tumors over time. Regular tests like colonoscopies can find polyps early and stop them from turning into cancer. Doctors can also treat colon cancer early, before symptoms show up, through these tests.
Key Takeaways
- Colon cancer is the third most common cancer diagnosed in the U.S.
- Early detection through screening is crucial, as it can lead to better treatment outcomes.
- Regular colonoscopies can detect polyps and prevent them from developing into cancer.
- Screening for colon cancer is recommended starting around age 45, or earlier for those with increased risk factors.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help reduce the risk of colon cancer.
What is Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer starts in the large intestine, also called the colon. It grows from small growths called polyps inside the colon. Most polyps are not cancerous, but some can turn into colon cancer over time.
Colon cancer can happen in any part of the colon. It’s also called colorectal cancer when it affects the rectum too.
Colon Cancer Overview
Colon cancer is a top cause of cancer deaths in the U.S.. It’s a serious disease that can be deadly if not caught and treated early. Your risk goes up with age, family history, diet, and lifestyle.
Location and Development
The colon is the last part of our digestive system. Colon cancer starts as polyps, which can turn into cancerous tumors if not treated. These polyps can appear anywhere in the colon. If not removed, they can turn into colon cancer over time.
“Colon cancer is a serious condition that can be life-threatening if not detected and treated early.”
Early detection and regular screening are key to preventing and treating colon cancer. Finding and removing polyps can lower the risk of colon cancer.
Learning about colon cancer is the first step to keeping your colon healthy. It helps reduce the risk of this serious disease.
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer may not show symptoms at first. But as it grows, signs can appear. Many people with colon cancer don’t show symptoms, and some symptoms don’t mean cancer. Knowing the signs and getting help if you notice them is key.
Early Signs and Symptoms
Early signs of colon cancer include changes in bowel habits lasting more than a few days. You might feel like you’re not fully done after using the bathroom. Also, look out for rectal bleeding, blood in the stool, and stomach pain.
Advanced Symptoms
As colon cancer gets worse, symptoms get more serious. You might see more bleeding, severe stomach pain, and trouble with bowel movements. Also, if cancer spreads, you could have a big liver, jaundice, or trouble breathing.
Many symptoms of colon cancer can also mean other things, like infections or irritable bowel syndrome. So, if you’re worried, see a doctor right away. This helps get the right diagnosis and treatment fast.
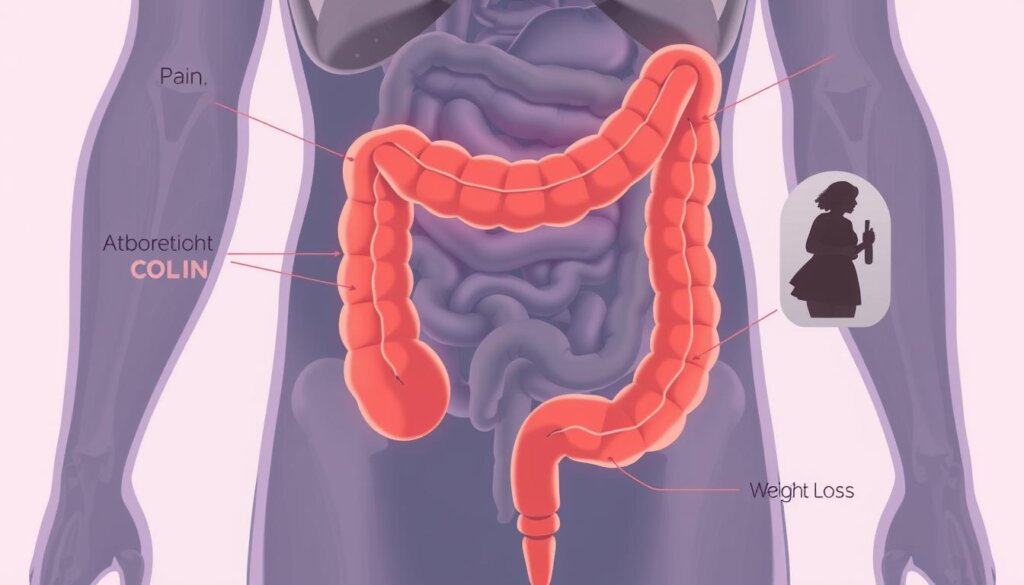
Getting screened for colon cancer early is very important. It helps find cancer sooner, making treatment easier. Doctors use tests like colonoscopy, biopsies, and scans to find and check how far cancer has spread.
“Colon cancer often does not present symptoms until it has grown or spread, which is why early screening is so important.”
Knowing the symptoms of colon cancer and getting help quickly can help find cancer early, leading to better treatment results.
Causes and Risk Factors
Researchers still don’t know all about colon cancer causes. But, they think DNA changes in colon cells play a big role. Lifestyle choices and environmental factors also increase the risk.
Genetic Factors
About 5-10% of colon and rectal cancer cases come from inherited genes. This includes Lynch syndrome and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). People with a family history or genetic syndromes should be screened often.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle choices are key in colon cancer. Half of all cases are linked to things we can change. This includes eating too much red meat, not moving enough, being overweight, smoking, and drinking too much alcohol.
Being overweight, especially for men, raises the risk of colon cancer. People with type 2 diabetes are also at higher risk.
Exposure to radiation in the abdomen or pelvis increases risk. Inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis also raise the risk due to chronic inflammation.
Colon cancer risk grows with age, mostly after 50. African Americans and American Indian/Alaska Native people face higher risks.
Risk Factor | Impact on Colon Cancer |
|---|---|
Genetic Factors | Inherited genetic syndromes like Lynch syndrome and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) can increase the risk of colon cancer by 5-10%. |
Lifestyle Factors | Modifiable factors such as a diet high in red and processed meats, lack of physical activity, obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol use can contribute to more than half of all colorectal cancer cases. |
Environmental Factors | Radiation exposure to the abdomen or pelvis, as well as inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis, can also elevate the risk of colon cancer. |
Age and Ethnicity | The risk of colon cancer increases with age, with the majority of cases occurring in individuals over 50. Certain racial and ethnic groups, such as African Americans and American Indian/Alaska Natives, have a higher incidence of the disease. |
“Colon cancer is a complex disease, with a variety of factors contributing to its development. By understanding the underlying causes and risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their chances of this life-threatening condition.”
Colon Cancer Screening and Prevention
Regular screening is key for catching colon cancer early. The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends that adults 45 to 75 get screened. They suggest starting screening soon after turning 45 and doing it regularly.
People 76 to 85 should talk to their doctors about screening. Those at higher risk, like those with family history or genetic syndromes, should also talk to their doctors.
Importance of Regular Screening
Screening tests, like colonoscopy, can find and remove polyps before they turn into cancer. Many screening options include colonoscopy, guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT), and fecal immunochemical test (FIT). The right test and how often to do it depend on your risk level.
Preventive Lifestyle Choices
Living a healthy lifestyle can also lower your risk of colon cancer. Eating lots of fruits and veggies, exercising, staying at a healthy weight, and not smoking or drinking too much alcohol can help. It takes about 10 to 15 years for polyps to turn into cancer, so making these choices can make a big difference.
You can fight colon cancer by screening regularly and living a healthy lifestyle. This combo can save lives and lessen the disease’s impact.
“Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, but it is also one of the most preventable cancers.”
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If doctors think you might have colon cancer, they will do a full check-up. They will also order tests to find out how bad it is. These tests might include a colonoscopy, biopsy, CT scan, or blood tests to look for proteins like CEA.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
A colonoscopy looks inside the colon and rectum for growths or polyps. If something looks off, a biopsy can take a small tissue sample for analysis. Imaging tests like CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans help determine how far the cancer has spread.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for colon cancer depends on how far it has spread. It might include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy. For early cancer, doctors might use less invasive methods like polypectomy or laparoscopic surgery.
For bigger cancers or those in the lymph nodes, chemotherapy is often used after surgery to prevent it from coming back. Radiation therapy can shrink a tumor before surgery or help with symptoms when surgery isn’t possible. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are newer options, often used with chemotherapy for advanced cancer.
Palliative care can also help, focusing on pain relief and improving life quality.
Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
Colonoscopy | Inspect the colon and rectum for abnormal growths or polyps |
Biopsy | Collect a small tissue sample for further analysis |
CT scan, MRI, PET scan | Determine the stage of the disease and assess cancer spread |
Colon cancer treatment is complex and tailored to each person. Your healthcare team will work with you to find the best plan. Knowing about tests and treatments helps you take charge of your health.
“Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial in the fight against colon cancer. Regular screening and prompt action can significantly improve outcomes for patients.”
Colon Cancer Stages and Prognosis
Colon cancer is staged based on the extent of the tumor and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the. The overall five-year survival rate for colorectal cancer is 65 percent. If caught early, the survival rate is much higher, at 90.9 percent for localized cancer.
The prognosis can change based on the patient’s health, the type of cancer, and the treatment plan. For colon cancer between 2013 and 2019, survival rates were 91% for early stages, 73% for regional, and 13% for distant. Rectal cancer survival rates between 2012 and 2018 were 90% for early stages, 74% for regional, and 18% for distant.
Survival rates are based on past outcomes of people with the same cancer type and stage. They may not include later developments or individual factors that can affect prognosis.
“Factors influencing prognosis include age, overall health, cancer location within the colon, genetic changes in cancer cells, treatment response, and other variables.”
As treatments get better, the outlook for colon and rectal cancer may also improve. Knowing the cancer staging system is key to understanding the disease’s seriousness and planning treatment.
Living with Colon Cancer
Life after a colon cancer diagnosis can be tough. But, with the right care, you can keep thriving. It’s key to managing the disease’s physical and emotional effects and treatment.
Self-Care and Follow-Up Care
Regular check-ups and tests are vital for catching cancer early. Survivorship care plans help with exams and tests to watch for cancer return. Having good health insurance is also crucial for getting the care you need.
Healthy habits like a good weight, exercise, and balanced diet can boost your health. But, talk to your doctor before starting new supplements, as they can be risky.
Support Resources
Colon cancer can be tough on your body and mind, but you’re not alone. Cancer support groups, counseling, and rehab can offer big help.
Remember, you’re not alone in this fight. Focus on self-care, keep up with follow-up care, and use support services. This way, you can face colon cancer’s challenges and aim for a healthy, fulfilling life.
Potential Long-Term Side Effects of Colon Cancer Treatment | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
Fatigue | Pacing activities, prioritizing rest, and engaging in light exercise |
Peripheral Neuropathy | Medications, physical therapy, and assistive devices |
Bowel Changes | Dietary modifications, medication, and pelvic floor therapy |
Urinary Problems | Pelvic floor exercises, medication, and bladder training |
Sexual Health Concerns | Counseling, medication, and use of adaptive devices |
“Survivorship is not just about curing cancer, but about living life to the fullest after a cancer diagnosis.”
Colon Cancer at Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic leads in colon cancer treatment. It offers cancer care expertise and a multidisciplinary approach, and its teams of doctors work together to help those with colon cancer.
Patients at Mayo Clinic have a smooth experience. They meet with doctors on the same day, which is rare in the U.S. and shows that Mayo Clinic’s care is top-notch.
Mayo Clinic is always looking to improve. They try new things in surgery, like using robots. This makes surgery safer and shorter.
They also try new treatments for tough cases, which gives hope to those who thought they had no options.
Mayo Clinic works with many doctors, which means they can perform complex surgeries that others can’t. This ensures that each patient gets the best care.
“Mayo Clinic’s extensive experience and expertise in colorectal cancer care ensure that patients receive the most advanced and effective treatments available.”
Colon Cancer Risk Factors | Colon Cancer Prevention |
|---|---|
|
|
Colon Cancer Research and Clinical Trials
Research and clinical trials are key in fighting colon cancer. At places like Mayo Clinic, scientists are always looking for new ways to find and treat the disease. They aim to make treatments better for those with colon cancer.
Joining clinical trials can give you access to the latest treatments. It also helps in finding better ways to stop, find, and handle colon cancer. For example, there are trials on new treatments like immunotherapies and drug mixes.
The Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Family Registry at Memorial Sloan Kettering supports genetic studies, helps find the causes of certain cancers, informs people about their risk, and connects them with special care.
The Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Registry at Johns Hopkins has existed since 1973. It has greatly helped in studying family cancers, having found genes linked to certain cancers.
FAQ
What is colon cancer?
Colon cancer starts in the colon, the first part of the large intestine. It often affects older adults but can happen at any age. It begins as small clumps of cells called polyps inside the colon.
While most polyps are not cancerous, some can turn into colon cancers over time.
What are the symptoms of colon cancer?
Many people with colon cancer don’t show symptoms at first. When symptoms appear, they might include changes in bowel habits, like diarrhea or constipation.
Other symptoms are rectal bleeding, blood in the stool, and ongoing abdominal discomfort. You might also feel like your bowel doesn’t empty completely.
As the cancer grows, symptoms can get worse. This includes more bleeding, severe abdominal pain, and bowel obstruction.
What are the risk factors for colon cancer?
Genetic factors, like inherited syndromes and family history, can raise your risk. Lifestyle and environmental factors also play a role.
Eating a lot of red and processed meats, not exercising, being overweight, smoking, and drinking too much alcohol can increase your risk.
How can colon cancer be prevented?
Regular screening, like colonoscopy, is key for early detection and prevention. Colonoscopies can find and remove precancerous polyps before they turn into cancer.
Living a healthy lifestyle helps too. This includes eating fruits and veggies, exercising, staying at a healthy weight, and not smoking or drinking too much alcohol.
How is colon cancer diagnosed and treated?
If colon cancer is suspected, a healthcare provider will do a physical exam and order tests. These include a colonoscopy, biopsy, CT scan, or blood tests.
These tests help figure out the type, stage, and extent of the cancer. Treatment options depend on the cancer’s stage and may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a mix of these.
What is the prognosis for colon cancer?
Colon cancer is staged based on the tumor’s size and spread. Early-stage cancers, caught and treated early, usually have a better prognosis.
However, the prognosis can vary. It depends on the patient’s overall health, the cancer type, and the treatment’s success.
What support is available for people living with colon cancer?
Self-care and follow-up care are crucial for those living with colon cancer. This includes managing treatment side effects, staying healthy, and seeing healthcare providers regularly.
Support groups, counseling, and rehabilitation programs can also help. They help with the physical and emotional challenges of living with colon cancer.
Why is Mayo Clinic recognized for its expertise in colon cancer care?
Mayo Clinic is a leader in colon cancer diagnosis and treatment. Its teams of oncologists, surgeons, and healthcare professionals work together to provide comprehensive care.
Mayo Clinic’s experience and expertise ensure patients get the best treatments available.
How is colon cancer research advancing?
Research and clinical trials are key to understanding and treating colon cancer. Researchers at Mayo Clinic are exploring new tools and treatments.
They aim to improve outcomes for patients. Joining clinical trials can give access to new treatments and help develop better ways to prevent and manage colon cancer.