FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer. It kills over 7,000 Americans each year. It’s crucial to know its symptoms and treatment options. This disease often starts as a new or changing mole.
It can also appear on healthy skin. Catching it early is key. If found early, melanoma has a 99% cure rate. This article will cover melanoma’s signs, causes, prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and survival rates.
Key Takeaways
- Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, characterized by the uncontrolled growth of pigment-producing cells.
- Early detection is critical, as melanoma has a 99% cure rate when caught early.
- Melanoma can display warning signs using the “ABCDE” acronym: Asymmetry, Border irregularities, Color changes, Diameter exceeding 6mm, and Evolving features.
- Melanomas can also appear as small brown or black streaks under nails or as bruises.
- Treatment options for melanoma include surgery, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the stage and severity of the disease.
What is Melanoma?
Overview
Melanoma is a serious skin cancer. It starts in the melanocytes, the cells that make skin color. It often begins on sun-exposed areas like arms, back, face, and legs.
But it can also appear in less sun-exposed spots, like palms, soles, or under nails. It’s the most dangerous skin cancer because it spreads fast if not caught early.
The risk of melanoma is rising, especially in young people and women. Most melanomas come from UV light, like sunlight or tanning beds. It’s responsible for most skin cancer deaths, even though it’s rare.
Early detection is key. Melanomas are almost always curable if found early.
Melanoma can be superficial spreading, nodular, lentigo maligna, or acral lentiginous. Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are more common but less deadly. Moles can increase melanoma risk.

Knowing about melanoma’s origins, types, and risks is vital. Being aware of its signs helps catch it early. This way, people can take action to protect their skin and get medical help if needed.
Signs and Symptoms of Melanoma
Moles and Lesion Changes
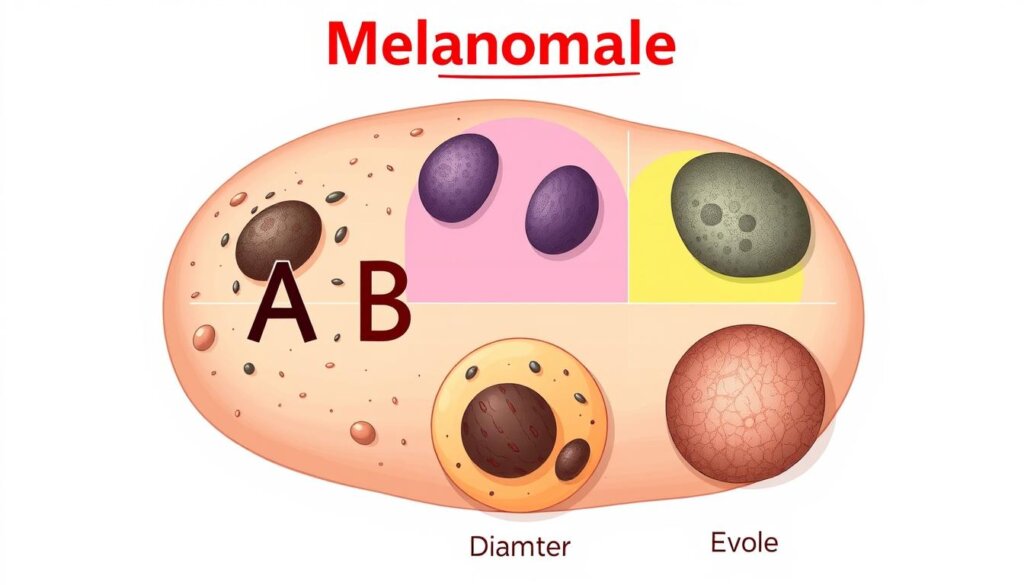
The first sign of melanoma is often a change in an existing mole or a new growth on the skin. Melanomas can look different, but they often have certain traits. These include being asymmetrical, having irregular borders, showing multiple colors, being over 6 millimeters, and changing in size, shape, or color.
The “ABCDE” rule helps spot potential melanomas. Look for Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter greater than 6 mm, and Evolving or changing appearance.
Melanomas can show up in places with little sun, like palms, soles, or under nails. They might look dark, flat, or irregularly-shaped. Some types, like Acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM), are more common in people of color. They can appear colorless or lightly pigmented.
Melanoma Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
Asymmetry | The two halves of the mole or lesion do not match. |
Border Irregularity | The edges of the mole or lesion are uneven, ragged, or blurred. |
Color Variation | The mole or lesion has multiple colors, such as shades of brown, black, red, white, or blue. |
Diameter | The mole or lesion is larger than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser). |
Evolving | The mole or lesion changes in size, shape, or color. |
Early detection of melanoma is key, as it’s highly treatable when caught early. Knowing the signs and symptoms helps people watch their skin. They should seek medical help for any concerning changes.
“Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, but it is highly treatable when detected early. The ABCDE rule is a simple way to remember the key signs to look for when checking your skin.”
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of melanoma is still a mystery. But we know that ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is a big risk. UV radiation can damage skin cells’ DNA, leading to melanoma.
Other risks for melanoma include a family history of the disease. Also, having many moles or atypical moles is a risk. Fair skin that burns easily, a weakened immune system, and living near the equator or at high elevations are also risks.
- About 1 in 10 people with melanoma have a family history.
- Those with lighter skin face a higher melanoma risk than darker-skinned people.
- Red or blond hair, blue or green eyes, or skin that freckles or burns easily increase melanoma risk.
- The risk of melanoma grows with age, but it can also affect the young. Melanoma is common in those under 30.
- In the U.S., men are more likely to get melanoma than women, but risk varies by age.
- People with xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) face a high risk of melanoma and other skin cancers at a young age.
UV radiation is the main risk for skin cancer, including melanoma. UVB radiation causes sunburns and blistering, leading to most skin cancers, like melanoma. People who work outside, go to the beach, or play sports outdoors are at higher risk.
Risk Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Exposure to UV Radiation | Too much UV radiation, from the sun, tanning beds, or other sources, is the main risk for melanoma. |
Family History | Those with a family history of melanoma face a higher risk. |
Skin Type | Fair-skinned people, especially those with light eyes, hair, and a tendency to burn, are at higher risk. But melanoma can happen to anyone. |
Mole Count | Having many moles, including unusual ones, raises melanoma risk. |
While melanoma can affect anyone, some are at higher risk. This includes those with certain skin types, sun exposure history, and genetic factors. Knowing and managing these risks is key to preventing and catching melanoma early.
“Melanoma is not just a skin cancer, it’s a serious form of cancer that can spread to other organs if not detected and treated early.” – Dr. Jane Doe, Dermatologist
Prevention Strategies
Keeping your skin safe from the sun’s harmful rays is key to melanoma prevention. One top way to lower your risk is to cut down on UV exposure. This can come from the sun or tanning beds. Most doctors say no to tanning beds and sunlamps because they raise melanoma risk.
Starting to use tanning beds before 30 can increase melanoma risk.
When outside, find shade, wear clothes that cover you, and use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. Most skin cancers come from too much UV exposure. This includes the sun, tanning beds, and sunlamps. UV rays are strongest from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. daylight saving time.
If your area’s UV index is 3 or higher, protect your skin.
Skin self-exams are vital for catching melanoma early. Kids should also avoid too much sun to prevent skin damage. People with weak immune systems, like those with organ transplants, are at higher risk.

By following these sun protection and tanning avoidance tips, you can lower your melanoma risk. Regular skin checks can also help catch the disease early, when it’s easier to treat.
Diagnosis of Melanoma
Finding melanoma early is key for good treatment and better results. A doctor will first do a detailed skin check. They use a tool called a dermoscope to look at any odd moles or spots.
If a mole looks like it might be melanoma, a biopsy is done. This means taking out the whole mole or a piece of it for a closer look. It helps tell if it’s cancer or not.
The doctor might also check nearby lymph nodes. This is to see if the cancer has spread. They might use CT or PET scans to see how far the cancer has gone.
Places like the Center for Melanoma Oncology at Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center have experts just for melanoma. They work fast to test and plan care, cutting down on visits.
Knowing the stage of melanoma is very important. It helps figure out how serious it is and what treatment to use. Melanoma is staged from 0 (just starting) to Stage IV (very advanced).
Getting the right diagnosis and stage is vital for treatment. Doctors use many tools, like biopsies and scans, to check the melanoma fully.
Staging and Treatment Options
The stage of melanoma is key in choosing the right treatment. Melanoma is more likely to spread than other skin cancers. Treatments include surgery, radiation, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
Early-Stage Melanoma
For early melanomas, surgery is often the first step. This involves removing the tumor and some healthy skin around it. Sometimes, a biopsy of the lymph nodes is done to check for cancer spread. If there’s a chance of the cancer coming back, treatments like immunotherapy or targeted therapy might be suggested.
Advanced Melanoma
For melanomas that have spread, treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy. Palliative care may also be used to ease symptoms and improve life quality. Clinical trials offer new treatments for stage III or IV melanoma.
. It can come back after treatment. Treatment success depends on many factors, like tumor thickness and cancer spread.
“Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer, but it is also one of the most treatable if caught early. Early detection and proper treatment are key to managing this disease.”
Melanoma
Melanoma is a serious skin cancer that grows in the melanocytes, the cells that make pigment. It’s the most dangerous skin cancer because it can spread fast if not caught early. Even though it’s rare, it causes most deaths from skin cancer.
The number of melanoma cases has gone up over 30 years. This is likely because of more sun and tanning bed use. It can show up anywhere, even in places that don’t get much sun, like palms and soles.
Most melanomas start in normal skin, not in moles. If caught early, the survival rate is very high, about 99 percent. But, sadly, about 8,290 people will die from it in the U.S. in 2024.
In 2024, about 200,340 melanoma cases will be diagnosed in the U.S. Most of these will be in situ, meaning they’re still in the skin’s top layer. But, 100,640 cases will be invasive, meaning they’ve spread deeper. Of these, 59,170 will be in men and 41,470 in women.
Acral lentiginous melanoma is common in people of color. Nodular melanoma makes up 10 to 15 percent of all cases.
Melanoma Survival Rates by Stage | Percentage |
|---|---|
Localized Melanoma | 99% |
Regional Melanoma | 66% |
Distant Melanoma | 27% |
The survival rate for melanoma patients varies by stage. For early-stage melanoma, it’s 99 percent. But, for distant melanoma, it drops to 27 percent. Brain metastases are a serious complication that needs special treatment.
Neoadjuvant therapy, like immunotherapy, is becoming a promising treatment for melanoma. The sentinel lymph node is important for predicting how the disease will progress.
“Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that can often be cured if found early.”
The American Academy of Dermatology says to watch for changes in skin spots. Look for spots that are not symmetrical, have irregular borders, or change color. Moles bigger than a pencil eraser or spots that change should be checked by a doctor.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The chance of survival for melanoma depends on when it’s found. If caught early, before it spreads, the 5-year survival rate is over 99%. But, as it gets worse, the survival rate drops a lot. Things like how thick the tumor is and if it’s spread to lymph nodes matter a lot.
Finding melanoma early is key. If it’s just in the skin, the 5-year survival rate is over 99%. But, if it’s spread, the rates are much lower. Overall, the 5-year survival rate for all melanoma is 94%. Early detection and treatment can lead to long-term survival or even a cure.
Survival rates change with the disease stage. For example, stage IA melanoma has a 5-year survival rate of about 97%. But, stage IV melanoma’s 5-year survival rate is only 15% to 20%. About one-third of melanoma patients have cancer spread to distant places.
Remember, survival rates are just estimates. They don’t always match what happens to one person. Younger people and those with weak immune systems face tougher challenges. But, new treatments might improve survival chances even more.
“Early detection is crucial, as it allows for more effective treatment and better long-term outcomes.”
Conclusion
Melanoma is a serious skin cancer that needs quick action to fight it. Melanoma has grown fast worldwide over 50 years. It’s most common in people with light skin and near the equator.
Melanoma is a big problem in older and young adults. It causes most skin cancer deaths, even though it’s rare. In 2017, the U.S. saw 87,110 new melanoma cases. Treatment costs have jumped by 288% in just nine years.
In the U.S., melanoma costs $3.3 billion a year. This is part of the $8.1 billion spent on skin cancer. Melanoma also costs over $3.5 billion in indirect costs yearly.
Early detection is key to beating melanoma. It has a 99% cure rate if caught early. The 5-year survival rate is 99% for early cases, 66% for spread, and 27% for distant metastasis.
Knowing the signs and avoiding UV exposure can lower your risk. Regular skin checks are also important. With new treatments, many people can beat melanoma and live long lives.
In short, melanoma is a serious issue that needs our attention. By learning about it and being careful, we can protect our skin and health. This helps us fight melanoma and improve our chances of a good outcome.
FAQ
What is melanoma?
Melanoma is a serious skin cancer. It starts in the melanocytes, the cells that make pigment. It’s the most dangerous skin cancer and can spread fast if not treated early.
What are the signs and symptoms of melanoma?
The first sign is often a change in a mole or a new growth. Melanomas can look asymmetrical, have irregular borders, and be many colors. They are usually bigger than 6 millimeters and change over time.
What causes melanoma and who is at risk?
UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds is a big risk factor. Other risks include a family history of melanoma, many moles, fair skin, weakened immune, and living near the equator.
How can melanoma be prevented?
Limit UV radiation by staying in the shade, wearing protective clothes, and using sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. Avoid tanning beds. Regular self-exams can help catch changes early.
How is melanoma diagnosed?
A healthcare provider will examine a suspicious spot with a dermoscope. If it looks like melanoma, a biopsy might be done to remove the tissue for testing.
What are the treatment options for melanoma?
Treatment depends on the stage. Early-stage melanomas are often treated with surgery. Advanced cases might get surgery, radiation, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.
What is the prognosis and survival rate for melanoma?
Survival rates vary by stage. Early-stage melanoma has a 99% 5-year survival rate. But, as it progresses, survival rates drop significantly.