FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Did you know only 1 in 100 people worldwide have celiac disease? This is a condition where the immune system reacts to gluten and damages the small intestine. But, eating gluten-free can be pricey. Prepared gluten-free foods cost more than regular ones. Luckily, there are many healthy, gluten-free grains that won’t empty your wallet.
We’ll look at the good stuff in gluten-free grains like quinoa, buckwheat, sorghum, amaranth, and teff. These grains are full of nutrients and make eating fun and safe from gluten.
Key Takeaways
- Gluten-free grains are a nutritious alternative to gluten-containing grains like wheat, barley, and rye.
- Following a gluten-free diet can be expensive, but incorporating healthy gluten-free grains can help you save money.
- Quinoa, buckwheat, sorghum, amaranth, and teff are all versatile, nutrient-dense gluten-free grains to explore.
- Gluten-free grains provide essential nutrients like fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals.
- Exploring a variety of gluten-free grains can help you create a diverse and balanced diet.
What Is a Gluten-Free Diet?
A gluten-free diet means not eating foods with gluten. Gluten is in wheat, barley, rye, and some oats. It’s key for people with celiac disease, an illness where gluten harms the small intestine and stops nutrient absorption. It also helps those with non-celiac gluten sensitivity, who get stomach pain, bloating, and headaches from gluten.
Defining a Gluten-Free Diet
On this diet, you can’t have foods with wheat, barley, rye, or triticale. Oats might have gluten and need to be labeled as gluten-free. Foods to skip include bread, cereals, pasta, sauces, and snacks.
The Purpose of a Gluten-Free Diet
This diet helps manage celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity symptoms. It stops intestinal damage and boosts health.
“Gluten-free diets have become increasingly popular, with the U.S. Food & Drug Administration defining gluten-free products as containing less than 20 parts per million (ppm) of gluten.”
For those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, reading labels is key. Many companies offer gluten-free foods, some by mail or in stores.
Gluten-Free Grains
Many grains don’t have gluten and are full of fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals. These include quinoa, buckwheat, sorghum, amaranth, teff, corn, rice, and millet. Adding these grains to your meals helps you get the nutrients you need without gluten.
Nutritional Benefits
Gluten-free grains are full of good stuff. Blue cornmeal has twelve grams of protein and ten grams of fiber per cup. Fonio is about 7.5% protein, is sugar-free, and gives you zinc and iron. Job’s tears can help lower cholesterol and blood sugar because of their fiber.
Sorghum gives you about twenty grams of protein and twelve grams of fiber per cup. Teff grain has twenty grams of protein and ten grams of fiber per cup.
Cooking and Serving Suggestions
It’s easy to add gluten-free grains to your meals. They work great as a base for dishes like pilafs, stir-fries, and casseroles. Or, you can mix them into soups, salads, and baked goods.
Many grains, like quinoa, buckwheat, and millet, taste mild and nutty. This makes them perfect for both sweet and savory dishes. You can try many different recipes with them.
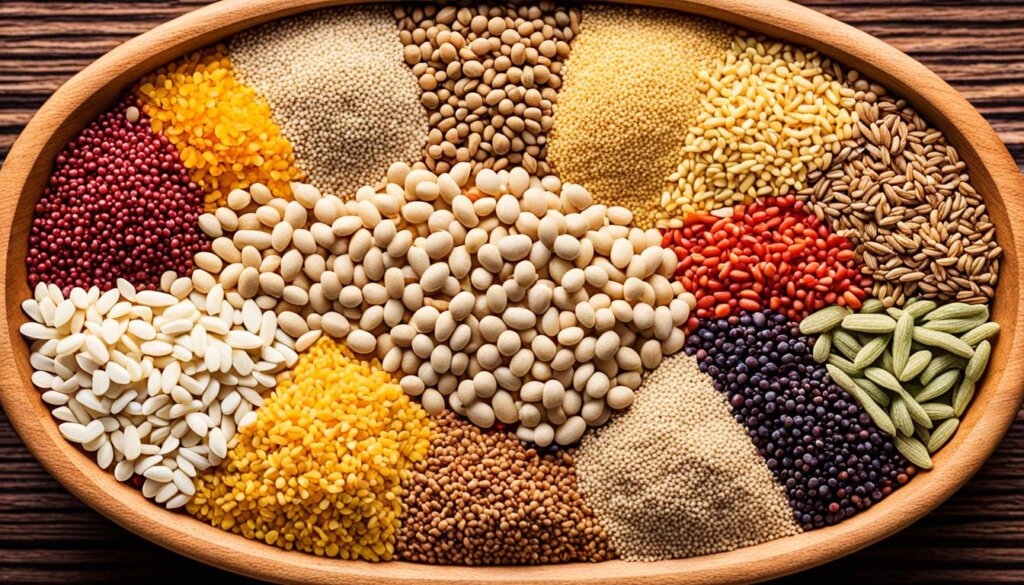

Think about how versatile gluten-free grains are. They’re a great choice for your meals. They offer health benefits and add variety and flavor to your cooking.
Quinoa: The Trendy Gluten-Free Grain
Quinoa is an ancient grain that’s become very popular lately. It comes from the mountains of Peru, Chile, and Bolivia. People have eaten it for over 5,000-7,000 years.
Quinoa is special because it’s a complete protein. This means it has all nine essential amino acids. This makes it great for those who can’t eat gluten or follow a vegetarian diet.
Nutritional Highlights
Quinoa is full of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, besides being a complete protein. Eating half a cup of cooked quinoa gives you about 39 grams of carbs and a low glycemic index. It’s packed with magnesium, potassium, iron, and folate. This makes it a key part of a gluten-free diet.
Recipes and Uses
Quinoa can be used in many gluten-free dishes. It goes well in salads, casseroles, baked goods, and pilafs. Its mild, nutty taste fits with both sweet and savory foods.
Adding quinoa to your meals can make them healthier and more interesting. It’s a trendy and nutritious choice for your cooking.
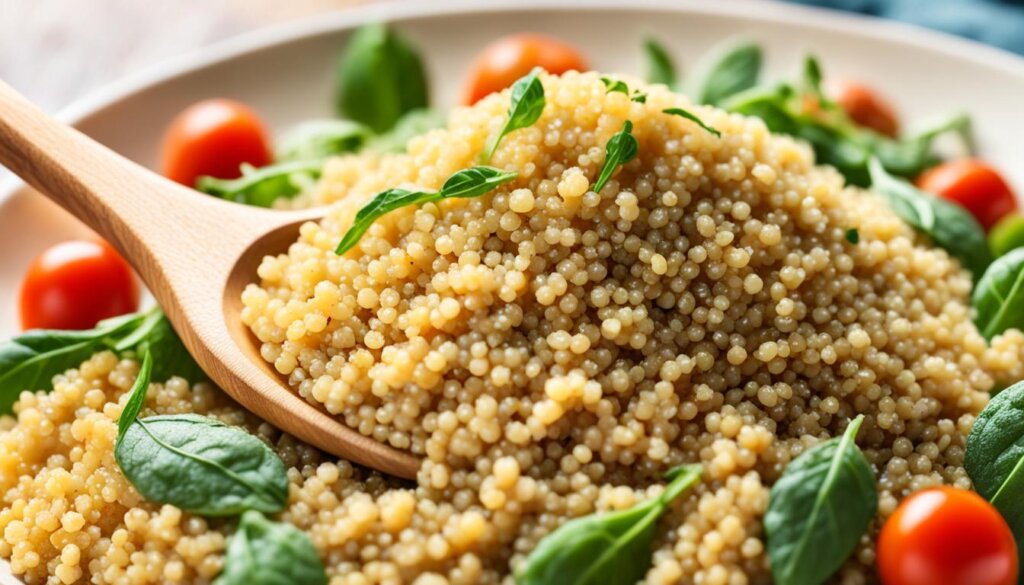

“Quinoa is a most welcome addition to vegetarian diets and perfect for those with food sensitivities including gluten, wheat, and soy intolerances.”
Buckwheat: A Nutritious Pseudo-grain
Buckwheat isn’t related to wheat and is gluten-free. It’s full of antioxidants like rutin and quercetin. These help fight inflammation and protect the brain. It can also lower cholesterol and blood pressure, cutting down heart disease risk.
You can make many gluten-free dishes with buckwheat, like noodles and pancakes. It’s packed with nutrients: 92 calories, 19.9 grams of carbs, 2.7 grams of fiber, 3.38 grams of protein, and 0.62 grams of fat per 100 grams. Plus, it has calcium, iron, and magnesium.
Buckwheat is good for more than just eating. It may help with type-2 diabetes symptoms. Its antioxidants could also make heart health better by lowering heart disease risk. Studies show it can lower insulin, cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol levels.
The buckwheat market is booming, reaching over $1.4 billion in 2023, and is expected to hit $1.8 billion by 2028. This growth is thanks to more people avoiding gluten due to celiac disease. Its health benefits and versatility make it popular.
Beyond food, buckwheat is great for the environment as a cover crop. It improves soil, reduces erosion, and helps with nutrients and nitrogen. This pseudo-grain is a top choice for a gluten-free diet and for the planet.

Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Calories | 92 |
Carbohydrates | 19.9g |
Fiber | 2.7g |
Protein | 3.38g |
Fat | 0.62g |
Calcium | 7mg |
Iron | 0.8mg |
Magnesium | 51mg |
Buckwheat is a superfood that’s gluten-free and full of antioxidants. It’s great for the heart and can be part of a healthy diet. Its popularity is growing worldwide, showing it’s a top choice for health-conscious eaters.
“Buckwheat is a nutrient-dense pseudo-grain that can be a great addition to a gluten-free diet. Its unique nutritional profile and versatility make it a versatile and beneficial choice for those seeking a healthy, gluten-free option.”
Looking to add more gluten-free options to your diet? Buckwheat is a great pick. It’s packed with nutrients and health benefits.
Sorghum: A Versatile Gluten-Free Grain
If you’re on a gluten-free diet or want to eat more whole grains, sorghum is a great choice. It’s gluten-free and packed with fiber, protein, and iron. It also has antioxidants that may help prevent heart disease.
Health Benefits of Sorghum
Sorghum is known for its nutrition. It’s full of fiber, which is good for your gut and can lower cholesterol. A half-cup of cooked sorghum gives you more protein than quinoa. It’s also loaded with iron, zinc, magnesium, and antioxidants.
The American Heart Association says eating whole grains like sorghum is good for your heart. Its fiber and antioxidants are great for your heart health. You can use sorghum in many dishes, from soups to baked goods, making it easy to follow a gluten-free diet.
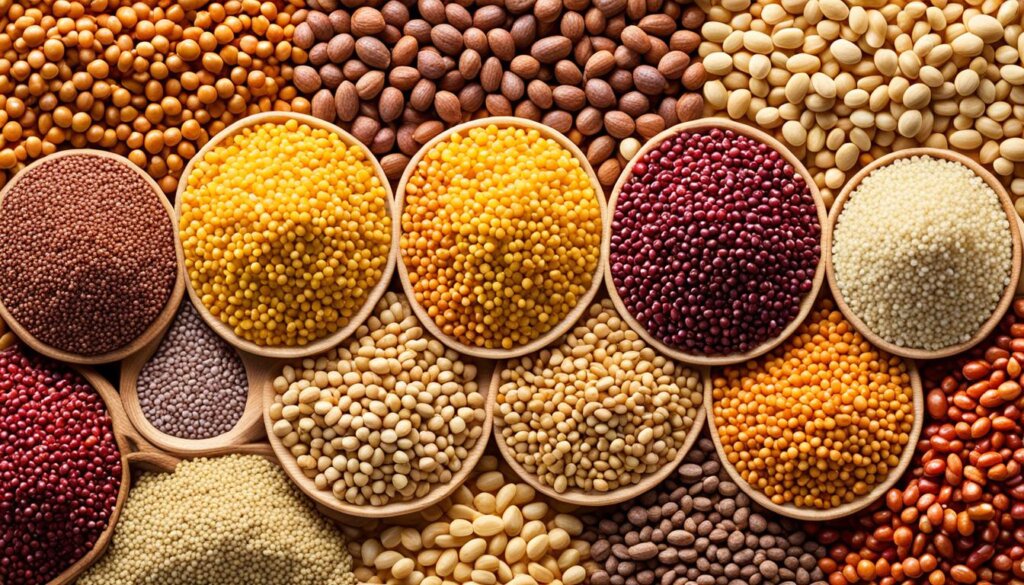

Sorghum’s unique taste and texture make it versatile in cooking. It’s perfect for gluten-free cookies, bread, or stews.
Pack Size | Price | Price per Pound | Stock Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
1 lb | $9.76 | $9.76 | 9 packs left |
1.5 lbs | $14.57 | $9.71 | 7 packs left |
3 lbs | $20.99 | – | – |
6 lbs | $34.97 | $5.83 | – |
10 lbs | $57.80 | $5.78 | 6 packs left |
20 lbs | $110.38 | $5.52 | – |
Sorghum is great for many recipes, like bread, cookies, desserts, and popcorn. It lasts up to 2 years, making it a handy pantry item. Plus, it’s gluten-free, non-GMO, organic, raw, and vegan, perfect for a healthy diet.
Oats: A Gluten-Free Option with Caveats
Oats are naturally gluten-free and packed with health benefits. They have a lot of soluble fiber called beta-glucan. This fiber can help lower cholesterol and control blood sugar levels.
But, oats might have gluten during processing. So, make sure to pick products labeled as gluten-free. You can eat oats for breakfast or add them to baked goods and granola.
Oats are gluten-free by nature. Yet, the FDA says foods can be labeled gluten-free if they have less than 20 ppm of gluten. Foods tested by third parties must have even less gluten, under 10 to 5 ppm. This shows why choosing certified gluten-free oats is key for those with celiac disease or gluten issues.
Some people with celiac disease can eat oats processed under a “Purity Protocol”. This is because oats have a protein called Avenin, similar to the proteins that cause celiac reactions. But, how people react to Avenin can vary a lot, from very few to about 20%. So, it’s best to talk to a doctor before eating oats if you have celiac disease.
Oats are the top breakfast food worldwide. One bowl of oatmeal can give you 3-5 grams of fiber. Most Americans don’t get enough fiber, so oats are a great choice. They’re also good for your heart because of their fiber and important vitamins and minerals like thiamine, zinc, and magnesium.
In short, oats are a great gluten-free choice with lots of health perks. But, always pick certified gluten-free oats to be safe for those with celiac disease or gluten issues. It’s also smart to talk to a doctor before adding oats to your diet.
Country | Oats Production (Metric Tons) |
|---|---|
Russia | 5,500,000 |
Canada | 3,200,000 |
United States | 1,000,000 |
Finland | 900,000 |
Poland | 700,000 |
“Oats are inherently gluten-free in their natural state, but they are often contaminated with gluten during processing, so it’s crucial to look for oat products that are certified gluten-free.”
Amaranth: An Ancient Grain with Modern Benefits
Amaranth is an ancient grain that has been around for over 8,000 years. It’s a superfood packed with nutrients that can help fight inflammation and lower the risk of chronic diseases. It’s also full of fiber, protein, and minerals, making it great for those on a gluten-free diet.
One cup of cooked amaranth has 251 calories, 46 grams of carbs, 9 grams of protein, and 4 grams of fat. It gives you 5 grams of fiber, which is 20% of what you need daily. Plus, it’s loaded with manganese, magnesium, and iron. Eating amaranth can help lower heart disease risk and reduce inflammation.
Ancient grains like amaranth are perfect for people with gluten sensitivities or Celiac disease. They’re packed with more nutrients than modern grains, including vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. They also have a lower glycemic index, which helps keep blood sugar stable and can lower type 2 diabetes risk.
You can use amaranth instead of couscous or rice in many dishes. It adds a nutty taste and texture to your food. Its anti-inflammatory effects and rich nutrients make it a great choice for a healthy, gluten-free life.
Teff: A Small Grain with Big Nutrition
Teff is an ancient grain from Ethiopia and Eritrea. It’s packed with nutrition in a small size. This gluten-free cereal is high in protein, fiber, B vitamins, and minerals like iron and calcium. Teff flour is great for your health.
Teff has a lot of protein, like other grains. Eating teff bread gives you about 45% of the daily iron you need. Teff flour is also a whole grain, so you get all its nutrients.
Teff is also good for weight control and digestion. It has a low glycemic index, which helps control blood sugar and makes you feel full. The fiber in teff keeps your gut healthy and improves digestion.
Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Protein | 11.4g |
Fiber | 5.7g |
Calcium | 180mg |
Iron | 5.71mg |
Teff is also very versatile. You can make gluten-free dishes like porridge and baked goods with it. It tastes a bit like nuts and adds nutrition to your food.
“Teff is a staple food in Ethiopia and Eritrea, showing its importance in their traditional food.
If you want to try new gluten-free foods or add a nutritious grain to your diet, teff is a great pick. It’s full of nutrients and easy to use in cooking, making it a smart choice for a healthy life.
Corn: A Versatile Gluten-Free Grain
Corn is a gluten-free grain eaten all over the world. It’s full of fiber and has lutein and zeaxanthin. These help keep your eyes healthy and lower the risk of eye problems. You can enjoy corn in many ways, like grilling it or adding it to dishes.
Corn is great for a gluten-free diet because it’s so versatile. You can make everything from cornbread to polenta with it. It also has important vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, magnesium, and phosphorus.
Corn is also easy on the wallet and easy to find in stores. This makes it a good choice for those eating gluten-free. If you want to eat more corn or try new gluten-free grains, it’s a good pick.
“Corn is a versatile and nutritious gluten-free grain that can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. It’s a great addition to any healthy diet.”
In conclusion, corn is a great gluten-free grain with lots of health benefits. It’s full of lutein and zeaxanthin and is easy to use in cooking. Adding corn to your diet can help your eye health and give you new gluten-free options.
Brown Rice: A Nutritious Gluten-Free Option
Both white and brown rice don’t have gluten. But, brown rice is packed with more nutrients. It has more fiber, selenium, and magnesium than white rice. Eating brown rice can help with weight control and lower the risk of diabetes and heart disease.
All types of rice, like plain brown rice, are gluten-free. But, you should avoid wheat, rye, and barley if you have gluten issues. Most rice in the U.S. is safe for those with gluten problems because it doesn’t have gluten.
Brown rice is great as a side dish or in many gluten-free meals. It has more B vitamins, vitamin E, and iron than white rice. Plus, it can lower the risk of type 2 diabetes. If you have digestive problems, white rice might be easier to digest because it has less fiber.
When picking rice, make sure it’s labeled or certified as gluten-free to avoid gluten contamination. Choosing plain rice without extra seasonings helps keep your diet gluten-free when eating out.
Rice Type | Gluten-Free | Nutritional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Brown Rice | Yes | Higher in fiber, selenium, and magnesium compared to white rice. Reduces the risk of diabetes and heart disease. |
White Rice | Yes | May be a better option for individuals with digestive issues due to lower dietary fiber content. |
Basmati Rice | Yes | Naturally gluten-free, with a distinct aroma and flavor. |
Jasmine Rice | Yes | Naturally gluten-free, with a sweet and fragrant taste. |
Conclusion
Adding different gluten-free grains to your meals can be great for your health. These grains, like quinoa and brown rice, are full of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and protein. They help make tasty, healthy meals and snacks for your health and wellness.
But, not all gluten-free grains are the same. Some have very little gluten, while others have a lot. It’s key to check labels and plan your meals well to stay on a balanced diet. This way, you can get the most nutrition from gluten-free grains and stay healthy.
A gluten-free diet works best when it’s tailored to you. Always talk to your doctor to find the right diet for your needs. With the right grains and a balanced diet, you can stay healthy and enjoy great food.
FAQ
What is a gluten-free diet?
A gluten-free diet means eating foods without gluten. This is key for people with celiac disease or other health issues linked to gluten. Gluten can cause an immune system reaction that harms the small intestine. It can also lead to symptoms like belly pain, bloating, and headaches, even without intestinal damage.
What foods should I avoid on a gluten-free diet?
Stay away from foods with wheat, barley, rye, and triticale. Oats might have gluten too, so make sure they’re labeled gluten-free. Common foods to skip include bread, cereals, pastas, sauces, and snacks.
What are some healthy gluten-free grains I can incorporate into my diet?
Try “pseudograins” like quinoa, buckwheat, sorghum, amaranth, teff, corn, rice, and millet. They’re full of fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals. Adding them to your meals helps you get the nutrients you need while avoiding gluten.
What are the benefits of incorporating quinoa into a gluten-free diet?
Quinoa is a superfood that’s gluten-free and a complete protein. It’s packed with fiber and vitamins like magnesium and B vitamins. Adding quinoa to your diet makes it easier to follow a gluten-free plan.
How can I use buckwheat in my gluten-free meals?
Buckwheat isn’t related to wheat and is naturally gluten-free. It’s full of antioxidants that help fight inflammation and protect the brain. Use it to make noodles, pancakes, or other gluten-free dishes.
What are the health benefits of sorghum?
Sorghum is a gluten-free grain rich in fiber, protein, and minerals like iron. It also has antioxidants that may lower the risk of heart disease. Its texture and taste make it a great substitute for barley in many dishes.
Can I eat oats on a gluten-free diet?
Oats are gluten-free and offer lots of health benefits, like fiber and beta-glucan. Beta-glucan can help lower cholesterol and control blood sugar. But, make sure to pick oats that are certified gluten-free. Enjoy oats as cereal or in baked goods and granola.
What are the benefits of incorporating amaranth into a gluten-free diet?
Amaranth is an ancient grain with anti-inflammatory compounds that may reduce disease risk. It’s also high in fiber, protein, and minerals. Use it as a couscous or rice substitute in various dishes.
How can teff be used in gluten-free cooking and baking?
Teff is a tiny grain rich in protein, fiber, and B vitamins. It can help with metabolism and feelings of fullness. Use it to make porridge, baked goods, and other gluten-free dishes.
What are the benefits of incorporating corn into a gluten-free diet?
Corn is gluten-free and full of fiber and antioxidants. These antioxidants support eye health and may reduce the risk of eye diseases. Enjoy corn grilled, or roasted, in soups, salads, or baked goods.
Why is brown rice a better choice than white rice for a gluten-free diet?
Brown rice is more nutritious than white rice, being higher in fiber and minerals. It can help with weight management and reduce diabetes and heart disease risk. Use it as a side dish or in various gluten-free meals.