FTC disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links and we will be compensated if you click on a link and make a purchase.
Adrenal cancer is very rare, affecting only 1-2 people per million. Yet, it impacts many, with about 600 new cases in the U.S. each year. It’s a special kind of cancer that needs careful treatment to help patients.
The adrenal glands sit on top of the kidneys. They help control many body functions like metabolism and blood pressure. When cancer grows in the adrenal cortex, it can mess up hormone production. This leads to various symptoms and health problems.
Key Takeaways
- Adrenal cancer is an extremely rare type of endocrine cancer, affecting only 1-2 people per million.
- Approximately 600 patients are diagnosed with adrenal cancer each year in the United States.
- Adrenal cancers can be aggressive and spread rapidly to other parts of the body.
- Early detection is crucial, as the five-year survival rate for early-detected adrenal cancer is 74%.
- Adrenal tumors can lead to hormonal imbalances, causing a range of symptoms like weight changes and fatigue.
What is Adrenal Gland Cancer?
The adrenal glands sit on top of the kidneys. They are small and triangular. These glands make hormones that help with stress, metabolism, and blood pressure. Adrenal gland cancer is rare and starts in the outer part of the gland. They can also grow benign tumors like adenomas or pheochromocytomas.
Adrenal Glands and Their Function
The adrenal glands have two parts: the outer cortex and the inner medulla. The cortex makes hormones like cortisol and aldosterone. These hormones help with many body functions. The medulla makes hormones like epinephrine, which helps with stress.
Definition of Adrenal Gland Cancer
Adrenal gland cancer starts in the outer cortex of the gland. It can cause too much or too little hormone production. This leads to symptoms.
Types of Adrenal Gland Tumors
Adrenal glands can also grow benign tumors like adenomas and pheochromocytomas. Adenomas are common and usually don’t cause symptoms. Pheochromocytomas are rare and can make too much hormone.
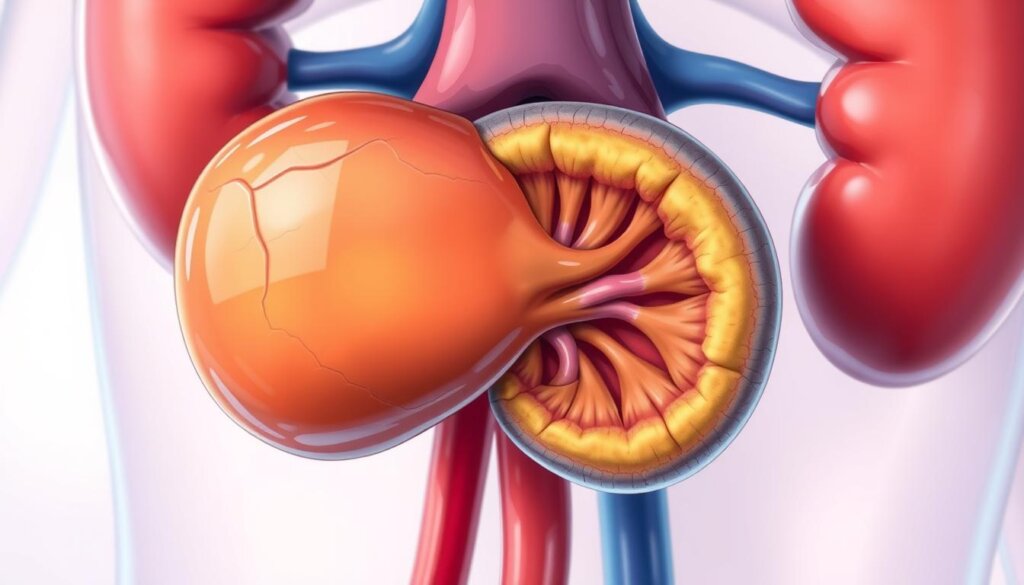
Type of Adrenal Gland Tumor | Characteristics |
|---|---|
Adrenal Adenoma |
|
Adrenal Carcinoma |
|
Pheochromocytoma |
|
“Adrenal gland cancer is part of the group of neuroendocrine tumors, which can start in hormone-producing glands throughout the body, with adrenal glands being a common site.”
Symptoms of Adrenal Gland Cancer
Adrenal gland cancer is rare, hitting kids under 5 and adults in their 40s and 50s. Early detection offers a cure chance. But, if it spreads, the cure odds drop. Most growths are benign, like adenoma or pheochromocytoma.
Early Signs and Symptoms
Early signs include weight gain, muscle weakness, and hormonal shifts. Women might see more facial hair and irregular periods. Men could notice bigger breasts and smaller testicles.
In about half, symptoms come from tumor hormones. Kids often grow more hair due to androgens from the tumor.
Advanced Symptoms
As it gets worse, symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and back pain appear. Adults might notice symptoms when the tumor is big enough. High cortisol can cause Cushing syndrome, with weight gain and weakness.
Aldosterone tumors lead to high blood pressure and muscle cramps. A big tumor can cause pain and make eating hard.
“If adrenal cancer is detected early, there is a possibility for a cure; however, if the cancer has spread beyond the adrenal glands, the chances of a cure decrease.”
Early signs include weight gain and hormonal changes. As it gets worse, symptoms like vomiting and back pain appear. Learning about hormonal changes can help spot signs early and get medical help fast.
Causes and Risk Factors
Adrenal gland cancer’s exact cause is still a mystery. Yet, research has found some genetic mutations and syndromes that raise the risk. Up to 15% of these cancers are linked to genetic defects, especially in kids. Disorders like Li-Fraumeni syndrome and Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) also increase the risk.
Genetic Mutations
Genetic changes often lead to abnormal cell growth and tumors in the adrenal gland. About 85% of adrenal cancers happen by chance, while 15% are inherited. Li-Fraumeni syndrome, for example, raises the risk of several cancers, including adrenal cortex cancer.
Inherited Syndromes
Some syndromes increase the risk of adrenal gland cancer. MEN1, for instance, leads to tumors in multiple endocrine glands. About one-third to one-half of those with MEN1 develop adrenal adenomas or enlarged glands. Lynch syndrome and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome also raise the risk of adrenal cortex cancer.
Smoking and exposure to chemicals like BPA and phthalates are also risk factors. These can cause hormonal imbalances and possibly lead to cancer. But, it’s key to remember that adrenal gland cancer is rare.
“Understanding the genetic and environmental factors that can increase the risk of adrenal gland cancer is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.”
Adrenal Gland Cancer Diagnosis
Diagnosing adrenal gland cancer involves blood and urine tests, and imaging like CT scans and MRIs. These tools help find out how far the cancer has spread. This is key for planning treatment.
Blood and urine tests check for hormone levels. Hormones like cortisol and androgens can show if there’s a tumor. These tests help understand the tumor’s activity.
Imaging tests are crucial for finding adrenal cancer. A chest x-ray checks for lung cancer. CT scans find tumors and see if cancer has spread.
MRI scans give detailed images of soft tissues. They help tell if a tumor is cancerous or not. PET scans help decide if a tumor is likely cancerous, helping doctors choose treatment.
Sometimes, a biopsy is done to confirm cancer. But, it’s rare before surgery to avoid spreading cancer. Usually, the adrenal gland is removed for lab tests. This confirms cancer and finds the cancer type.
Family history is also important for understanding cancer risk. High hormone levels in blood and urine mean more tests are needed.
Healthcare providers use many tests to understand adrenal gland cancer. They find out where and how far it has spread. This helps them plan the best treatment for each patient.
Treatment Options for Adrenal Gland Cancer
Adrenal gland cancer is rare and complex. But, there are many effective treatments. These can help manage the disease and improve outcomes.
Surgery (Adrenalectomy)
Surgery to remove the adrenal gland is the main treatment. If the cancer hasn’t spread, this surgery can cure it. The surgeon removes the whole gland to get rid of all cancer.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy may follow surgery to kill any leftover cancer cells. It’s especially useful for aggressive cancers.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, especially mitotane, can be used with surgery or radiation. It helps kill cancer cells and prevent it from coming back. It’s a good option for late-stage or recurring cancer.
The right treatment plan depends on the disease’s stage, the patient’s health, and how far the cancer has spread. A team of healthcare providers can help find the best treatment. They work together to create a plan that meets the patient’s needs.
Early detection and quick treatment are key for the best results in adrenal gland cancer. If you or a loved one has this condition, talk to your healthcare team. Discuss all treatment options to create a plan that fits your needs.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Adrenal Gland Cancer
Treating adrenal gland cancer needs a team of experts. This team includes endocrinologists, oncologists, surgeons, and radiation oncologists. Working together, they make sure the patient gets the best care. Each expert adds their skills to create a strong treatment plan.
The endocrinologist checks for hormonal imbalances. They figure out if the tumor works right. The oncologist then makes a detailed plan. This plan might include surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, based on the tumor.
The surgeon removes the bad adrenal gland. The radiation oncologist suggests radiation to kill more cancer cells. This team makes sure the treatment fits the patient’s needs.
Healthcare Professionals | Role in Adrenal Gland Cancer Treatment |
|---|---|
Endocrinologist | Evaluates hormonal imbalances and determines functional status of the adrenal tumor |
Oncologist | Develops the comprehensive cancer treatment plan, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, and/or chemotherapy |
Surgeon | Performs the adrenalectomy, the surgical removal of the affected adrenal gland |
Radiation Oncologist | Recommends radiation therapy to target any remaining cancer cells or to manage metastatic disease |
This adrenal cancer treatment team works together. They make sure the patient gets the best care. This teamwork helps the patient have a better chance of success.
Follow-up Care and Monitoring
After treatment for adrenal gland cancer, regular check-ups are key. This care helps manage side effects, watch for cancer coming back, and keep the patient healthy.
Long-term Hormone Management
If both adrenal glands were removed, patients need hormone shots for life. Those on mitotane might need more doctor visits to check blood levels and side effects.
Surveillance for Recurrence
CT scans are used to check for cancer coming back. Blood and urine tests help see if hormone treatments are working.
Creating a care plan after treatment is very important. It includes regular check-ups, tests for cancer, and advice on diet and exercise.
Helping with nutrition issues like losing appetite and weight is also key. Dietitians can make special plans for patients.
Keeping health insurance after treatment is crucial. The costs of tests and doctor visits can be high. It’s important for survivors to have access to healthcare.
There’s no clear way to stop adrenal cancer from coming back. But, not smoking is advised because it might lower the risk. Talking to doctors about dietary supplements is also important, as their benefits are not proven.
If cancer comes back, treatment depends on where it is, past treatments, and the patient’s health. Survivors also face a higher risk of other cancers, so they need to be closely watched.
“Maintaining healthy hormone levels and closely monitoring for potential cancer return are crucial for the patient’s well-being and long-term prognosis.”
By sticking to a detailed follow-up plan, patients can help their recovery. They can manage side effects and catch any cancer coming back early.
Adrenal Gland Cancer: A Rare but Treatable Condition
Adrenal gland cancer is rare, with about 1-2 cases per 1 million people each year. Early detection and treatment can lead to a cure. Even if the cancer has spread, treatment can slow it down and improve life quality.
The outlook for adrenal gland cancer depends on its stage. Early-stage cancer has a 50-60 percent five-year survival rate. But, cancer that has spread has a much lower survival rate, around 10-20 percent. Some genetic conditions, like Li-Fraumeni syndrome and MEN1, raise the risk of getting this cancer.
Adrenal gland cancer symptoms vary. Functioning tumors can cause weight changes, high blood pressure, anxiety, and irregular periods. Non-functioning tumors may cause pain and a noticeable mass in the belly.
Though adrenal gland cancer is serious, modern medicine makes it more treatable. A team of experts can help with surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. This approach can lead to better outcomes.
“Adrenal gland cancer is a rare and complex condition, but with early detection and a tailored treatment plan, patients can have a good chance of overcoming this challenge.”
Even though adrenal gland cancer is rare, it affects about 300 to 500 people in the U.S. each year. It’s crucial to know the symptoms and get medical help if you notice any changes. With proper care and support, people can manage this cancer and live well.
Living with Adrenal Gland Cancer
Getting a diagnosis of adrenal gland cancer can be scary. But, with the right support and care, patients can manage its challenges. Adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare disease that affects kids and adults in their 40s and 50s. Women are more likely to get it than men.
Living with adrenal gland cancer means finding emotional support. Counseling and support groups offer a safe place to share and connect. Even if treatment works, there’s a chance the cancer could come back, making support key. Staying positive and focusing on well-being helps patients’ health in the long run.
Patients may need to change their daily lives due to treatment and disease management. Most are treated with surgery and then chemotherapy. Having a strong support system is vital. It helps patients deal with changes and get the help they need to live well.
Living with adrenal gland cancer is tough, but there’s hope. With the right support, adjusting to the disease, and staying positive, patients can thrive. They can find joy in their lives, even with this rare and complex condition.
Conclusion
Adrenal gland cancer is rare but very important to know about. Most adrenal gland tumors are not cancerous, but some are. These can come from cancers like lung or breast, which are the most common.
About 30% to 70% of adrenal masses found in cancer patients are from other cancers. These can show up years after the first cancer treatment.
Even though only a small percent of adrenal masses are cancer, it’s key to watch for it. Adrenocortical carcinomas, or ACC, are very rare but deadly. Early detection and a team effort in treatment can help a lot.
Knowing about adrenal gland cancer summary and key takeaways about adrenal cancer helps a lot. It lets you spot signs early and get help fast. Working with your healthcare team is crucial for managing this rare disease.
FAQ
What are the adrenal glands, and what is their function?
The adrenal glands sit on top of the kidneys. They are small and triangular. They make hormones that help with many things like metabolism and blood pressure.
What is adrenal gland cancer?
Adrenal gland cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the outer part of the adrenal gland. It can also cause non-cancerous growths like adenomas or pheochromocytomas.
What are the early symptoms of adrenal gland cancer?
Early signs include weight gain and muscle weakness. You might see pink or purple marks on your skin. Hormone changes can also cause hair growth or loss.
What are the advanced symptoms of adrenal gland cancer?
As it gets worse, you might feel sick to your stomach or have back pain. You could also lose weight without trying.
What causes adrenal gland cancer?
We don’t know exactly why it happens. But it might be because of genetic changes. Some families are more likely to get it.
How is adrenal gland cancer diagnosed?
Doctors use blood and urine tests to check hormone levels. They also do CT scans and MRIs to find tumors.
What are the treatment options for adrenal gland cancer?
Surgery to remove the gland is the main treatment. If it’s caught early, this might cure it. Sometimes, radiation or chemotherapy are used too.
How is adrenal gland cancer treated?
A team of doctors works together to treat it. This team includes endocrinologists and surgeons. They make a plan that works best for you.
What happens after treatment for adrenal gland cancer?
After treatment, you’ll need to see doctors often. You might need hormone shots. They also check for cancer coming back.
Is adrenal gland cancer a rare and treatable condition?
Yes, it’s rare but treatable if caught early. Even if it spreads, there are ways to slow it down and improve life quality.
How can patients cope with the challenges of living with adrenal gland cancer?
Getting diagnosed is tough, but there’s help. Doctors, support groups, and counseling can make a big difference. They help with the physical and emotional parts of living with cancer.