FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Are Omega-3 fatty acids good for you?
Omega 3 is an essential fatty acid that plays a vital role in your body and mind functions.
Did you know your brain is primarily composed of Omega 3 fatty acids? Some people think of fat as a purely harmful component, but it is vital to the very structures of the body that make life possible.
Once you learn about the benefits of omega 3s, you will begin to think more critically about what you eat.
Getting a little pickier about eating good fat sources is an easy way to supercharge any diet you may be planning.
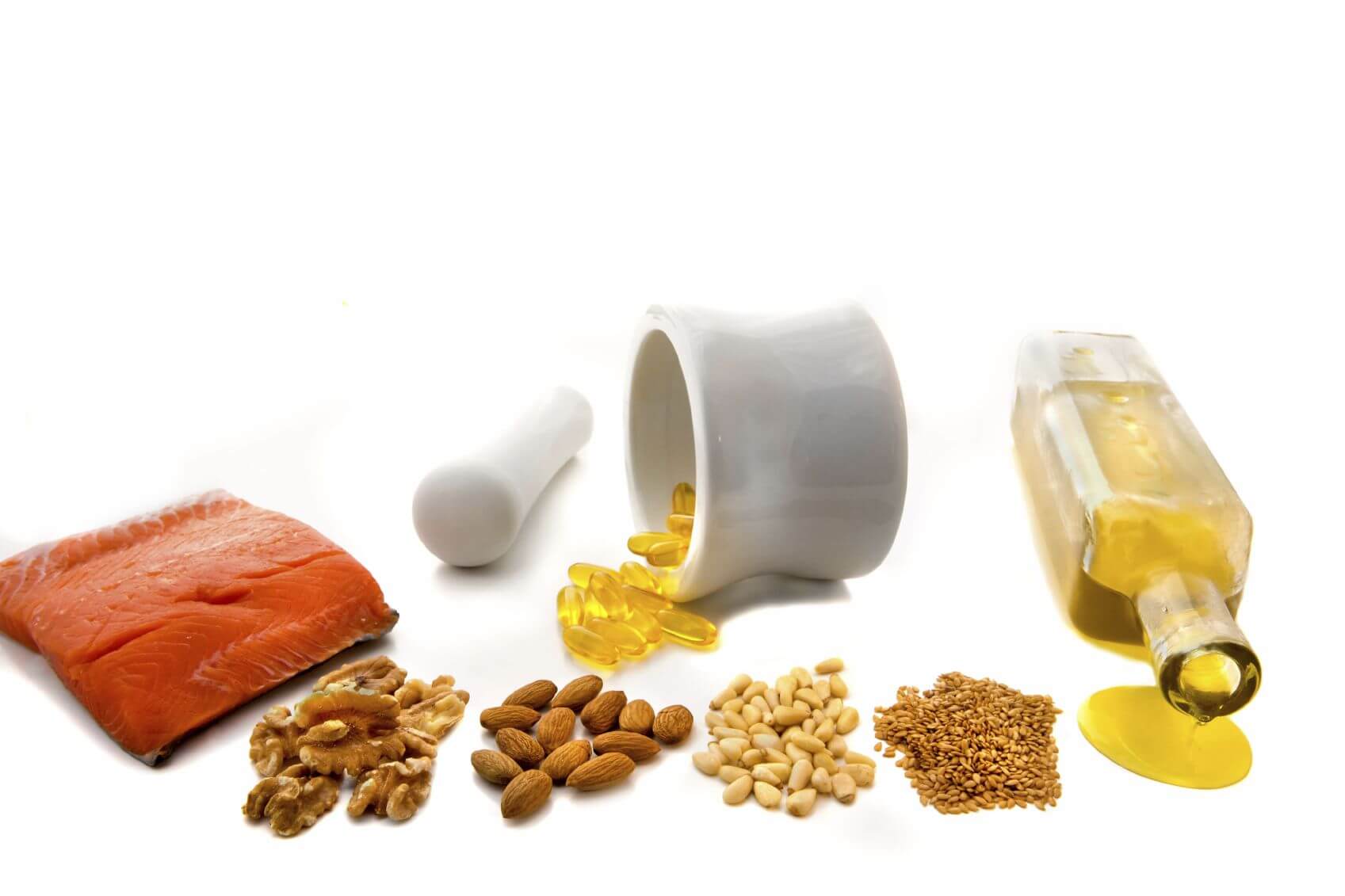
Finding foods that are known to be rich in omega-3s is essential for restoring health in men, women, and children.
Understanding Omega-3 Fatty Acid
Omega-3 fatty acids – Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) play a vital role in controlling inflammation and bodily function.
Foods that we consume are mainly divided into three main groups, which are:
- Proteins
- Fats
- Carbohydrates.
Fats are energy-dense food because they contain nine calories in every gram of fat, regardless of the type of fats. Moreover, Proteins and carbohydrates contain four calories per gram.
Moreover, fat is composed of two-part: Fatty acids and Glycerol
The fatty acid is again sub-divided into two parts, which are:
- Saturated fats (remain solid at room temperature)
- Unsaturated fats (remain liquid at room temperature).
Unsaturated fat is again divided into two types:
- Monounsaturated fat
- Polyunsaturated fat
So the Omega-3 fatty acid comes under the polyunsaturated fat.
Fatty acids are of two types: Essential fatty acids and Nonessential fatty acids.
Our body cannot synthesize essential fatty acids, but it is required for biological process.
On the other, Non-essential fatty acids can be synthesized by our body through various biochemical reactions.
Here, Omega-3 fatty acid is an essential fatty acid that our body cannot produce but is necessary for various biological processes.
Fats are made up of fatty acid blocks bonded together to make chains, so fat is measured by the number of fatty acid chains.
So fats have a long-chain fatty acid (LCFA), a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA), or a medium-chain fatty acid (MCFA).
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Essential fatty acids are vital to the functioning of the human body.
Unlike some vitamins, the body cannot manufacture them, so they must be present in our diet. They come in several forms and can be obtained from various foodstuffs.
Two types of essential fatty acids are:
- Omega-3
- Omega-6
Although there is no exact official recommendation for omega-3, it is generally thought that Omega-3 and Omega-6 should be balanced in our diet.
The typical American diet contains between 10 and 20 times more Omega-6 than Omega-3.
The high amount of Omega-6 fatty acid promotes the pathogenesis of many diseases like cancer, autoimmune disease, and cardiovascular disease. Research indicates that we should consume more omega-3 and less omega-6.
Before looking at sources of omega-3, we need to know something about the different types of omega-3 or polyunsaturated fats.
The 3 main types of Omega-3 Fatty Acid are:
- ALA – alpha linolenic acid
- EPA – eicosapentaenoic acid
- DHA – docosahexaenoic acid
These are not created equal. The main benefits of omega-3 come from EPA and particularly DHA.
We need to understand this when looking at food and supplement labels.
ALA comes from plant sources such as;
- Flaxseeds
- Soybeans
- Pumpkin seeds
- Walnuts.
EPA and DHA are found in many types of oily fish and krill, a kind of shrimp.
The brain is primarily composed of these fatty acids, mainly DHA and, to a lesser extent EPA.
These fatty acids are essential for the nervous system and growth and development.
DHA and EPA are thought to provide most of the health benefits of omega-3, although the role of EPA is less well understood.
The body can synthesize DHA from the other types, but it is inefficient. It is better to consume DHA directly to receive the benefits from it.
If you cannot eat fish or its products, the best alternative is algae.
Fish do not produce DHA either. They obtain DHA from the algae that they eat.
If you can’t eat the fish, try health food shops for a supplement made from Algae. It is a better omega-3 source than the heavily promoted flaxseed oil.
Why do you need Omega-3 fatty acids?
So what are some of the popular health benefits of fish oil?
Despite all the research and the evidence so far, there is still a lot to be learned. A major factor in our health problems is inflammation throughout the body.
Research suggests that omega-3 fatty acids help reduce inflammation and may also help in reducing the risk factors of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and arthritis.
Earlier in the article, we have mentioned that the concentration of DHA and EPA in the brain is important for cognitive performance and behavioral function.
Many doctors recommend fish oil supplements in the last trimester of pregnancy to aid fetal development.
Infants who do not get enough omega-3 during pregnancy are at risk of developing vision and nerve problems.
A deficiency of omega 3 in the body can result in fatigue, dry skin, poor memory, mood swings or depression, poor circulation, and heart problems.
The evidence for the benefits of omega-3 is most substantial about heart disease and associated problems.
What are the Health Benefits of Omega-3 fatty acid
Reduce the risk of Heart disease
Clinical evidence suggests that EPA and DHA help reduce significant risk factors for heart disease, including high cholesterol and high blood pressure.
They have been shown to lower levels of triglycerides (fats carried in the blood) and reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke for people who have already experienced a heart attack.
Omega-3 fatty acids may also help prevent the hardening of the arteries by slowing the development of artery-clogging plaque and blood clots.
Extensive population studies suggest that omega-3 from moderate fish consumption helps protect against stroke caused by plaque buildup in the arteries that lead to the brain.
It was observed that intake of at least two servings of fish per week could reduce the risk of stroke by as much as 50%.
However, excessive fish consumption could increase the risk of bleeding and potentially fatal hemorrhagic stroke, a type of stroke caused by arterial leaks in the brain.
Reduce High cholesterol
Fatty fish in the diet has increased HDL (good) cholesterol and reduced triglycerides.
Studies indicate that a high intake of Omega-3 fatty acid help in reducing high cholesterol and increasing HDL cholesterol.
ALA from walnuts has been reported to reduce total levels of cholesterol.
Lower High Blood Pressure
A range of clinical studies indicates that fish oil supplements high in omega-3 fatty acids can lower people’s blood pressure with untreated hypertension.
Support Diabetes
Research revealed that Diabetes is often associated with high triglycerides and low HDL levels.
Omega-3 from fish oil can help to lower triglycerides and raise HDL. ALA has not been found to have the same results as fish oil.
Some diabetes patients are not able to convert ALA efficiently. You should, however, consult your doctor before taking a fish oil supplement.
Relief from Rheumatoid arthritis
Most clinical studies into omega-3 supplements for arthritis have focused on rheumatoid arthritis.
There has been some relief from the symptoms, such as joint pain and morning stiffness. Some people with RA were able to reduce the dosage of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Fish oil only gives symptomatic relief and does not affect the progress of the disease.
Omega-3 may also be helpful in osteoarthritis, but more study is required.
New Zealand green-lipped mussel, available in supplements, has been reported to relieve joint stiffness and pain, improve walking pace and increase grip strength for some people with osteoarthritis.
Helps in Osteoporosis
According to research, Omega-3 may help increase calcium levels in the body and improve bone strength, although not all trials have been positive.
People deficient in EPA and gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), an omega-6 fatty acid, is also observed that people are more likely to suffer bone density.
A study took place on a group of women over 65 with osteoporosis. Those who took EPA and GLA had less bone loss than those given a placebo. Some of them even experienced increased bone density.
Helps in Mental Health
In recent years, mental health has been a particular focus of study, with many trials looking at different conditions.
There have been some encouraging results that indicate Omega-3 fatty acid is helpful in mental health, but they are not conclusive. More work is needed.
Alleviate Depression
Results are mixed on the effectiveness of omega-3 in alleviating depression symptoms.
Some patients have been able to reduce their dosage of prescription antidepressants when combined with omega-3.
Not all trials have been able to reproduce these results. Taking omega-3 alone is not beneficial. Do not discontinue medication without seeking professional advice.
Different studies of people with bipolar disorder again produce conflicting results.
Some people who took fish oil and their standard prescription treatments experienced fewer mood swings and relapses than the control group.
But another 4-month long study did not find that EPA helped reduce symptoms.
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
It was observed that children with ADHD may have low levels of EPA and DHA. In a clinical study of nearly 100 boys, those with reduced omega-3 fatty acids had more behavioral problems such as temper tantrums than those with normal levels.
However, studies into whether fish oil supplements help reduce symptoms of ADHD had mixed results.
Some studies have found that omega-3 improved ADHD symptoms and their methodology has been questioned.
More research is needed, but an improved diet high in omega-3 is considered a reasonable approach to ADHD.
Prevent Skin disorders
Studies of people with psoriasis and consumption of Omega-3 fatty acids have again produced contradictory results.
Those who took EPA alongside their normal medication did better than those treated with just medication. Another large study found no benefit from fish oil.
Reduce Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Some studies have suggested that omega-3 fatty acids may help when combined with standard IBD medication.
Further, the study has shown how Omega-3 fatty acids help reduce intestinal inflammation.
Prevent Cancer
A range of studies has shown that a diet rich in omega-3 may be beneficial in preventing or slowing the progress of Colon, Breast, and Prostate cancer.
More study is needed in these areas, but the present results are encouraging.
Slow the progress of Macular Degeneration
Clinical trials comparing the diets of a group of people with macular degeneration to those without appeared to show a link.
A diet with a good balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids was less likely to suffer from macular degeneration.
The case for fish oil supplements
An important fact is that omega-3 essential fatty acids are required in our diet.
Despite what the American Heart Association says, the typical diet is out of balance, and more omega-3 is needed. The question is, how to get it.
Misleading labels
The main health-giving ingredients of omega-3 fatty acids are; DHA and EPA, mainly found in fish & algae.
Other sources of omega-3 contain little or no DHA. Even if you try to eat a healthy diet, modern food production methods have depleted our food of much of its nutritional value.
Things like meat and eggs are no longer such good sources of omega-3.
Supermarket shelves can contain products with ‘added omega-3′, but these can be highly misleading.
They don’t say what type of omega-3 it is, and the amounts are often exaggerated.
Look for the label that clearly describes the type of Omega-3 fatty acid and the amount of DHA and EPA in its content.
Check for contamination
You will have heard the reports of fish containing high levels of heavy metals like mercury and lead, PCBs, and other harmful substances.
The fish absorb these from polluted waters, building up their bodies over time. The same happens when we eat the fish, with potentially serious consequences.
Of course, contaminated fish could lead to contaminated fish oil!
An environmental group, tested several leading brands and found them to contain varying contaminants levels, which should be disclosed on the product labeling.
You need to know that you are getting a high-quality fish oil supplement from a trusted supplier.
Source of fish oil
The best type of fish is sourced from the most pristine oceans to minimize contamination risk.
Molecular distillation guarantees purity and concentration to ensure enough DHA and EPA per recommended dose.
The quality fish provides the most potent anti-inflammatory qualities in fish oil.
Independent laboratories should test the product to maintain product standards. Also, they should disclose the complete information on the level for peace of mind.
The problem is finding an excellent Omega-3 supplement you can trust. Product labels don’t have much room for information, and websites often don’t provide it.
Conclusion
The increased consumption of the correct type of omega-3 fatty acid helps get relief from the above-listed health conditions.
On the other hand, the research is hardly conclusive, and more study is needed. Many new research results focus more on the potential of omega-3 fatty acids.
There is enough evidence to justify continuing with daily fish oil supplements.