FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a rare head and neck cancer. It affects only 3 out of every 1 million people in the United States each year. It’s important to know its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Key Takeaways
- Nasopharyngeal cancer is a rare type of head and neck cancer. It starts in the nasopharynx, the tissue between the back of the nose and the back of the mouth.
- The most common symptom is a painless lump on the back of the neck. It can also cause hearing loss, facial pain, and numbness.
- Treatment depends on the cancer’s stage. It may include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or both.
- Nasopharyngeal cancer is more common in certain parts of the world, like Southeast Asia. It affects men more than women.
- Risk factors include the Epstein-Barr virus, family history, tobacco use, and a diet high in salt-cured foods.
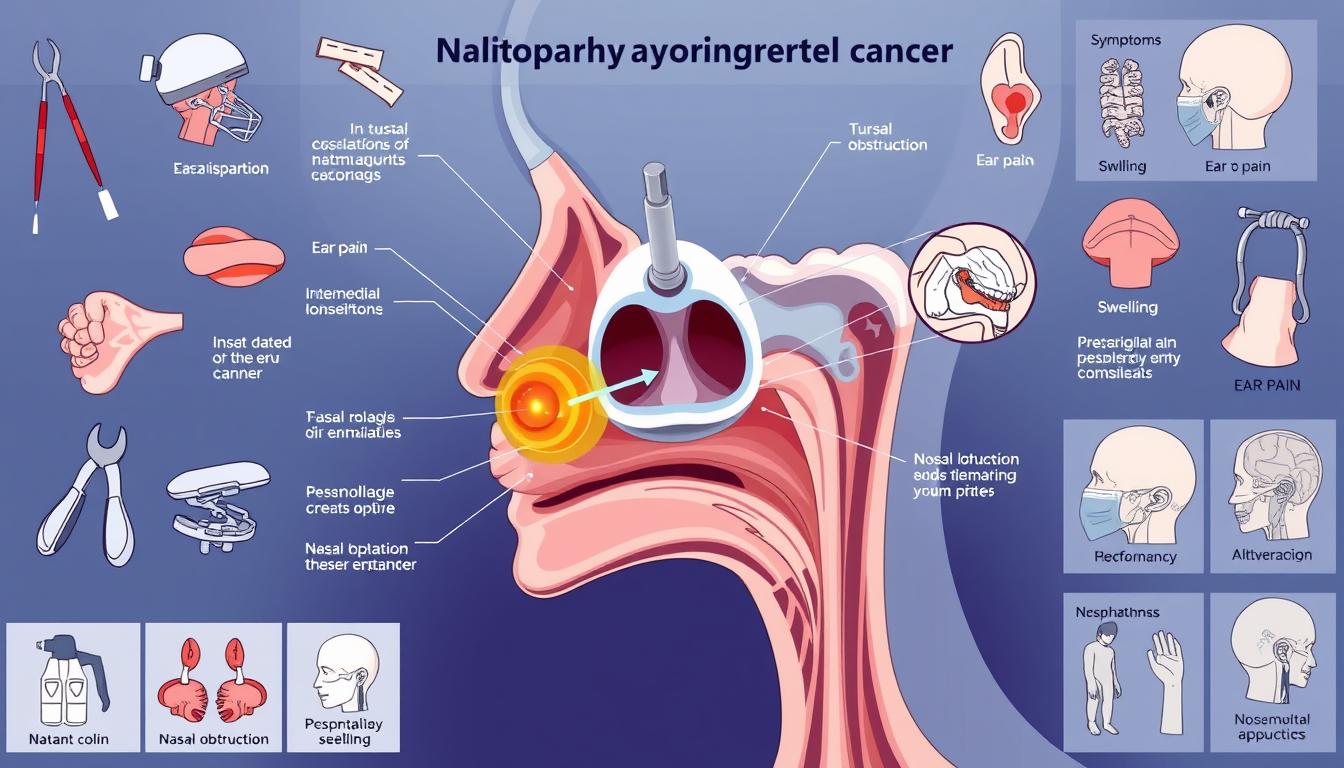
What is Nasopharyngeal Cancer?
Nasopharyngeal Cancer: A Rare Type of Head and Neck Cancer
Nasopharyngeal cancer starts in the nasopharynx, the top part of the throat behind the nose. It often begins in squamous cells, which is rare compared to other throat cancers. There are different kinds, like keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma and non-keratinizing undifferentiated carcinoma.
This cancer is rare in the U.S., with less than one case per 100,000 people each year. But it’s more common in places like Southeast Asia.
In the U.S., people of all races can get nasopharyngeal cancer. Eating a lot of salt-cured foods and being exposed to the Epstein-Barr virus can raise your risk.
Type of Nasopharyngeal Cancer | Characteristics |
|---|---|
Keratinizing Squamous Cell Carcinoma | The most common type of NPC, characterized by the presence of keratin |
Non-keratinizing Differentiated Carcinoma | Characterized by well-differentiated tumor cells with minimal keratinization |
Non-keratinizing Undifferentiated Carcinoma | Characterized by poorly differentiated tumor cells with no keratinization |
Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma | A rare and very aggressive subtype of NPC |
Other tumors like lymphomas and sarcomas can also happen in the nasopharynx. But they are not as common. Benign tumors, like angiofibromas, are rare and mostly found in young people. These tumors are usually not serious.
“Nasopharyngeal cancer is a unique type of head and neck cancer that originates in the nasopharynx, the uppermost part of the pharynx located behind the nose.”
Symptoms of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a rare head and neck cancer. It might not show symptoms early on. But, as it grows, symptoms like a neck lump, blood in saliva, and bloody nasal discharge appear. Other signs include nasal congestion, ringing in the ears, hearing loss, and sore throat.
It’s key to see a doctor if you notice any unusual changes. These symptoms can also happen with other health issues.
Some common nasopharyngeal cancer symptoms are:
- Neck lump or mass
- Bloody nasal discharge or nosebleeds
- Nasal congestion
- Ringing in the ears or hearing loss
- Ear infections
- Sore throat
- Headaches
These symptoms can also mean other health problems. So, getting a doctor’s diagnosis is very important. Catching nasopharyngeal cancer early and treating it quickly can greatly improve your chances of recovery. If you have any persistent or worrying symptoms, don’t hesitate to get medical help.
“Nasopharyngeal cancer is a complex disease that requires a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the potential symptoms is the first step in seeking timely medical care.”
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors
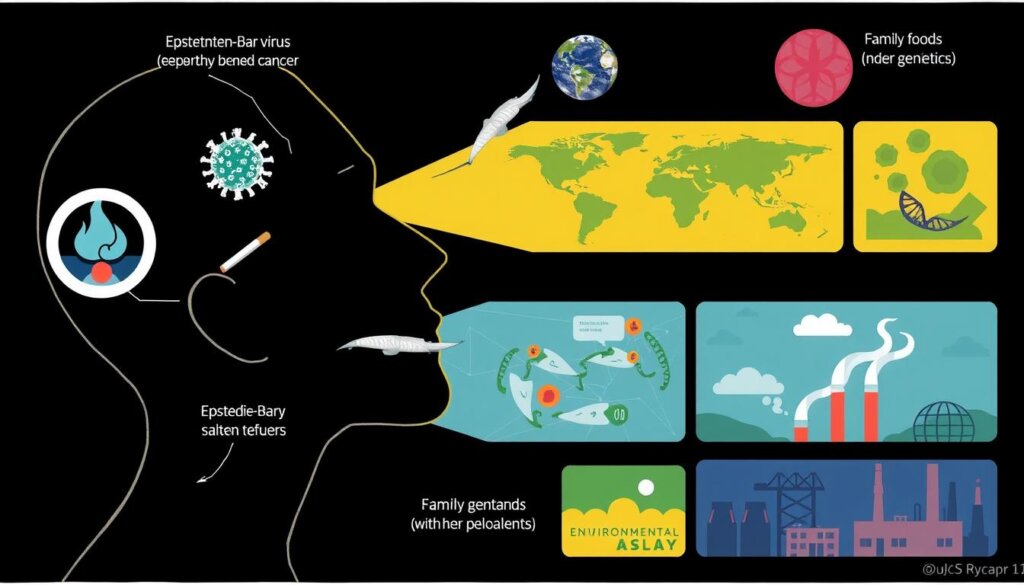
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a complex disease. The exact cause is not fully understood. However, researchers have found several risk factors that can increase the chance of getting this rare cancer.
One main risk factor is infection with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). In the UK, up to 80% of cases are linked to EBV. People from certain ethnic and geographic backgrounds, like those from Asia, North Africa, and the Arctic, are at higher risk.
Family history also plays a role. If a close relative has had nasopharyngeal cancer, you’re more likely to get it too. Eating certain foods, like salt-cured foods, can also increase your risk. A study in Hong Kong found that eating Cantonese-style salted fish can cause nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Unhealthy lifestyle choices, like drinking a lot of alcohol and smoking, also raise your risk. In the UK, smoking causes 25% of nasopharyngeal cancer cases.
While these factors can increase your risk, not everyone with them will get the disease. Knowing the causes and risk factors can help you take steps to lower your risk. It’s also important to seek early diagnosis if you notice any concerning symptoms.
Diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Diagnosing nasopharyngeal cancer needs a detailed check-up and special tests. The goal is to know the tumor’s size, where it is, and if it has spread. It also aims to find out the exact type of cancer.
The first step is a physical check. Your doctor will look for any signs in the nasopharynx, the top part of your throat. Then, they might do a nasopharyngoscopy. This uses a small camera to see inside your nasopharynx.
If something looks odd, a biopsy will be suggested. This could be an endoscopic biopsy or a fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy. Both take a small sample of tissue for testing.
Your doctor might also use MRI and PET-CT scans for more info. These scans show how big the tumor is and if it has spread. They help decide the best treatment.
Blood tests, like the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) test and the HPV test, might be done too. They help to understand the cause of cancer and guide treatment.
By combining physical checks, biopsies, scans, and blood tests, doctors can accurately diagnose nasopharyngeal cancer. They then create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
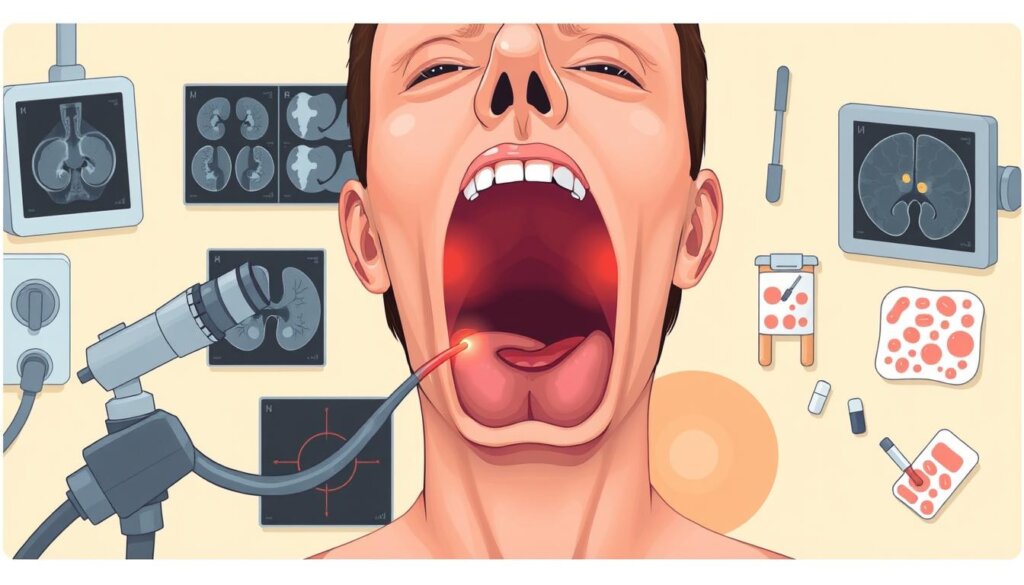
“The diagnostic process often involves multiple types of biopsies to confirm the presence of NPC, with endoscopic and fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsies being common methods.”
Treatment Options for Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Exploring Effective Treatment Strategies
Nasopharyngeal cancer treatment often uses a mix of radiation and chemotherapy. Radiation is usually the main treatment. It might be used alone or with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy helps shrink tumors before radiation or treats cancer that has spread.
The treatment plan depends on the cancer’s stage, the patient’s health, and other factors.
Radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma uses external beam radiation. This kills cancer cells with high-energy beams. Side effects include skin redness, hearing loss, and dry mouth.
To deal with a dry mouth, rinse with warm salt water, keep the mouth moist, and avoid acidic or spicy foods and drinks.
Chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal cancer can be pills or intravenous. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy before radiation might improve survival rates, but more research is needed.
Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
Radiation Therapy | High-energy beams are directed at the tumor to kill cancer cells. It can cause temporary side effects like skin redness, hearing loss, and dry mouth. |
Chemotherapy | Drugs are used to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. It can be given in pill form or through intravenous administration. |
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy | Chemotherapy is administered before radiation therapy to improve survival rates, although more research is needed. |
Surgery | It is rarely used as a treatment option, but it may be used to remove cancerous lymph nodes in the neck. |
Surgery is rarely used for nasopharyngeal cancer. But it might remove cancerous lymph nodes in the neck.
“Radiation therapy often causes dry mouth as a side effect, leading to various complications such as difficulty eating and speaking.”
Nasopharyngeal cancer stages range from I to IV. The cancer is classified by its size and spread. Diagnosis includes physical exams, nasal endoscopy, and biopsy tests.
Imaging tests like CT, MRI, PET scans, and X-rays help find how far the cancer has spread.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is mostly squamous cell carcinoma. The most common place it starts is the fossa of Rosenmuller, making up 50% of cases. In Asia, especially China, nasopharyngeal cancer is very common. Being Chinese is a risk factor, no matter where you live.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified nasopharyngeal carcinoma into three types. These are Type 1 (keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma), Type 2 (differentiated nonkeratinizing carcinoma), and Type 3 (undifferentiated carcinoma).
Over the last decade, deaths from nasopharyngeal cancers have gone down. This is thanks to early detection and better treatments. In non-endemic areas like the Americas and Europe, nasopharyngeal cancer is rare. It happens less than 1 time per 100,000 people.
In places like China, the rate can be up to 21 cases per 100,000 people. Men are more likely to get nasopharyngeal carcinoma. They are also more likely to die from it compared to women.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The outlook for nasopharyngeal cancer depends on several key factors. These include the tumor size, cancer stage, and how well the patient responds to treatment. Early-stage cancer has a better chance of survival, with an 82% 5-year survival rate. But, as cancer advances, survival rates fall to 72% and 49% for regional and distant stages, respectively.
Survival rates don’t always show how cancer will progress or come back after diagnosis. Age, health, treatment response, and EBV DNA levels in the blood also play big roles. New treatments like immunotherapies and targeted drugs might lead to better outcomes.
The type of tumor also affects prognosis. Type 1 tumors, linked to EBV in 70% to 80% of cases, are less treatable. Types 2 and 3, more common in EBV cases, respond better to treatment.
The overall 5-year survival rate for nasopharyngeal cancer is 63%. But, with better detection and treatment, patient outcomes could get better.
Remember, these numbers are just estimates. Each person’s situation is unique. It’s crucial to talk to your doctor about your specific case and treatment options.
Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Early Detection and Prevention
Nasopharyngeal cancer is rare but more common in some parts of Asia. In these areas, doctors might screen people at high risk. This includes those with a family history or Epstein-Barr virus infection. However, in the U.S. and other places, routine screening is not usually done.
There’s no sure way to stop nasopharyngeal cancer. But avoiding certain things can help. This means not eating too much salt-cured food, not drinking too much alcohol, and not smoking. A healthy lifestyle and avoiding risks can lower your chance of getting this cancer.
Finding nasopharyngeal cancer early is very important. It can make treatment work better and increase survival chances. Doctors use tools like Epstein-Barr viral tests and plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA tests to find it. New technologies like machine learning and genetic models are also helping to find it early and understand who is at risk.
Knowing how important early detection and prevention are can help you protect your health. This can lower your risk of getting this rare and tough cancer.
Diagnostic Tool | Description |
|---|---|
EBV Antibody Test | Measures the levels of Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in the blood, which can be elevated in nasopharyngeal cancer cases. |
Endoscopic Biopsy | A procedure where a small tissue sample is collected from the nasopharynx during an endoscopic examination for laboratory analysis. |
CT Scan | Provides detailed information about the size, location, and potential spread of the tumor, aiding in treatment planning. |
MRI | Helps distinguish between cancerous, non-cancerous, and inflamed areas in the head and neck region. |
PET Scan | Identifies potential metastasis to lymph nodes or other distant sites by detecting changes in metabolic activity. |
PET-CT Scan | It combines detailed information from CT and PET scans to provide a comprehensive assessment of the tumor and its spread. |
“Early detection is key when it comes to treating nasopharyngeal cancer effectively. By staying vigilant and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can improve their chances of catching this rare form of cancer in its early stages.”
Living with Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Coping Strategies and Support Resources
Getting a diagnosis of nasopharyngeal cancer is tough, both in body and mind. But, there are ways and places to help you and your family deal with it.
Talking openly with your healthcare team is very important. They can help with side effects like trouble swallowing and dry mouth. Working with your doctors and nurses helps keep your life good.
Being part of a support group is also very helpful. It lets you meet others who know what you’re going through. You can find groups in person or online, made just for nasopharyngeal cancer patients.
There are many resources for dealing with the daily life of nasopharyngeal cancer. This link has info on follow-up care and managing side effects.
You’re not alone in this fight. By getting support and using available resources, you can handle the tough parts and stay well.
“The support I got from my healthcare team and other cancer survivors was key. I’m thankful for the help that let me get strong again and enjoy life fully.”
Conclusion
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a rare and complex disease. It affects the head and neck area. Advances in medical research have improved treatment and life quality for many patients.
Knowing the symptoms, risk factors and treatment options helps you take charge of your health. Working with your medical team is key. Regular check-ups and early detection are crucial for a good outcome.
You’re not alone in this fight. Healthcare professionals, support groups, and resources offer help and support. With determination and the right support, you can overcome challenges and focus on your health.
FAQ
What is nasopharyngeal cancer?
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a rare head and neck cancer. It starts in the nasopharynx, the upper part of the pharynx behind the nose. It often begins in the squamous cells lining the nasopharynx.
What are the common symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer?
Early nasopharyngeal cancer might not show symptoms. However, as it grows, symptoms can include a neck lump, blood in saliva, and bloody nasal discharge. Other signs are nasal congestion, ringing in the ears, hearing loss, and frequent ear infections.
Also, sore throat and headaches can occur.
What are the risk factors for nasopharyngeal cancer?
The exact cause of nasopharyngeal cancer is still unknown. But risk factors include Epstein-Barr virus infection and ancestry from certain areas. Family history and exposure to salt-cured foods and alcohol and tobacco also increase risk.
How is nasopharyngeal cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosing nasopharyngeal cancer starts with a physical exam. Then, tests like nasopharyngoscopy with biopsy, MRI, and PET-CT scan are done. An Epstein-Barr virus blood test and possibly an HPV test may also be used.
These tests help find the tumor’s size and location. They also check if the cancer has spread.
What are the treatment options for nasopharyngeal cancer?
Treatment often combines radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Radiation therapy is usually the main treatment. It might be used alone or with chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy helps shrink the tumor before radiation. It also treats cancer that has spread.
What is the prognosis for nasopharyngeal cancer?
The prognosis depends on the tumor size, cancer stage, and treatment response. Early-stage cancer has a better prognosis and higher survival rates. More advanced stages have lower survival rates.
Is there screening for nasopharyngeal cancer?
In areas where the cancer is common, like parts of Asia, screening tests are offered. These are for people at high risk, like those with a family history or Epstein-Barr virus infection. However, in the U.S. and other areas, routine screening is not common.
How can I cope with nasopharyngeal cancer?
Dealing with nasopharyngeal cancer is tough, both physically and emotionally. It’s key to work closely with your healthcare team. They can explain your treatment and any side effects.
Joining a support group or seeking counseling can also help. It’s a way to cope with the emotional and practical sides of living with this disease.