FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Every year, over 18,000 Americans get diagnosed with esophageal cancer. This is a shocking number that shows how serious this disease is. Esophageal cancer starts in the esophagus and can be deadly if not caught and treated early. This article will explain esophageal cancer, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments. Knowing the risk factors and how to prevent them is key to fighting this serious disease.
Key Takeaways
- Esophageal cancer is a serious condition that can be life-threatening if not detected and treated early.
- Men and those assigned male at birth over 60 are most likely to develop esophageal cancer.
- Chronic GERD and Barrett’s esophagus are major risk factors for esophageal cancer.
- Lifestyle factors like smoking, heavy drinking, and poor diet can increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Early detection is crucial for successful treatment of esophageal cancer.
What is Esophageal Cancer?
The esophagus is a muscular tube. It connects the mouth and the stomach. It lets food move from the throat to the digestive system. Esophageal cancer starts in the cells lining the esophagus. It can happen anywhere along the esophagus and spread to other parts if not treated.
Esophageal Anatomy
The esophagus has several layers. These include the innermost mucosal layer, the muscular layer, and the outer adventitial layer. Cancer can start in any of these layers. The most common types are adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Types of Esophageal Cancer
There are two main types of esophageal cancer:
- Adenocarcinoma: This starts in the glandular cells of the lower esophagus. It’s the most common in the U.S., mainly in white men.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: It begins in the flat cells of the upper esophagus. It’s the most common worldwide.
There are also rare types like small cell carcinoma, sarcoma, lymphoma, melanoma, and choriocarcinoma.
Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer
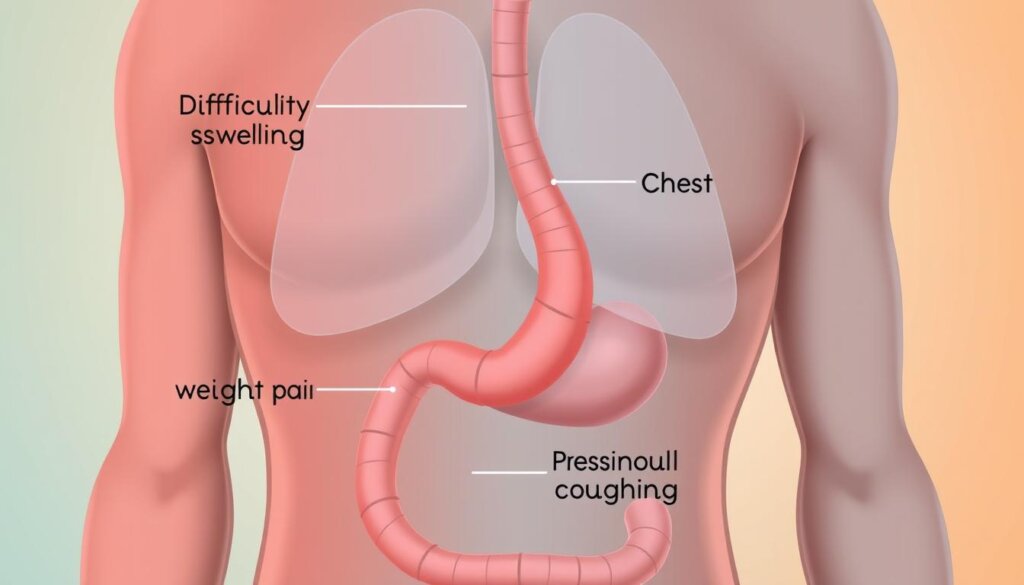
Esophageal cancer often doesn’t show symptoms early on, making it hard to catch. But as it grows, symptoms start to appear. Common signs include trouble swallowing, chest pain, unexplained weight loss, coughing, and hoarseness.
Difficulty Swallowing
Trouble swallowing, or dysphagia, is the most common symptom. As the tumor grows, it blocks the esophagus. This makes it hard to swallow food and liquids. People with this cancer often change their diet and eating habits.
Chest Pain
Chest pain or discomfort in the middle is another symptom. This pain comes from the tumor pressing on the esophagus or nearby tissues.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss is common in esophageal cancer patients. It’s due to swallowing troubles, less appetite, and the cancer’s high metabolic needs.
Other symptoms include hoarseness, chronic coughing, vomiting, bone pain, and bleeding into the esophagus.
Seeing a doctor is key if you notice changes in swallowing or other symptoms. Early detection and treatment can greatly improve outcomes for esophageal cancer patients.
“Most people with esophageal cancer are diagnosed because they have symptoms. It’s rare for people without symptoms to be diagnosed with this cancer.”
Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) | The most common symptom, caused by the tumor obstructing the esophagus. |
Chest pain | Discomfort in the middle part of the chest, due to the tumor pressing on the esophagus or surrounding tissues. |
Unexplained weight loss | Caused by swallowing difficulties, decreased appetite, and increased metabolic demands of the cancer. |
Hoarseness, chronic cough, vomiting, bone pain, bleeding | Other symptoms that may occur as the disease progresses. |
Unfortunately, most esophageal cancers don’t show symptoms until they’re advanced. Early detection and treatment are key to better outcomes for those with esophageal cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors
Esophageal cancer is a complex disease. We don’t know all the causes yet. But, research has found some key risk factors that can increase your chance of getting this cancer.
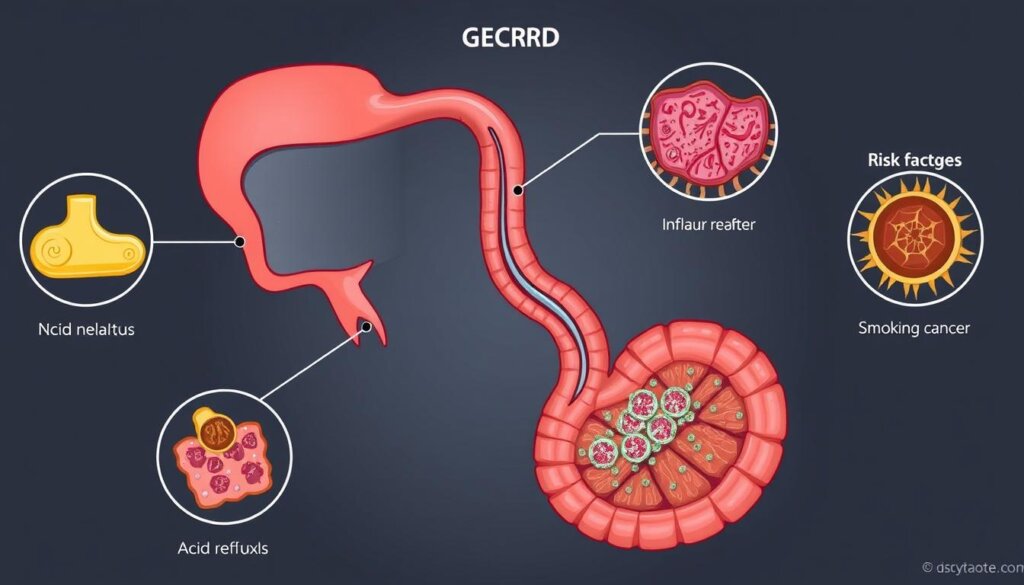
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a big risk factor for esophageal cancer. It’s a condition where acid keeps coming up. People with GERD are more likely to get a certain type of esophageal cancer.
Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus is another big risk factor. It’s a condition that can turn into cancer. People with Barrett’s esophagus are much more likely to get a certain type of esophageal cancer.
Lifestyle Factors
Some lifestyle choices can also raise your risk. Smoking a lot can double your chance of getting a certain type of esophageal cancer. Drinking too much alcohol can also increase your risk, especially for a certain type of cancer. Being overweight can also raise your risk of getting a certain type of esophageal cancer. But, eating lots of fruits and veggies and staying active can lower your risk.
Other things like radiation treatment, certain genetic conditions, and having had other cancers can also increase your risk.
Knowing about these risk factors can help you take steps to lower your risk. Going for regular check-ups and watching for any precancerous conditions is important. Also, living a healthier lifestyle can help prevent esophageal cancer.
Diagnosis of Esophageal Cancer
Diagnosing esophageal cancer needs several tests and procedures. The main method is an endoscopy. This is when a thin, flexible tube with a camera is put into the esophagus. It looks at the lining and takes tissue samples for biopsy.
This endoscopic procedure lets doctors see any problems or growths that might be cancer.
Other tests like barium swallow studies and X-rays are used too. They help find changes in the esophagus that might mean cancer. Biopsies are also key. They remove small tissue samples for analysis.
Tests like bronchoscopy, endoscopic ultrasound, CT, MRI, and PET scans give more detailed info. They show how far the cancer has spread. These tests help doctors decide on the best treatment.
Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
Endoscopy | Examine the esophagus and take biopsy samples |
Barium Swallow | Identify changes in the esophagus that may indicate cancer |
Biopsy | Analyze tissue samples to confirm cancer diagnosis |
Imaging Tests (CT, MRI, PET) | Determine the stage and spread of esophageal cancer |
Esophageal cancer is staged from 0 to 4. Stage 4 means the cancer has spread beyond the esophagus. Treatment choices depend on the cancer’s stage and how far it has spread.
“Esophageal cancer is often diagnosed when a person experiences symptoms like trouble swallowing and chest pain.”
Early stages of esophageal cancer can be hard to find because there are no symptoms. But, using many tests and procedures is key. It helps find the disease and choose the right treatment.
Treatment Options for Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer treatment is made just for each patient. It depends on the disease’s stage. Common treatments are surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. These are often used together.
Surgery
Surgery, called an esophagectomy, removes the cancer part of the esophagus. Then, the healthy parts are joined back together. Getting surgery at places like MD Anderson can lead to better results.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells with high-energy X-rays or protons. Patients get 25 to 30 treatments. These last about 15 minutes each, five to six weeks a day.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to fight esophageal cancer. It’s often paired with other treatments like radiation or surgery. Neoadjuvant therapy, a mix of radiation and chemotherapy, tries to shrink tumors before surgery.
Targeted therapy or immunotherapy might also be used. Researchers are looking into new treatments like biomarkers and epigenetic therapy.
Nutrition therapy, like special diets or supplements, is part of care. Patients may also need support services. This includes nutrition advice, physical therapy, and help with devices like feeding tubes.
“Esophageal cancer treatment is a complex and multifaceted process, requiring a comprehensive approach to address the unique needs of each patient.”
Esophageal Cancer Stages
Esophageal cancer is staged using the TNM system. This system looks at the tumor size and spread. It also checks if the cancer has reached nearby lymph nodes or distant organs.
The stages range from 0 to IV. Stage 0 is a very early, small tumor. Stage IV is a more advanced, spread-out cancer.
The stage of esophageal cancer at diagnosis is very important. It helps decide the best treatment and how well the patient will do. Doctors use surgery and imaging tests to stage the cancer.
Esophageal tumors are also graded. This grading goes from well-differentiated (grade 1) to poorly-differentiated (grade 3). Lower-grade cancers usually have a better outlook than higher-grade ones.
Stage | Tumor (T) | Nodes (N) | Metastasis (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Carcinoma in situ | No lymph node involvement | No distant metastasis |
I | Tumor invades lamina propria or submucosa | No lymph node involvement | No distant metastasis |
II | Tumor invades muscularis propria or adventitia | Lymph node involvement | No distant metastasis |
III | Tumor invades adjacent structures | Lymph node involvement | No distant metastasis |
IV | Any T | Any N | Distant metastasis |
The stage of esophageal cancer can change based on the tumor type. Squamous cell carcinoma stages range from 0 to IVB. Adenocarcinoma stages go from 0 to IIA. The tumor’s location in the esophagus affects squamous cell carcinoma but not adenocarcinoma.
“Stage IVB esophageal cancer indicates that the cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes and/or other organs, such as the liver and lungs, making it the most advanced stage.”
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The chance of surviving esophageal cancer depends on several things. This includes the disease’s stage when first found. In the US, esophageal cancer is rare, with about 4 new cases per 100,000 people each year. Most cases are esophageal adenocarcinoma, which is more common in the US than esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Also, men are more likely to get it than women.
The five-year survival rate for esophageal cancer is about 20%. But, this number changes a lot based on the disease’s stage. For cancers that are just in the esophagus, the survival rate is 49%. But, for cancers that have spread, it’s much lower, at 28% and 6% for regional and distant cancers, respectively. The American Cancer Society uses data from 2013 to 2019 for these statistics.
New treatments for esophageal cancer might help more people survive. Survival can also depend on age, health, how well the body responds to treatment and the tumor’s characteristics.
Worldwide, esophageal cancer is the sixth leading cause of death from cancer, with 500,000 new cases each year. The five-year survival rate for esophageal cancer is less than 10% globally. But, survival rates can change a lot based on the tumor type, disease stage, and treatment.
For example, early-stage esophageal cancer patients have better survival rates. They can live up to 31.2% of the time in the fifth year. But, for advanced-stage cancer, survival rates are much lower, at 8.2% in the fifth year. Age at diagnosis, tumor grade, and location also affect survival.
Eating healthy and staying active can help prevent esophageal cancer and improve survival chances. Early detection and treatment are key to better survival rates.
Prevention of Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is serious, but you can lower your risk. Making healthy food choices and lifestyle changes helps. Also, managing health issues is key to protecting your esophagus.
Dietary Changes
Eating more fruits and veggies can lower your risk of esophageal cancer. These foods are full of antioxidants that help protect your esophagus. Also, keeping a healthy weight is important. Being overweight, especially with GERD, raises your risk of esophageal cancer.
Lifestyle Modifications
Stopping smoking and drinking less alcohol are big steps to prevent esophageal cancer. Smoking and drinking too much alcohol are major risks. Also, exercising regularly can help lower your risk of esophageal cancer.
If you have GERD or Barrett’s esophagus, managing it is crucial. Avoiding certain foods and staying active can help. These steps can ease GERD symptoms and lower your cancer risk.
Using proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can also help if you have Barrett’s esophagus. But, it’s important to talk to your doctor about the long-term effects. Aspirin or NSAIDs might also help, but you need to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
By making these changes, you can lower your risk of esophageal cancer. Monitoring and treating GERD and Barrett’s esophagus early is also key to preventing cancer.
New research and trials are looking for better ways to prevent esophageal cancer. By staying informed and managing your health, you can greatly reduce your risk of this disease.
Ongoing Research and Clinical Trials
The fight against esophageal cancer is ongoing. Researchers are working hard to find better ways to detect and treat it. They are looking into new targeted therapies and immunotherapies.
One exciting area is the use of liquid biopsies. These tests check for cancer DNA in the blood. It’s a way to find cancer early without surgery.
Clinical trials are testing different treatments together. This includes chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies or immunotherapies. The goal is to find the best treatment for each person.
Researchers are also looking into immunotherapy drugs. These drugs help the body fight cancer. Some immunotherapy drugs are already approved for esophageal cancer. Trials are exploring how to use them with other treatments.
Joining clinical trials can give patients new treatments. It also helps doctors learn more about treating esophageal cancer. This way, patients can help improve care for everyone.
“Ongoing research and clinical trials are crucial for advancing our understanding and treatment of esophageal cancer. These efforts hold the promise of improving outcomes and quality of life for patients.”
As we keep working, we hope to find better treatments. These treatments will be tailored to each patient’s needs.
Conclusion
Esophageal cancer is a tough disease that needs a team effort to manage. Knowing the risks, symptoms, and new treatments helps people take action early. A study in 2012 showed how different types of this cancer affect people worldwide.
Research and trials are key to improving care for those with esophageal cancer. Studies have looked at how imaging helps doctors plan treatment. They also found out if adding chemotherapy before surgery helps more than surgery alone.
Patients can fight this disease better by knowing their options and working with doctors. Different groups face different challenges with esophageal cancer, showing the need for tailored care. Early detection is crucial to help everyone fight this disease.
FAQ
What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal cancer is a serious disease. It starts in the esophagus, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. If caught early, it can be treated.
What are the main types of esophageal cancer?
There are two main types: adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Adenocarcinoma starts in gland cells. Squamous cell carcinoma starts in thin cells. Other rare types include small cell carcinoma and sarcoma.
What are the common symptoms of esophageal cancer?
Symptoms include trouble swallowing, chest pain, and unexplained weight loss. These signs often show up when the disease is advanced.
What are the risk factors for developing esophageal cancer?
Risk factors include acid reflux and GERD, Barrett’s esophagus, and smoking. Heavy drinking and a diet low in fruits and veggies also increase risk. Being overweight or having chest radiation can also raise your risk.
How is esophageal cancer diagnosed?
Doctors use tests like endoscopy with biopsy and PET scans to diagnose. An endoscopy is common. It uses a camera tube to look inside the esophagus and take tissue samples.
What are the treatment options for esophageal cancer?
Treatments include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Surgery removes the cancerous part of the esophagus. Radiation and chemotherapy kill cancer cells. Targeted therapy or immunotherapy may also be used.
How is esophageal cancer staged?
The TNM system is used to stage esophageal cancer. It looks at the tumor size, lymph node involvement, and distant metastasis. Stages range from I to IV, with stage I being the least advanced.
What is the prognosis for esophageal cancer?
The prognosis depends on the stage at diagnosis. The 5-year survival rate varies from 5% for stage IV to 47% for stage I. Survival rates have improved with better detection and treatment.
How can I prevent esophageal cancer?
Preventing esophageal cancer is not guaranteed. But, you can lower your risk. Eat a healthy diet, limit alcohol, quit smoking, manage GERD, and keep a healthy weight.
What is the latest research on esophageal cancer?
Researchers are working to improve esophageal cancer care. They’re exploring new treatments and detection methods. Joining clinical trials can give you access to new treatments and help advance research.